HP Matrix Operating Environment Software User Manual
Page 154
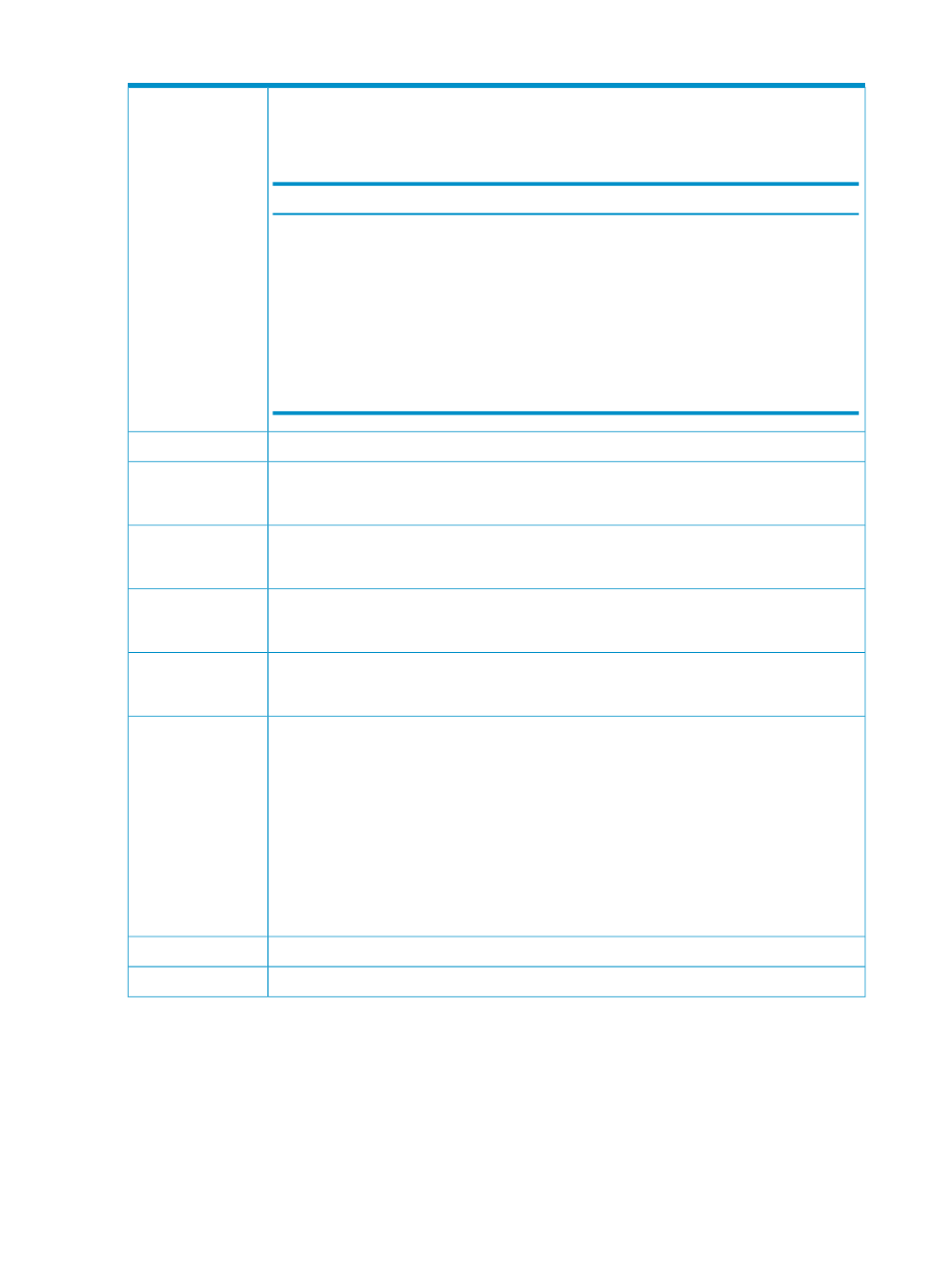
Table C-1 Units and Terminology (continued)
Measured in MB/s (10^6 bytes, megabytes per second).
Each sample represents an average reading over the past 5 minutes. These measurements are
obtained and calculated in the following manner:
Table C-3 Data collection for disk I/O bandwidth utilization by platform
Collected from
Calculation
Platform
pstat()
Total bytes transferred during the interval
HP-UX
/proc/diskstats
Total bytes transferred during the interval
Linux
PDH disk counters
Total bytes transferred out during the interval
Microsoft Windows
HP Virtual Machine
Management Pack
(VMM)
Imported as is
Proliant VM Host
and VMs
sys$getdvi
system
service DVI$_OPCNT)
Total bytes transferred during the interval
OpenVMS
disk I/O bandwidth
utilization
Gigabytes. Unit used for memory: (10^9 bytes)
GBs
Gigahertz. In Capacity Advisor, CPU capacity is defined in terms of clock speed expressed in
megahertz (10^6 hertz) or gigahertz (10^9 hertz). Clock speed refers to the rate at which a
computer performs its most basic operations such as adding two numbers.
GHz
The difference between the average resource utilization on a system and the maximum available
capacity. See
for an explanation of headroom rating (stars), and
information on interpreting the star ratings shown in automated solutions.
headroom
Capability of some Intel processors to create an additional virtual core that provides additional
processing efficiencies. Note that Capacity Advisor does not count Hyper-Thread virtual cores
separately.
Hyper-Threading
In Capacity Advisor, the hypervisor includes not only the virtualization platform, but also all
functions performed by the host OS, as well as all virtual machine monitoring processes
(everything on the VM host that is not a VM guest).
hypervisor
Capacity Advisor estimates hypervisor memory overhead by adding together all memory
used in support of running guests. This overhead can be estimated by adding together the
memory use of the following:
•
the host operating system that the hypervisor is running on (HP-UX, Linux, Windows)
•
the hypervisor process that manages and enables the execution of guests
•
An overhead constant per guest that can either be a standard value for each guest on the
host, or a function of the amount of RAM allocated to a guest depending on the virtualization
platform.
Except in the case of HP Virtual Machine, Capacity Advisor assumes a worst case scenario
where all guests are allocated 1GB of memory, as this will maximize the hypervisor memory
overhead.
hypervisor memory
overhead
Megabits (10^6 bits) per second. Unit used for networking throughput.
Mb/s
Megabytes per second (10^6 bytes per second). Unit used for storage media throughput.
MB/s
154
Units and terminology
