Vmware vsphere (esx 4), Microsoft hyper-v, Power calibration calculations – HP Matrix Operating Environment Software User Manual
Page 129: Determining idle/max values for non-blade servers, Vmware vsphere (esx 4) microsoft hyper-v
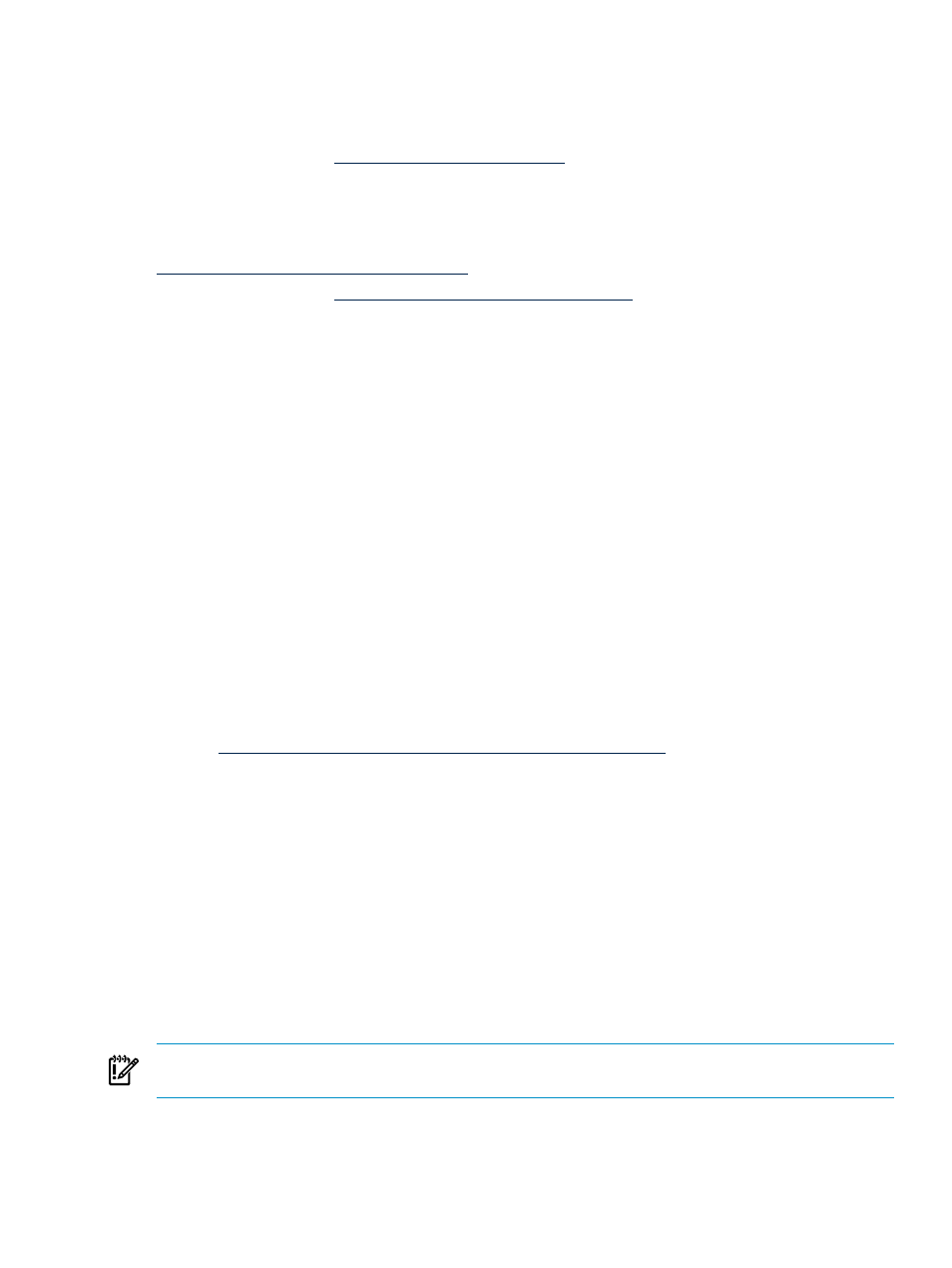
Total Physical Memory – (Total Physical Memory – 284 MB)/1.078
This formula is derived from a least squares fit of observed values in test systems running VMware
ESX. VMware documentation provides tables that outline how much memory overhead to expect
based on the number of virtual CPUs and the amount of memory allocated to guests.
For more information:
on the VMware web site.
VMware vSphere (ESX 4)
To compute a conservative estimate of the memory overhead of the hypervisor, use a value from
column 3 (2 VCPUS) in the table at this location:
For more information:
on the VMware web site.
Microsoft Hyper-V
Microsoft recommends at least 512 MB (.5 GB) of physical memory be available for basic
hypervisor features.
In addition, for each guest, plan on 32 MB of overhead for the first GB of RAM allocated to a
guest, and 8 MB for each additional GB of RAM allocated to a guest.
To compute the memory overhead introduced by the hypervisor, use the following formula:
512 MB + (Number of Guests x (32 MB for first GB of guest RAM + 8 MB per additional GB of
guest RAM))
Example: For a system hosting 2 guests with 2 GB of RAM, and 2 guests with 1 GB of RAM, the
Hypervisor Memory Overhead is as follows:
512 MB + (32 MB + 8 MB) + (32 MB + 8MB) + 32 MB + 32 MB =
512 MB + 40 MB + 40 MB + 32 MB + 32 MB =
656 MB (.64 GB)
Capacity Advisor assumes that a host will be filled with 1 GB guests when estimating the memory
overhead for Hyper-V. This provides a generous estimate of memory overhead, as this
configuration will maximize the size of the memory overhead. As a result, allowing Capacity
Advisor to estimate the Hypervisor Memory Overhead for Hyper-V will leave extra
on Hyper-V hosts.
Source:
on the Windows Hardware
Developer Central web site.
Power calibration calculations
Manual calibration uses CPU utilization data to estimate power utilization. Power utilization
can be estimated by looking at CPU utilization because power utilization is closely related to
CPU utilization. Further, the greater the CPU usage, the more power that is required to run and
cool the system.
Within the power calibration screens, you can specify the idle and maximum power usage values
that you want to use for power usage calculations. The values can be determined by checking
model and hardware configuration information. For your convenience, HP provides power
calculators to aid you in this process (noted below). Each power calculator allows for different
hardware configurations, such as amount of processors and memory, in order to yield the most
accurate results.
IMPORTANT:
Values given by these power calculators are only estimates. Actual results can
vary depending on application load, ambient temperature, and other factors.
Determining idle/max values for non-Blade servers
1.
Locate the appropriate power calculator for a given model number.
Power calibration calculations
129
