IAI America RCP2W-RA10C User Manual
Page 61
55
7. Cautions in Operation
2) Condition 2
The continuous operation torque of the cycle should be 2.08N•m or less.
Calculate the torque for continuous operation.
In Graph 2, shows the speed change of the actuator in continuous operation on the time-basis. In
Graph 3, shows the torque change in time-basis.
t
tw
t2a
f
2
t
d
2
t
to
t1a
f
1
t
d
1
t
V
T
Graph 2: Actuator Speed Change on Time-basis
Tw
T2f
T2d
T2a
T1d
T1a
tw
t2a
t2d
t2f
to
t1a
t
t1d
t1f
F
T
To
T1f
Graph 3: Torque Change on Time-basis
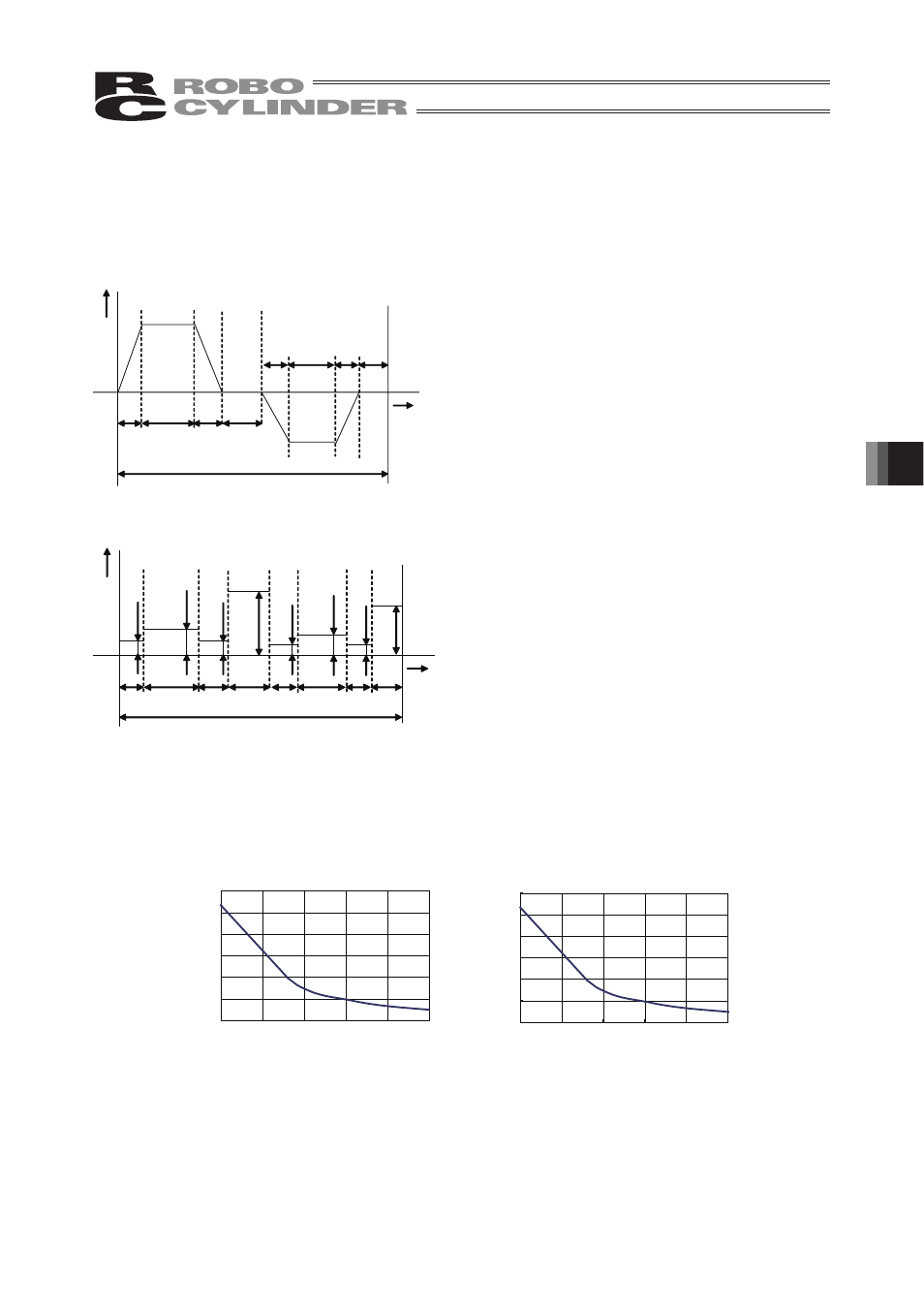
Read the motor torques T1a, T1f, T1d, T2a, T2f, T2d except for To and Tw shown in Graph 3 from
Graph 4. For the motor torques required for acceleration/deceleration, read the motor torque of
reached speed (constant speed) / 2 for the motor torque required for acceleration/deceleration.
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
0
30
60
90
120
150
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
0
60
120
180
240
300
Graph 4: Speed and Motor Torque
Speed [mm/sec]
Speed [mm/sec]
Motor Torque [N•m]
Motor Torque [N•m]
Lead 5
Lead 10
t
: Operation time in 1 cycle [s]
t1a : Acceleration time 1
t1f
: Constant speed operation time 1
t1d : Deceleration time 1
to
: Pressing operation time
*within the range of Condition 1
t2a : Acceleration time 2
t2f
: Constant speed operation time 2
t2d : Deceleration time 2
tw
: Standby time
T1a : Motor torque required for acceleration 1
T1f : Motor torque required for constant operation1
T1d : Motor torque required for deceleration 1
To
: Motor torque required for pressing operation
T2a : Motor torque required for acceleration 2
T2f : Motor torque required for constant operation 2
T2d : Motor torque required for deceleration 2
Tw : Motor torque required for standby
