Calculator function keys, Time (s) – PASCO Xplorer-GLX Users’ Guide User Manual
Page 54
48 C a l c u l a t o r
•
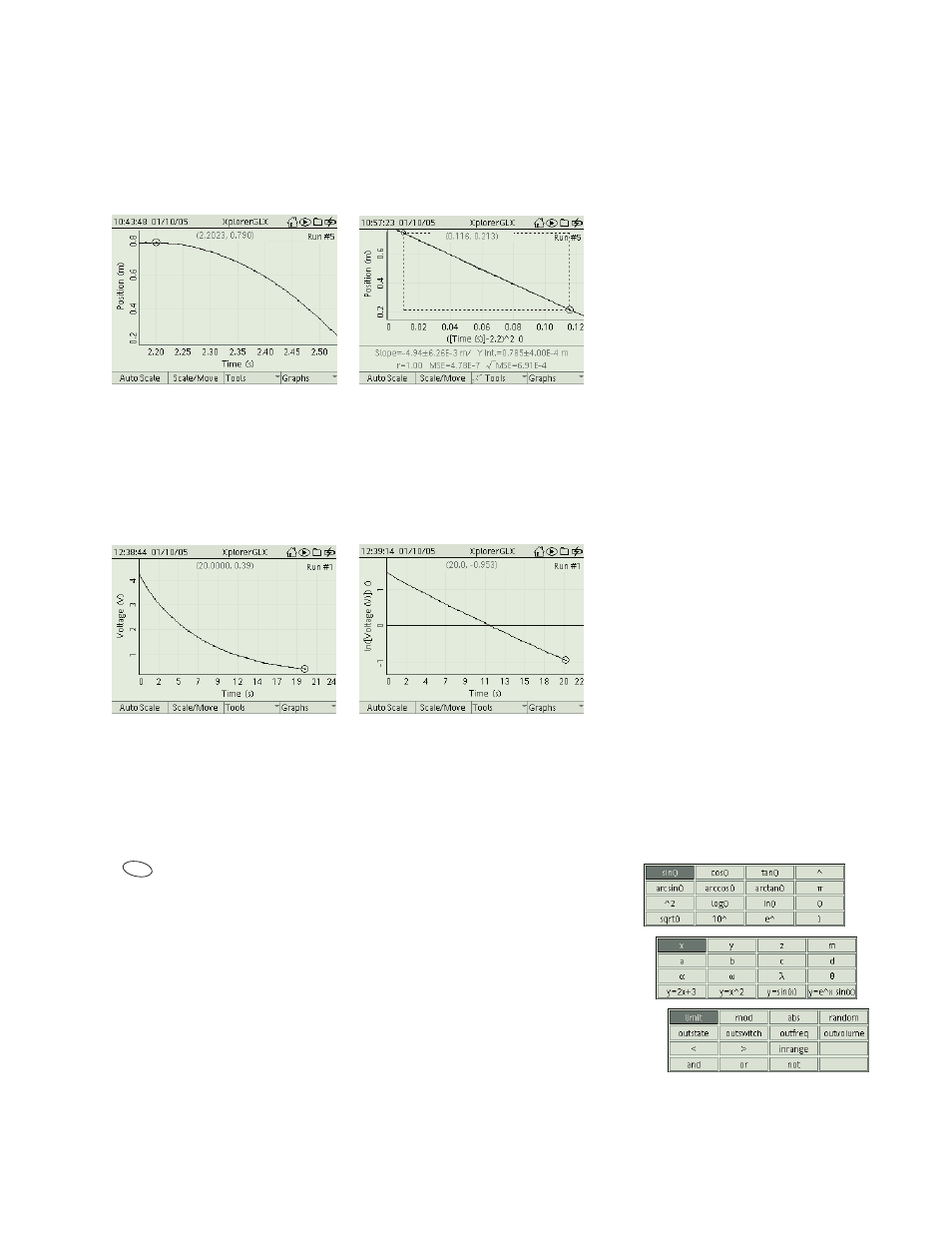
The position versus time graph of an object in free fall (below right) exhibits
a typical quadratic relationship. The object was dropped from a height of
0.79 m, with the release occurring 2.2 s after the start of data collection. The
graph can be linearized (as shown below right) by replacing Time on the hor-
izontal axis with the calculation (
[Time (s)]
-2.2)
^2
. The slope of the best-fit
line is
, where a is the acceleration of the object.
•
Voltage versus time graph for a discharging capacitor is shown below on the
left. The graph the natural log of voltage versus time is a linear (below right).
The slope of the line is
, where C is the capacitance and R is the
resistance through which the capacitor discharges.
Calculator Function Keys
F1 Functions
Press
(or click Functions) repeatedly to access the three Functions menus.
These menus contain the following items.
•
Functions: sin, cos, tan, arcsin, arccos, arctan, ^2, log, ln, sqrt, 10^, e^
•
Operators: ^ (the exponent operator)
•
Constants:
π
•
Commonly used symbols: x, y, z, m, a, b, c, d,
α, ω λ, θ
•
Sample expressions: y = 2x +3, y = x^2, y = sin(x), y = e^x sin(x)
•
Parentheses: a pair of parentheses and a single right parenthesis
•
Special Functions: limit, mod, abs, random
•
Output-control Functions: outstate, outswitch, outfreq, outvolume
•
Logic Operators and Functions:
<, >, inrange, and, or, not
a 2
⁄
Linearized free-fall data
Position vs. Time of an object in
free fall
1 RC
⁄
–
Linearized data for a discharging
capacitor
Voltage versus Time data for a
capacitor
The first and second Functions
menus
F1
