Adsl line maintenance, Sagem 3p@c – Sagem 4450E User Manual
Page 169
SAGEM 3P@C
3P@C Installation Manual
Page 12-12
Reproduction and communication in any form prohibited without the written permission of
SAGEM SA
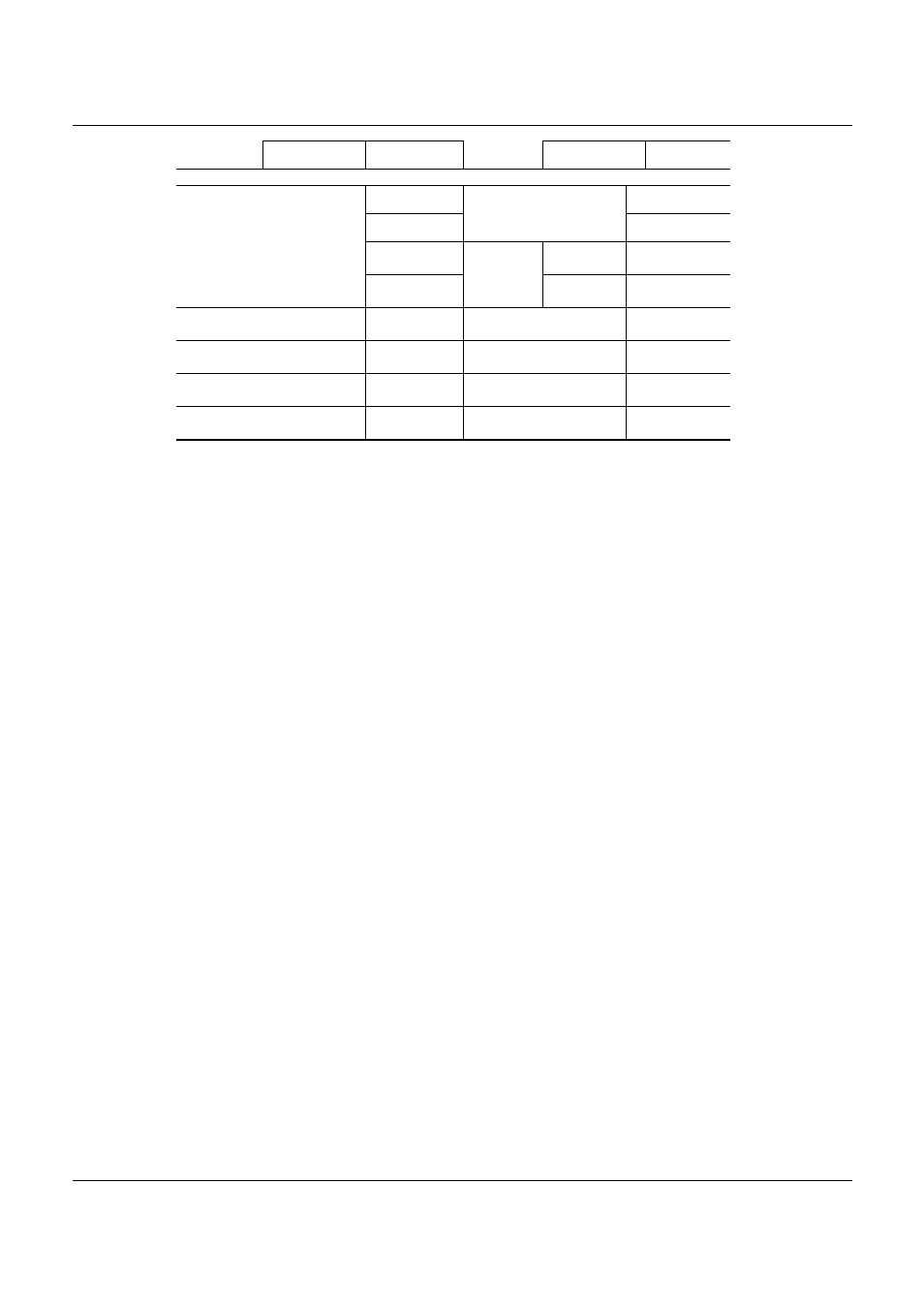
Downstream
Downstream
Actual connection parameters
G.dmt: [ ]
Fast: [ ]
G.lite: [ ]
Channel working mode
Interleaved:[ ]
T1.413: [ ]
Upstream
(ms)
Current working mode of
lines
Multimode:[ ]
interleave
d delay
Downstre
am (ms)
Downstream connection
rate (Kbps)
Upstream connection
rate (Kbps)
Downstream noise margin
(dB)
Upstream noise margin
(dB)
Downstream line
attenuation (dB)
Upstream line
attenuation (dB)
Downstream output power
(dB)
Upstream output power
(dB)
12.1.3. ADSL Line Maintenance
1.1.1.64
ADSL Users’ Common Faults and Handling
The common faults reported by the ADSL users can be divided into five categories as follows:
Unable to make calls and access the Internet.
Able to make calls but cannot access the Internet.
Able to access the Internet, but the speed for accessing is slow.
Unstable Internet accessing, and often being disconnected.
Others. Other faults in addition to the above four kinds of fault. Internet accessing is possible
but calls cannot be made, or noises exist in telephone.
Specific description
:
Unable to make calls and access the Internet.
In general, it is the fault of lines, which should be reported to the 112 test terminal. First exclude the line failure
and check whether the Internet accessing is possible after the telephone can be normally used.
Able to make calls but cannot access the Internet.
The cause for failure may be related to all the devices or links in the broadband network structure. The causes
for failure can be further located by obtaining the information, such as the status of the Modem (RTU) indicator
and operation and setting of the user computer operation. The detailed procedures are as follows:
1) Inquiry and record the model and indicator status of Modem.
The English abbreviation IDs of the RTU indicator for different models may vary, but in general, the Ethernet port
indicators, ADSL connection indicator and power indicator.
2) Judge the faults based on the status of indicators.
Power status of power indicators
If the RTU power indicator is off, it indicates that the RTU power supply has not been properly connected or is
the result of RTU failure; if the RTU power supply is confirmed to be normal, but all the RTU indicators are not
on, it surely is the RTU failure. If the power supply is properly connected, and the RTU power indicator is on, but
the Internet accessing is still impossible, the following analysis can be continued.
