Operation modes of ntp, Client/server mode, Symmetric peers mode – H3C Technologies H3C S5120 Series Switches User Manual
Page 554
1-5
z
Receive Timestamp: the local time at which the request arrived at the service host.
z
Transmit Timestamp: the local time at which the reply departed from the service host for the client.
z
Authenticator: authentication information.
Operation Modes of NTP
Devices running NTP can implement clock synchronization in one of the following modes:
z
Client/server mode
z
Symmetric peers mode
z
Broadcast mode
z
Multicast mode
You can select operation modes of NTP as needed. In case that the IP address of the NTP server or
peer is unknown and many devices in the network need to be synchronized, you can adopt the
broadcast or multicast mode; while in the client/server and symmetric peers modes, a device is
synchronized from the specified server or peer, and thus clock reliability is enhanced.
Client/server mode
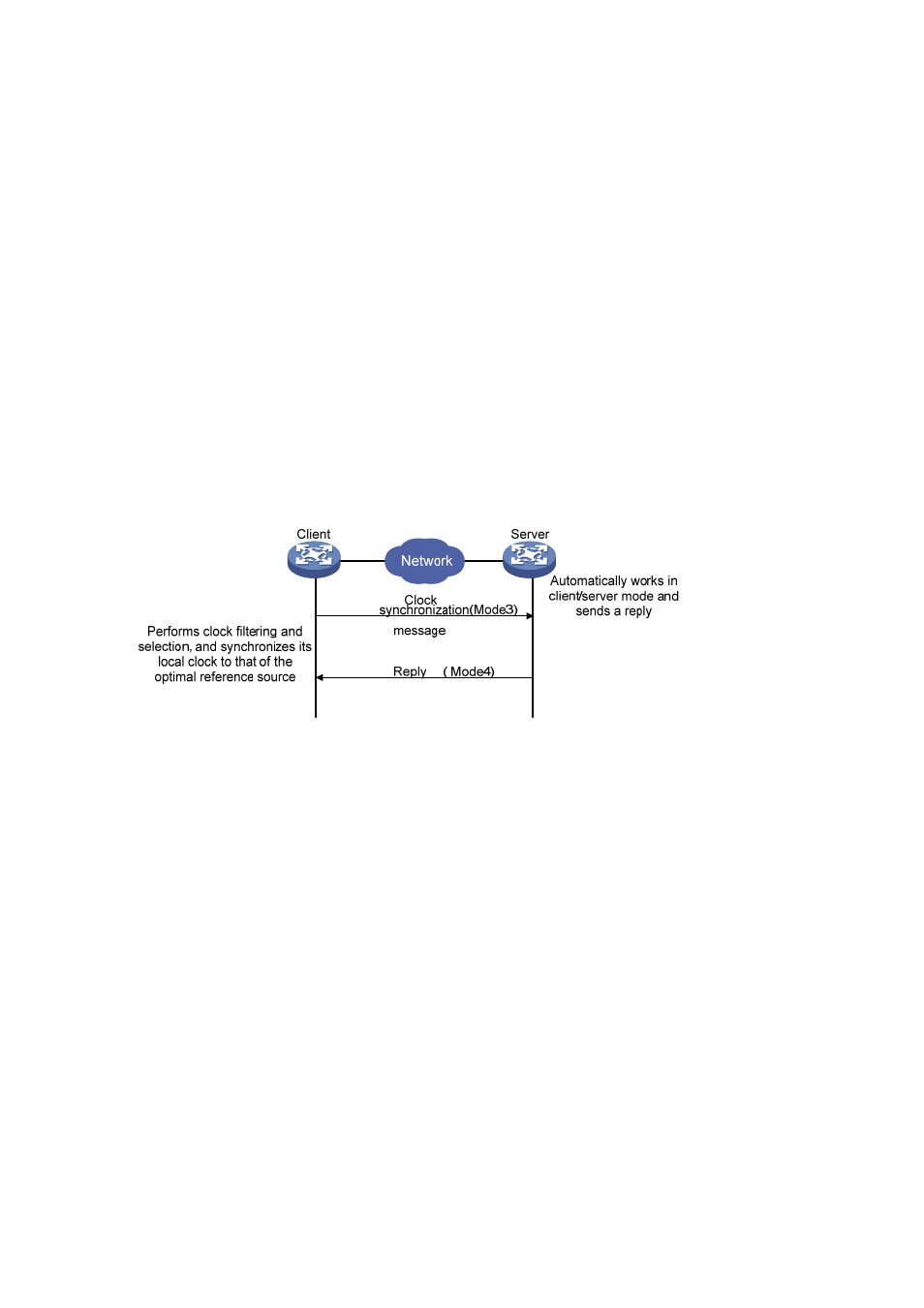
Figure 1-3 Client/server mode
When working in the client/server mode, a client sends a clock synchronization message to servers,
with the Mode field in the message set to 3 (client mode). Upon receiving the message, the servers
automatically work in the server mode and send a reply, with the Mode field in the messages set to 4
(server mode). Upon receiving the replies from the servers, the client performs clock filtering and
selection, and synchronizes its local clock to that of the optimal reference source.
In this mode, a client can be synchronized to a server, but not vice versa.
Symmetric peers mode
