Sp queuing, Wrr queuing – H3C Technologies H3C S5120 Series Switches User Manual
Page 364
5-2
Queue scheduling processes packets by their priorities, preferentially forwarding high-priority packets.
In the following section, Strict Priority (SP) queuing, Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ), and SP+WRR
queuing are introduced.
SP queuing
SP queuing is specially designed for mission-critical applications, which require preferential service to
reduce the response delay when congestion occurs.
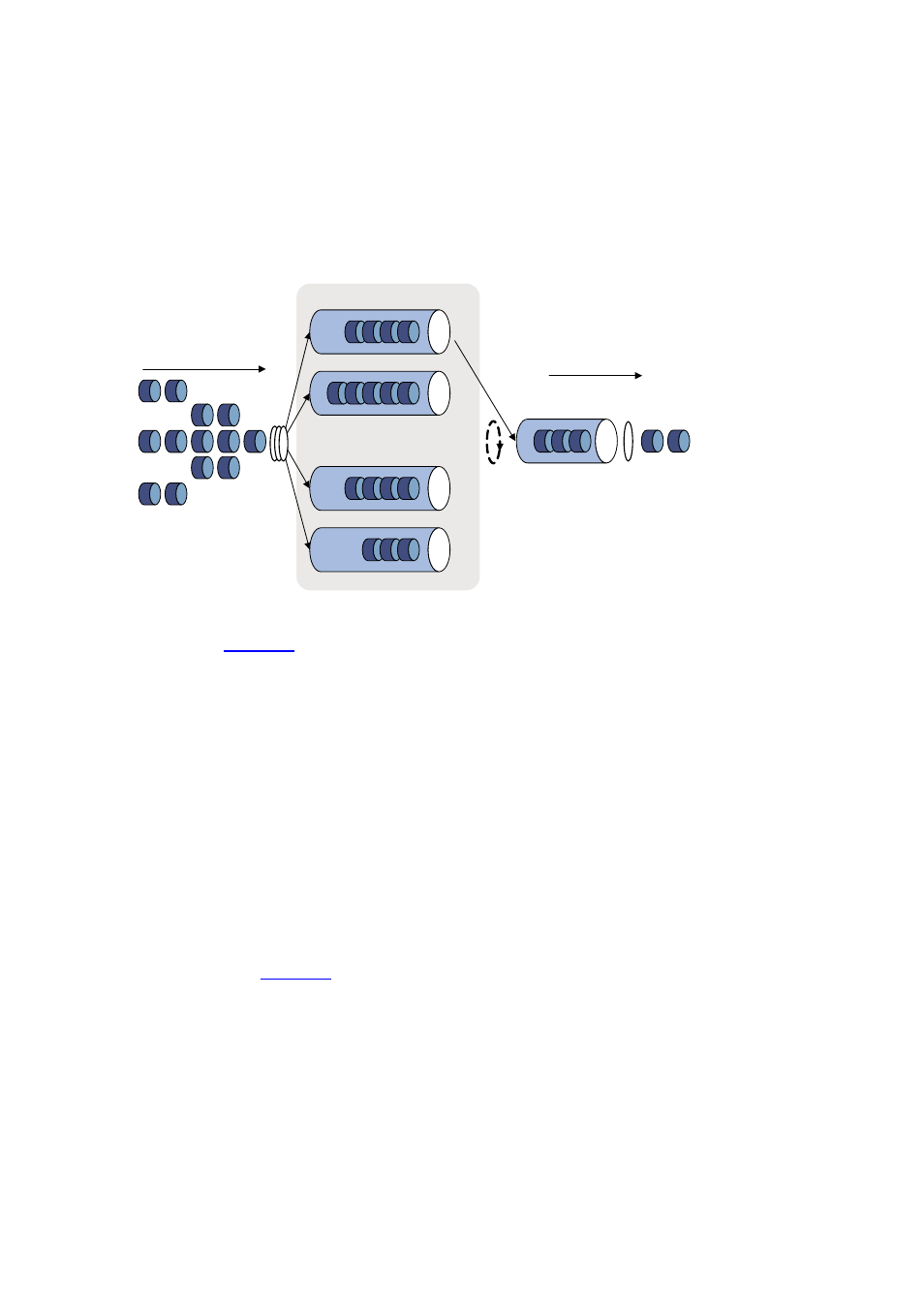
Figure 5-2 Schematic diagram for SP queuing
Queue 3
Queue 2
Queue 1
Queue 0
Packets to be sent through
this port
Packet
classification
High priority
Low priority
Sent packets
Interface
Sending queue
Queue
scheduling
As shown in
, SP queuing classifies eight queues on a port into eight classes, numbered 7 to
0 in descending priority order.
SP queuing schedules the eight queues strictly according to the descending order of priority. It sends
packets in the queue with the highest priority first. When the queue with the highest priority is empty, it
sends packets in the queue with the second highest priority, and so on. Thus, you can assign
mission-critical packets to the high priority queue to ensure that they are always served first and
common service packets to the low priority queues and transmitted when the high priority queues are
empty.
The disadvantage of SP queuing is that packets in the lower priority queues cannot be transmitted if
there are packets in the higher priority queues. This may cause lower priority traffic to starve to death.
WRR queuing
WRR queuing schedules all the queues in turn to ensure that every queue can be served for a certain
time, as shown in
.
