Radius packet format – H3C Technologies H3C S5120 Series Switches User Manual
Page 410
1-4
1) The host initiates a connection request carrying the username and password to the RADIUS client.
2) Having received the username and password, the RADIUS client sends an authentication request
(Access-Request) to the RADIUS server, with the user password encrypted by using the
Message-Digest 5 (MD5) algorithm and the shared key.
3) The RADIUS server authenticates the username and password. If the authentication succeeds, it
sends back an Access-Accept message containing the user’s authorization information. If the
authentication fails, it returns an Access-Reject message.
4) The RADIUS client permits or denies the user according to the returned authentication result. If it
permits the user, it sends a start-accounting request (Accounting-Request) to the RADIUS server.
5) The RADIUS server returns a start-accounting response (Accounting-Response) and starts
accounting.
6) The user accesses the network resources.
7) The host requests the RADIUS client to tear down the connection and the RADIUS client sends a
stop-accounting request (Accounting-Request) to the RADIUS server.
8) The RADIUS server returns a stop-accounting response (Accounting-Response) and stops
accounting for the user.
9) The user stops access to network resources.
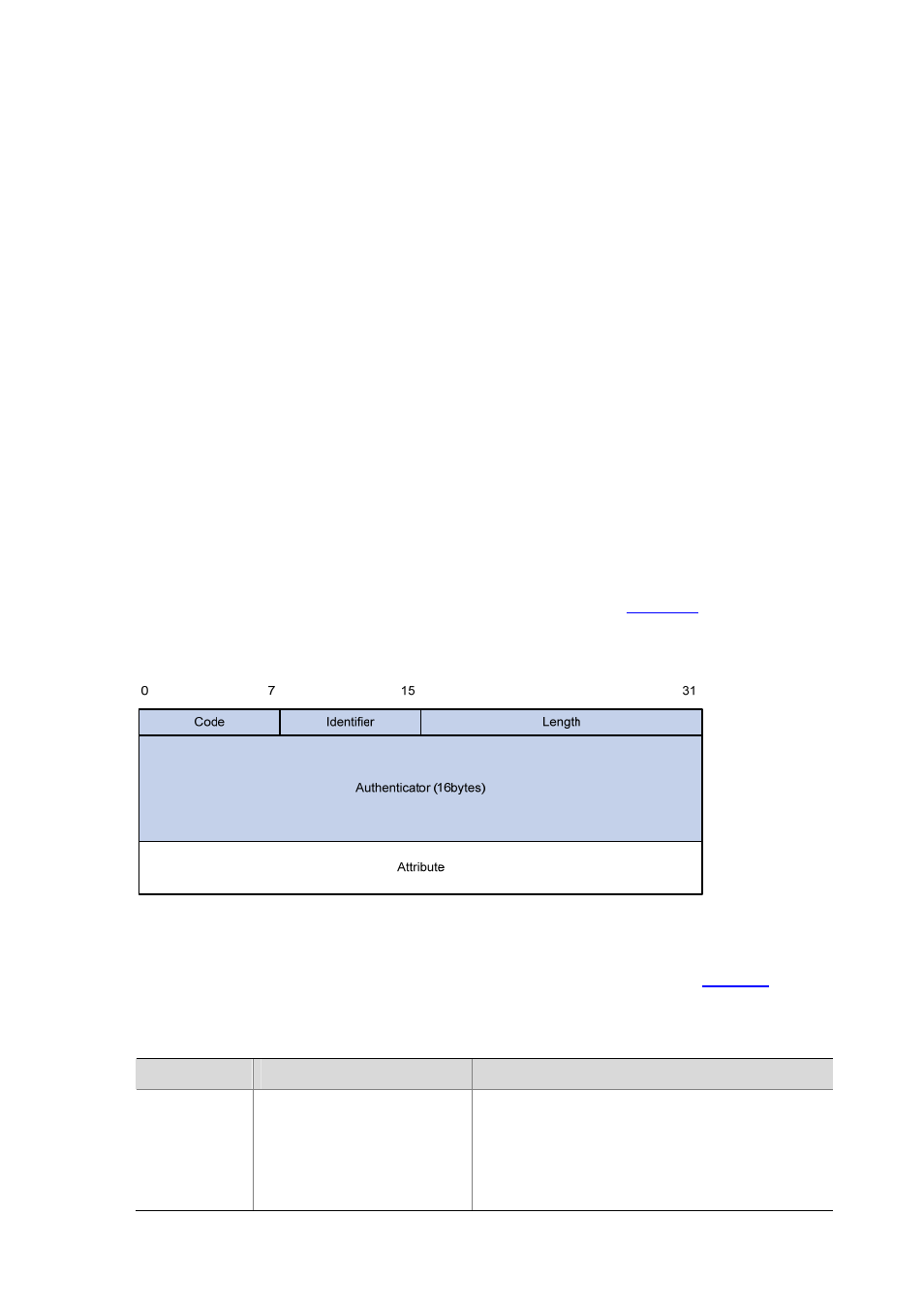
RADIUS Packet Format
RADIUS uses UDP to transmit messages. It ensures the smooth message exchange between the
RADIUS server and the client through a series of mechanisms, including the timer management
mechanism, retransmission mechanism, and slave server mechanism.
shows the RADIUS
packet format.
Figure 1-4 RADIUS packet format
Descriptions of the fields are as follows:
1) The Code field (1-byte long) is for indicating the type of the RADIUS packet.
gives the
possible values and their meanings.
Table 1-1 Main values of the Code field
Code
Packet type
Description
1 Access-Request
From the client to the server. A packet of this type
carries user information for the server to
authenticate the user. It must contain the
User-Name attribute and can optionally contain the
attributes of NAS-IP-Address, User-Password,
and NAS-Port.
