Configuring no agreement check – H3C Technologies H3C S5120 Series Switches User Manual
Page 198
1-33
z
Enable Digest Snooping on Device A’s and Device B’s ports that connect Device C, so that the
three devices can communicate with one another.
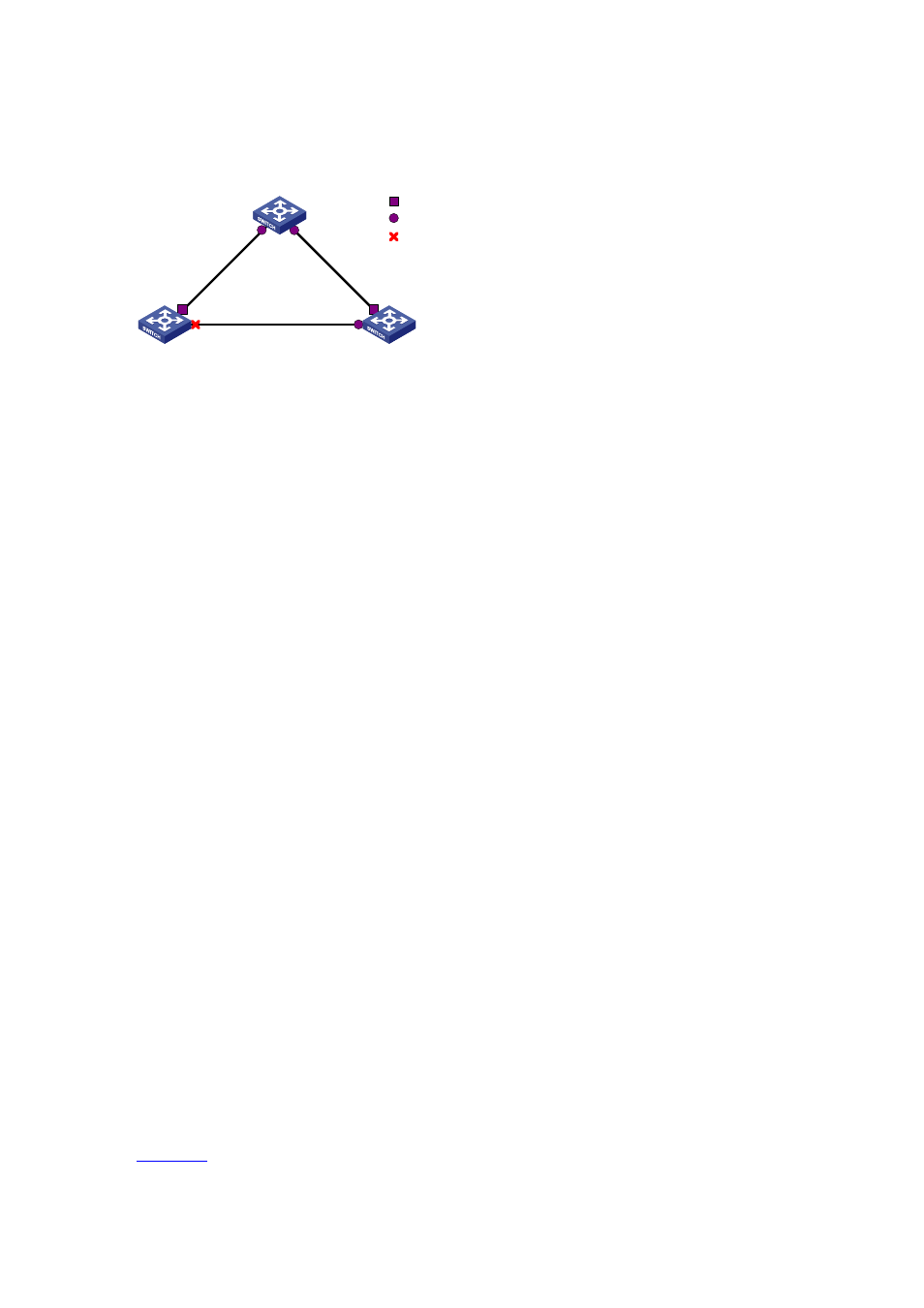
Figure 1-8
Digest Snooping configuration
GE1/0/2
GE1/0/1
GE1/0/2
GE1/0/2
GE1/0/1
GE1/0/1
Device A
Device B
Third-party device
Root port
Designated port
Blocked port
Device C
2) Configuration
procedure
# Enable Digest Snooping on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of Device A and enable global Digest Snooping on
Device A.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] stp config-digest-snooping
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[DeviceA] stp config-digest-snooping
# Enable Digest Snooping on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of Device B and enable global Digest Snooping on
Device B.
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] stp config-digest-snooping
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[DeviceB] stp config-digest-snooping
Configuring No Agreement Check
In RSTP and MSTP, two types of messages are used for rapid state transition on designated ports:
z
Proposal: sent by designated ports to request rapid transition
z
Agreement: used to acknowledge rapid transition requests
Both RSTP and MSTP devices can perform rapid transition on a designated port only when the port
receives an agreement packet from the downstream device. The differences between RSTP and MSTP
devices are:
z
For MSTP, the downstream device’s root port sends an agreement packet only after it receives an
agreement packet from the upstream device.
z
For RSTP, the down stream device sends an agreement packet regardless of whether an
agreement packet from the upstream device is received.
shows the rapid state transition mechanism on MSTP designated ports.
