Ssl protocol stack, Figure – H3C Technologies H3C S5120 Series Switches User Manual
Page 471
1-2
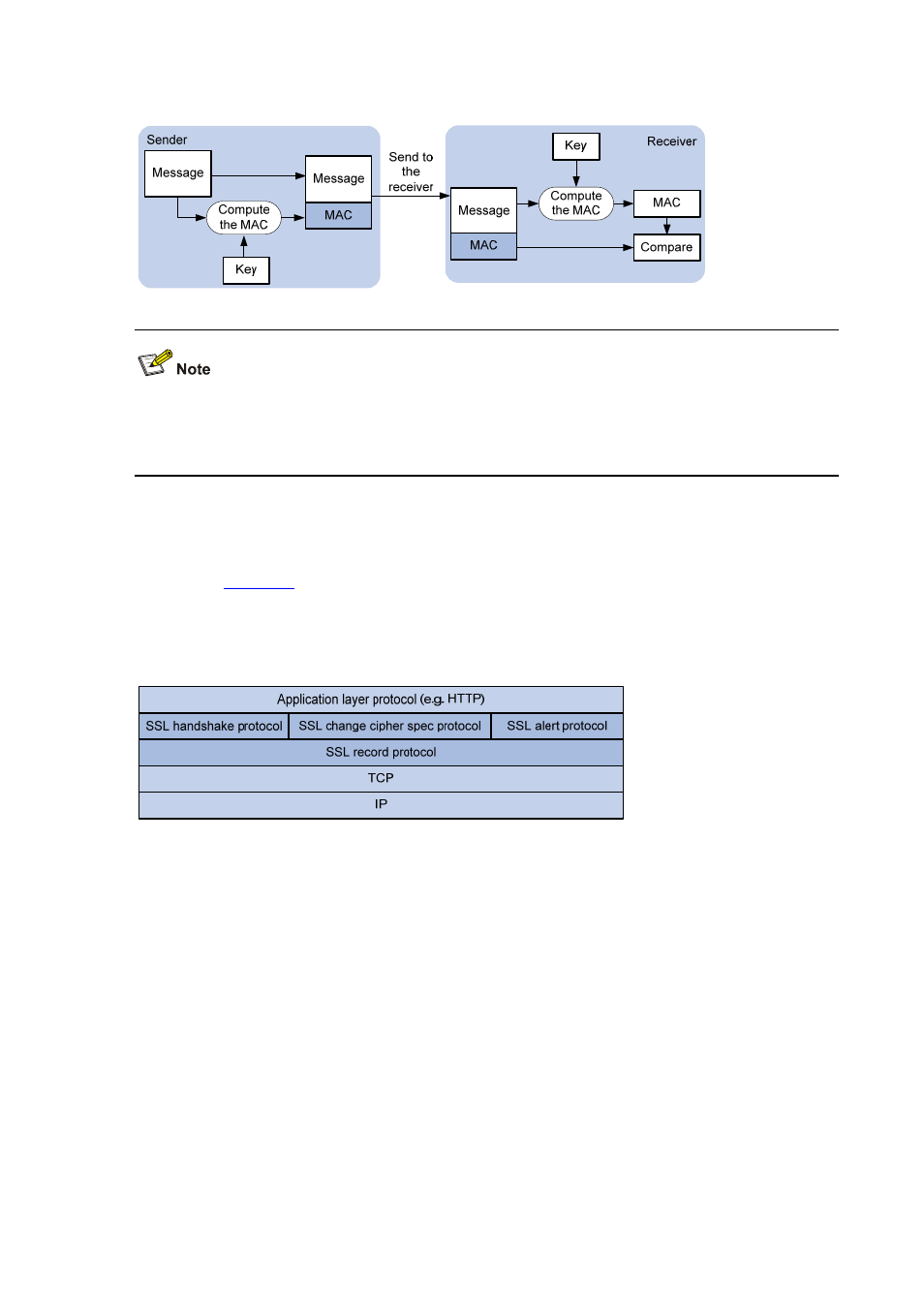
Figure 1-1 Message integrity verification by a MAC algorithm
z
For details about symmetric key algorithms, asymmetric key algorithm RSA and digital signature, see
Public Key Configuration.
z
For details about PKI, certificate, and CA, see PKI Configuration.
SSL Protocol Stack
As shown in
, the SSL protocol consists of two layers of protocols: the SSL record protocol at
the lower layer and the SSL handshake protocol, change cipher spec protocol, and alert protocol at the
upper layer.
Figure 1-2 SSL protocol stack
z
SSL record protocol: Fragments data to be transmitted, computes and adds MAC to the data, and
encrypts the data before transmitting it to the peer end.
z
SSL handshake protocol: A very important part of the SSL protocol stack, responsible for
negotiating the cipher suite to be used for secure communication (including the symmetric
encryption algorithm, key exchange algorithm, and MAC algorithm), securely exchanging the key
between the server and client, and implementing identity authentication of the server and client.
Through the SSL handshake protocol, a session is established between a client and the server. A
session consists of a set of parameters, including the session ID, peer certificate, cipher suite, and
master secret.
z
SSL change cipher spec protocol: Used for notification between the client and the server that the
subsequent packets are to be protected and transmitted based on the newly negotiated cipher
suite and key.
z
SSL alert protocol: Enables the SSL client and server to send alert messages to each other. An
alert message contains the alert severity level and a description.
