Figure 95 – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 376
361
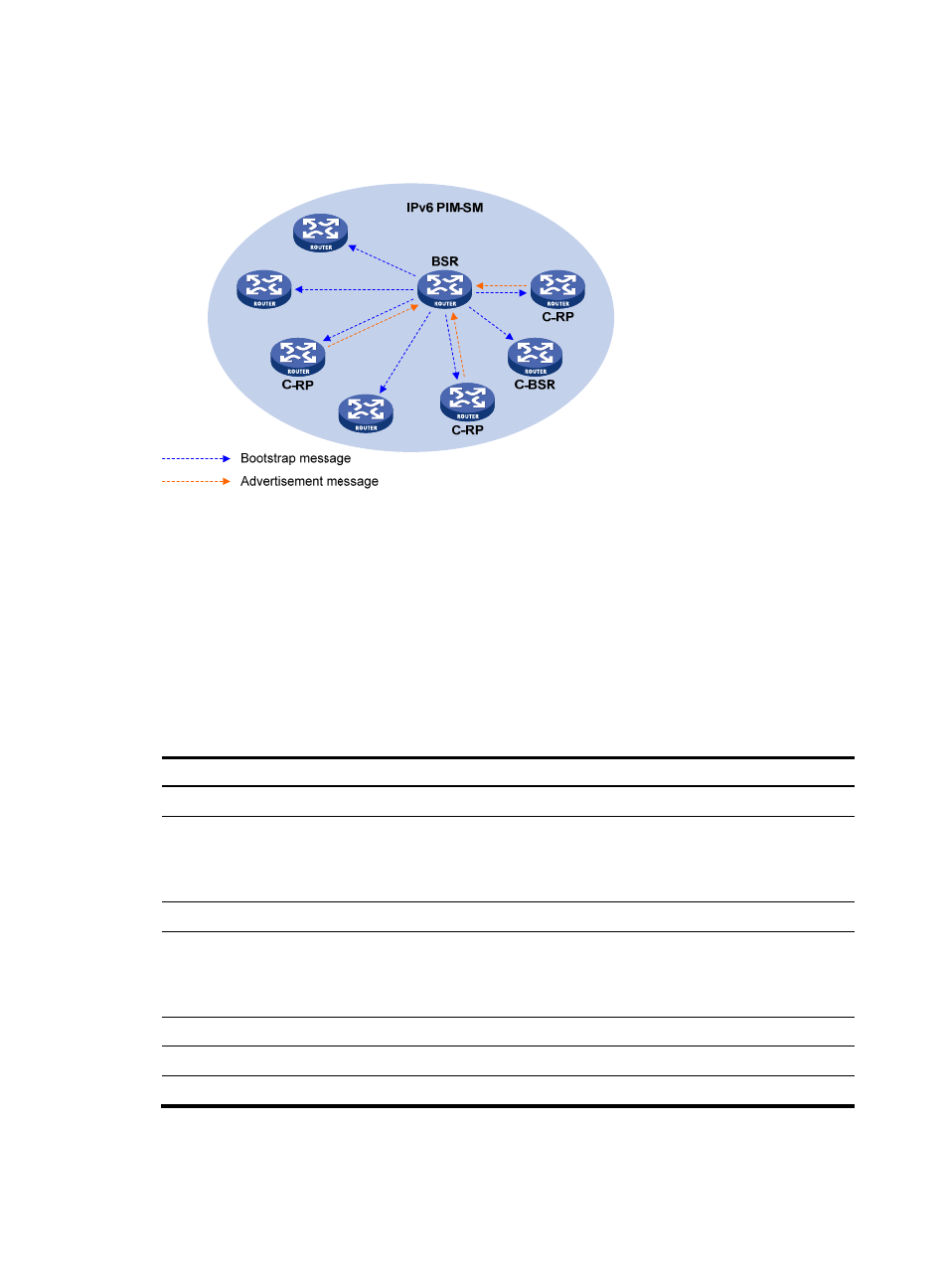
multicast groups and RPs. The BSR then encapsulates the RP-set in the bootstrap messages it periodically
originates and floods the bootstrap messages (BSMs) to the entire IPv6 PIM-SM domain.
Figure 95 BSR and C-RPs
Based on the information in the RP-sets, all routers in the network can calculate the location of the
corresponding RPs based on the following rules:
1.
The C-RP with the highest priority wins.
2.
If all the C-RPs have the same priority, their hash values are calculated through the hashing
algorithm. The C-RP with the largest hash value wins.
3.
If all the C-RPs have the same priority and hash value, the C-RP that has the highest IP address wins.
The hashing algorithm used for RP calculation is “Value (G, M, C
i
) = (1103515245 * ( (1103515245 * (G
& M) + 12345) XOR C
i
) + 12345) mod 2
31
.”
Table 11 Values in the hashing algorithm
Value Description
Value
Hash value.
G
The digest from the exclusive-or (XOR) operation between the 32-bit segments of
the IPv6 multicast group address. For example, if the IPv6 multicast address is
FF0E:C20:1A3:63::101, G = 0xFF0E0C20 XOR 0x01A30063 XOR
0x00000000 XOR 0x00000101.
M
Hash mask length.
C
i
The digest from the exclusive-or (XOR) operation between the 32-bit segments of
the C-RP IPv6 address. For example, if the IPv6 address of the C-RP is
3FFE:B00:C18:1::10, C
i
= 0x3FFE0B00 XOR 0x0C180001 XOR
0x00000000 XOR 0x00000010.
&
Logical operator of “and.”
XOR
Logical operator of “exclusive-or.”
mod
Modulo operator, which gives the remainder of an integer division.
