Rpf check rules for sa messages – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 222
207
○
If no receivers for the group exist in the domain, RP 2 neither creates an (S, G) entry nor joins
the SPT rooted at the source.
NOTE:
•
An MSDP mesh group refers to a group of MSDP peers that have MSDP peering relationships among
one another and share the same group name.
•
When using MSDP for inter-domain multicasting, once an RP receives information form a multicast
source, it no longer relies on RPs in other PIM-SM domains. The receivers can override the RPs in other
domains and directly join the multicast source-based SPT.
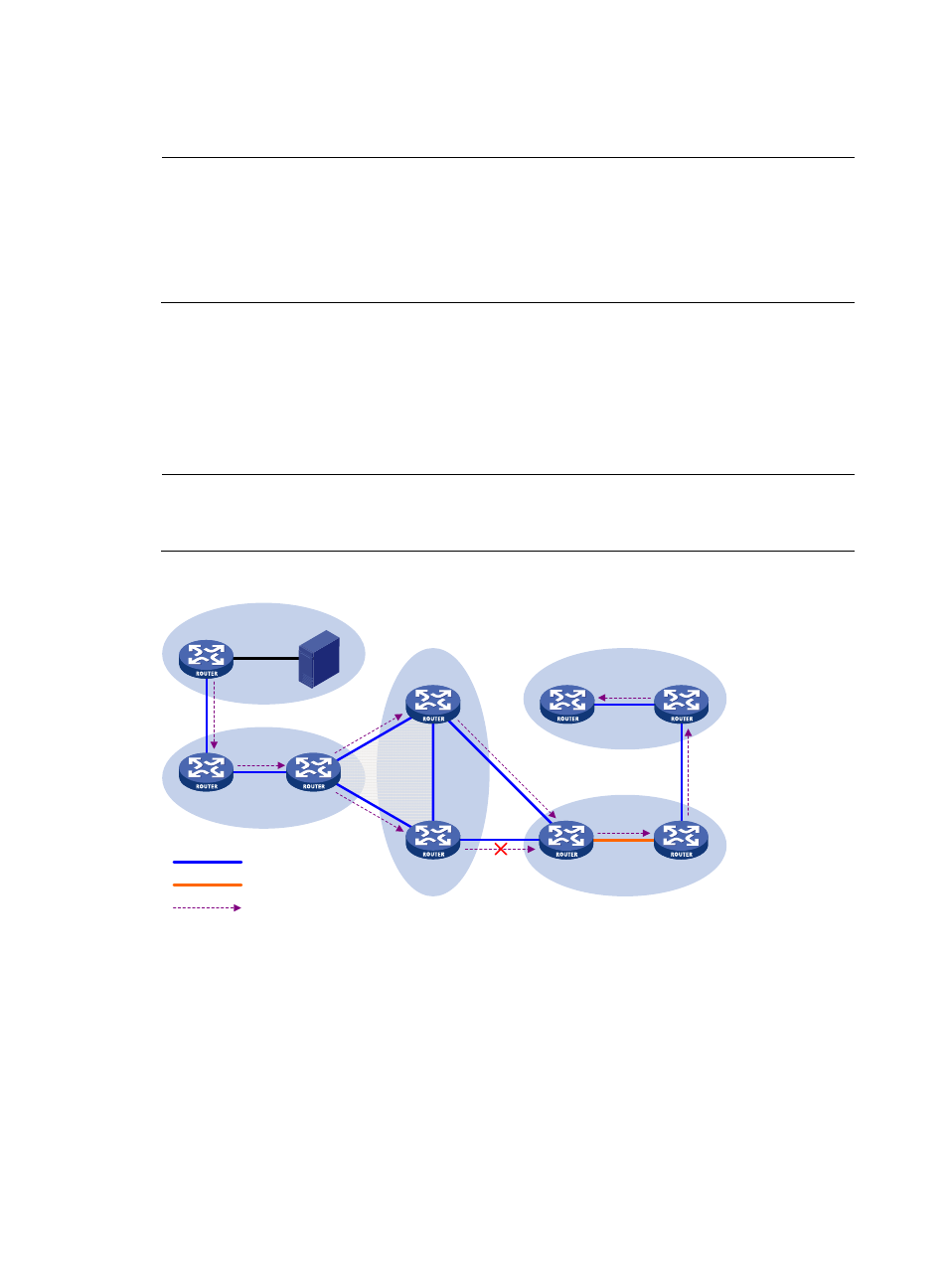
RPF check rules for SA messages
As shown in
, the autonomous systems in the network are AS 1 through AS 5, with IGP enabled
on routers within each AS and BGP or MBGP as the interoperation protocol among different ASs. Each
AS contains at least one PIM-SM domain, and each PIM-SM domain contains one ore more RPs. MSDP
peering relationships have been established among different RPs. RP 3, RP 4, and RP 5 are in an MSDP
mesh group. On RP 7, RP 6 is configured as its static RPF peer.
NOTE:
When an RP receives an SA message from a static RPF peer, the RP accepts the SA message and forwards
it to other peers without performing an RPF check.
Figure 60 Diagram for RPF check for SA messages
SA message
MSDP peers
AS 1
AS 2
AS 3
AS 4
AS 5
RP 1
RP 2
RP 3
RP 4
RP 5
RP 6
RP 7
RP 8
RP 9
Mesh group
Source
(1)
(2)
(3)
(3)
(4)
(7)
(6)
(5)
(4)
Static RPF peers
As shown in
, these MSDP peers dispose of SA messages according to the following RPF check
rules:
1.
When RP 2 receives an SA message from RP 1:
Because the source-side RP address carried in the SA message is the same as the MSDP peer
address, which means that the MSDP peer where the SA is from is the RP that has created the SA
message, RP 2 accepts the SA message and forwards it to its other MSDP peer (RP 3).
2.
When RP 3 receives the SA message from RP 2:
Because the SA message is from an MSDP peer (RP 2) in the same AS, and the MSDP peer is the
next hop on the optimal path to the source-side RP, RP 3 accepts the message and forwards it to
other peers (RP 4 and RP 5).
