Mld state, Receiver host state listening, Mld messages – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 344: Mld query message
329
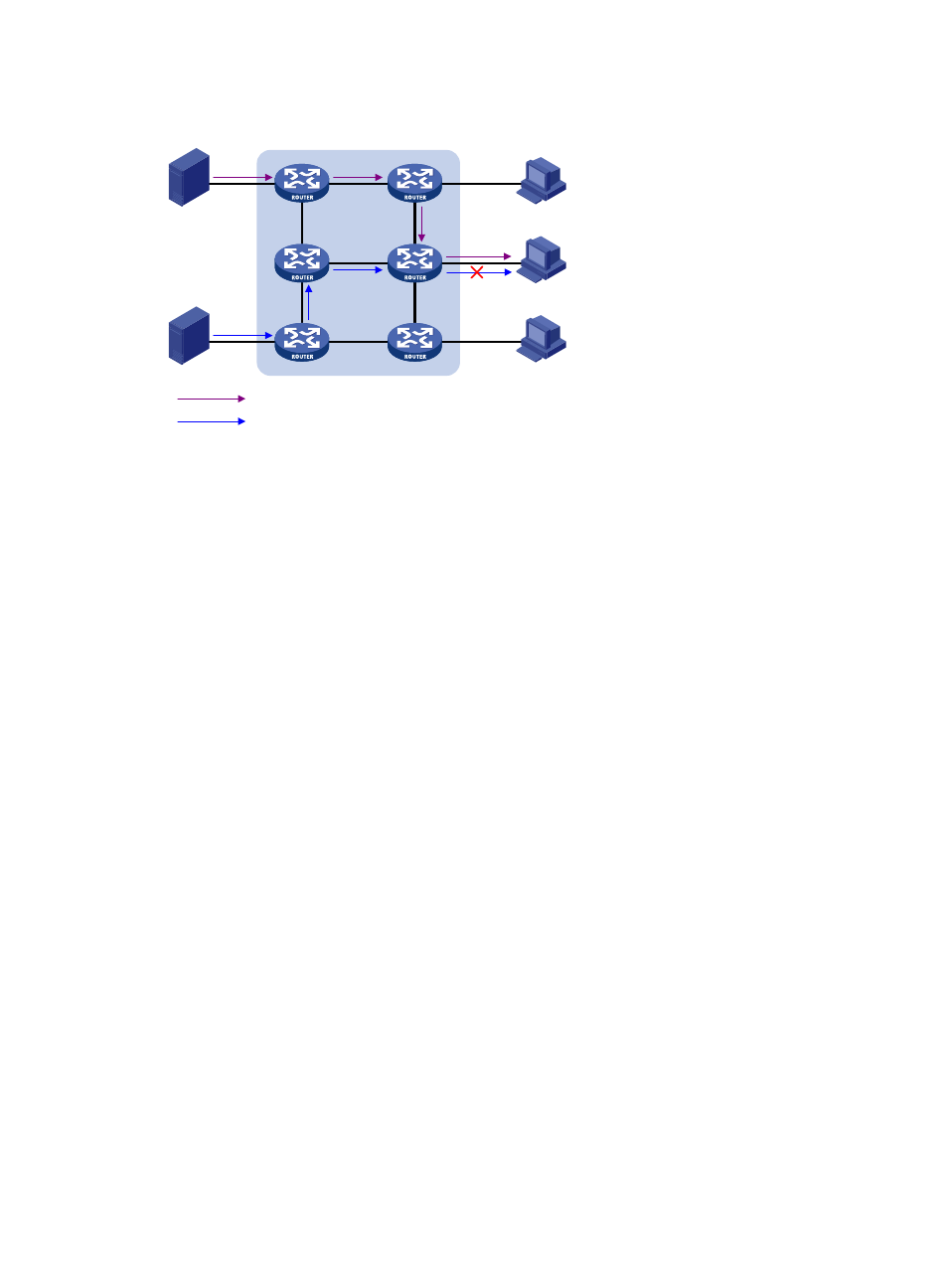
Figure 84 Flow paths of multicast-address-and-source-specific multicast traffic
Source 2
Receiver
Host A
Host B
Host C
Packets (S1,G)
Packets (S2,G)
Source 1
In the case of MLDv1, Host B cannot select IPv6 multicast sources when it joins IPv6 multicast group G.
Therefore, IPv6 multicast streams from both Source 1 and Source 2 will flow to Host B whether it needs
them or not.
When MLDv2 is running on the hosts and routers, Host B can explicitly express its interest in the IPv6
multicast data that Source 1 sends to G—denoted as (S1, G), rather than the IPv6 multicast data that
Source 2 sends to G—denoted as (S2, G). Thus, only IPv6 multicast data from Source 1 will be delivered
to Host B.
MLD state
A multicast router that is running MLDv2 maintains the multicast address state per multicast address per
attached subnet. The multicast address state consists of the following information:
•
Filter mode—The router keeps tracing the Include or Exclude state.
•
List of sources—The router keeps tracing the newly added or deleted IPv6 multicast source.
•
Timers—Filter timers, including the time that the router waits before switching to the Include mode
after an IPv6 multicast address times out, the source timer for source recording, and so on.
Receiver host state listening
By listening to the state of receiver hosts, a multicast router running MLDv2 records and maintains
information of hosts joining the source group on the attached subnet.
MLD messages
The following descriptions are based on MLDv2 messages.
MLD query message
An MLD querier learns the multicast listening state of neighbor interfaces by sending MLD query
messages. The dark area in
shows the format of an MLDv1 message.
