Aux interface signals, Aux interface signals -10 – Altera CPRI v6.0 MegaCore Function User Manual
Page 40
AUX Interface Signals
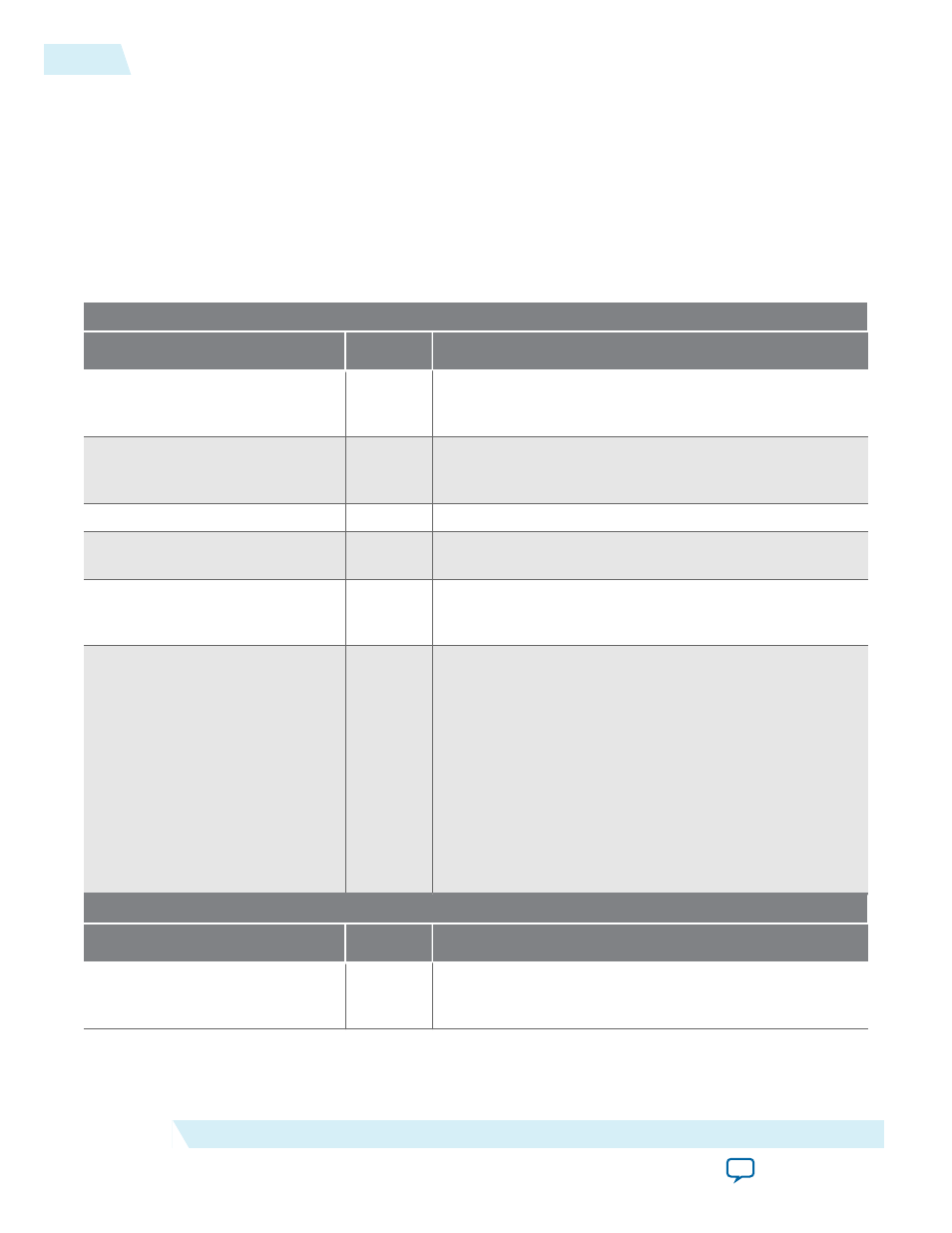
Table 3-5: AUX Interface Signals
If you turn on Enable auxiliary interface in the CPRI v6.0 parameter editor, the AUX interface is available. This
interface allows access to the entire CPRI frame and has the highest priority among the L1 interfaces.
You can alter the transmit write latency with the Auxiliary latency cycle(s) parameter. The default transmit
latency, when Auxiliary latency cycle(s) has the value of zero, is one
cpri_clkout
cycle. You can specify
additional latency cycles.
All interface signals are clocked by the
cpri_clkout
clock.
AUX RX Interface Status Signals
Signal Name
Direction
Description
aux_rx_rfp
Output
Synchronization pulse for start of 10 ms radio frame. The
pulse occurs at the start of the radio frame on the AUX RX
interface.
aux_rx_hfp
Output
Synchronization pulse for start of hyperframe. The pulse
occurs at the start of the hyperframe on the AUX RX
interface.
aux_rx_bfn[11:0]
Output
Current radio frame number on the AUX RX interface.
aux_rx_z[7:0]
Output
Current hyperframe number on the AUX RX interface.
Value is in the range 0–149.
aux_rx_x[7:0]
Output
Index number of the current basic frame in the current
hyperframe on the AUX RX interface. Value is in the
range 0–255.
aux_rx_seq[6:0]
Output
Index number of the current 32-bit word in the current
basic frame on the AUX RX interface. The value range
depends on the current CPRI line bit rate:
• 0.6144 Gbps: range is 0–3
• 1.2288 Gbps: range is 0–7
• 2.4576 Gbps: range is 0–15
• 3.0720 Gbps: range is 0–19
• 4.9152 Gbps: range is 0–31
• 6.1440 Gbps: range is 0–39
• 9.8304 Gbps: range is 0–63
• 10.1376 Gbps: range is 0–79
AUX RX Interface Data Signals
Signal Name
Direction
Description
aux_rx_data[31:0]
Output
Data the IP core presents on the AUX link. Data is
transmitted in 32-bit words. Byte [31:24] is transmitted
first and byte [7:0] is transmitted last.
3-10
AUX Interface Signals
UG-01156
2014.08.18
Altera Corporation
Functional Description
