Cpu timing, 1 oscillator, Scillator – Maxim Integrated Secure Microcontroller User Manual
Page 130: Figure 15-1. crystal connection
Secure Microcontroller User’s Guide
130 of 187
15. CPU TIMING
15.1 Oscillator
The secure microcontroller provides an on-chip oscillator circuit that can be driven either by using an
external crystal as a time base or from a TTL-compatible clock signal. The oscillator circuitry provides
the internal clocking signals to the on-chip CPU and I/O circuitry.
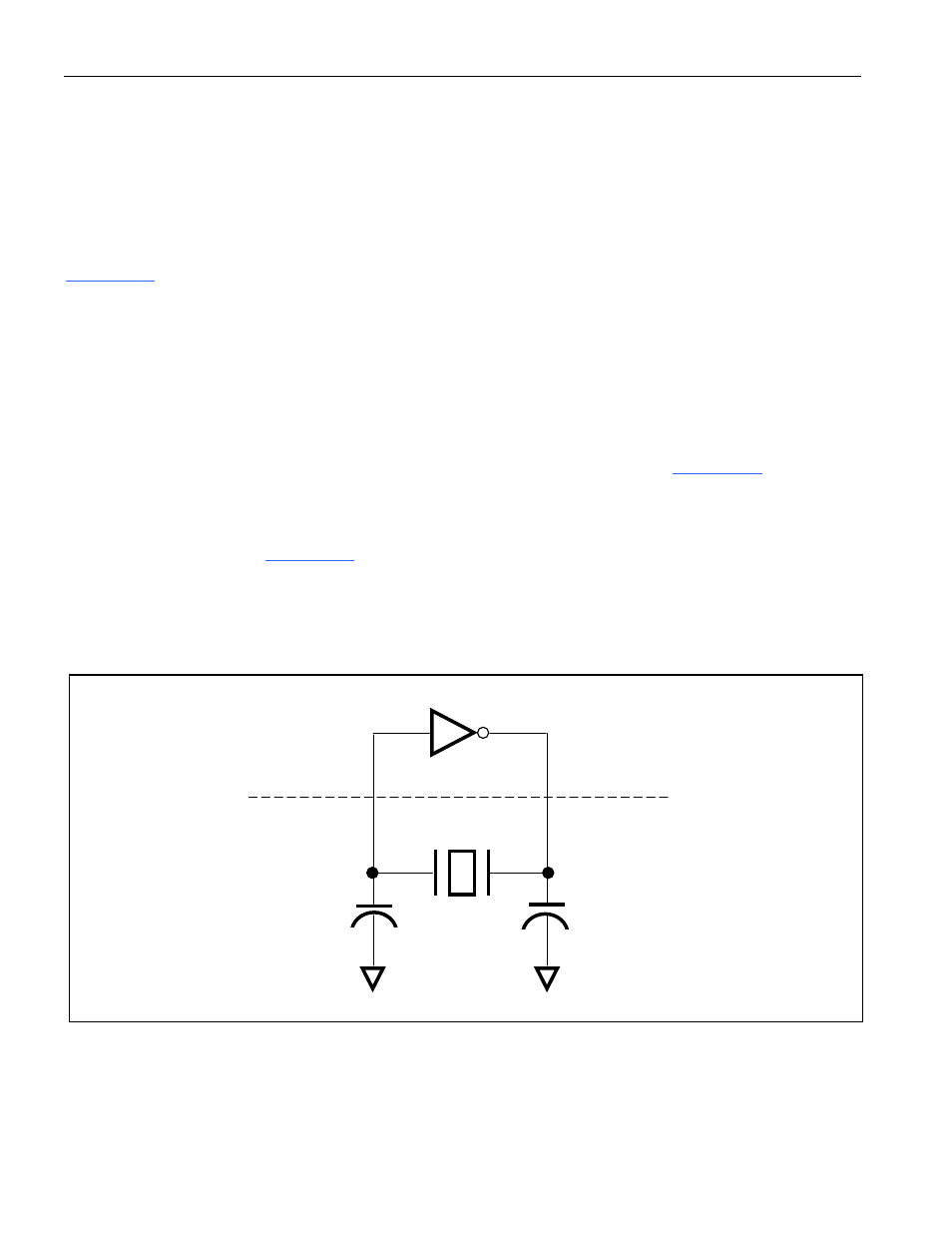
illustrates the required connections when using a crystal. Typically, the values of C1 and C2
should both be 33pF. If a ceramic resonator is used, C1 and C2 should be 47pF.
XTAL1. Input to the inverting oscillator amplifier and input to the internal clock generating circuits.
XTAL2. Output from the inverting oscillator amplifier. This pin is also used to distribute the clock to
other devices.
Oscillator Characteristics. XTAL1 and XTAL2 are the input and output, respectively, of an inverting
amplifier that can be configured for use as an on-chip oscillator, as shown in
. The crystal
should be parallel resonant, AT-cut type.
To drive the device from an external clock source, XTAL1 should be driven while XTAL2 is left
unconnected, as shown in
. There are no requirements on the duty cycle of the external clock
signal since the input to the internal clocking circuitry is through a divide-by-2 flip-flop. However,
minimum and maximum high and low times specified in the electrical specifications must be met to
insure proper operation.
Figure 15-1. Crystal Connection
SECURE
MICROCONTROLLER
XTAL1
XTAL2
33pF
33pF
