Rockwell Automation 900-TC32 Digital Temperature Controllers, Series B User Manual
Page 107
Publication 900-UM007D-EN-E - January 2011
Configuration & Basic Operation
3-37
• When there are large variations in ambient temperatures due to factors
such as seasonal changes or differences between day and night
temperatures
• When there are large variations in air flow in the control cabinet
• When heater characteristics change depending on the control system
temperature
• When an actuator with disproportional I/O, such as a
phase-control-type power regulator, is used
• When a heater is used with fast response characteristics
• When the control object or sensor has slow response
• When hunting occurs in AT or ST for any reason
Note:
PID constants are initialized to the factory settings when switching to
RT. When RT is selected, the derivative time setting unit becomes
second.
RT Features
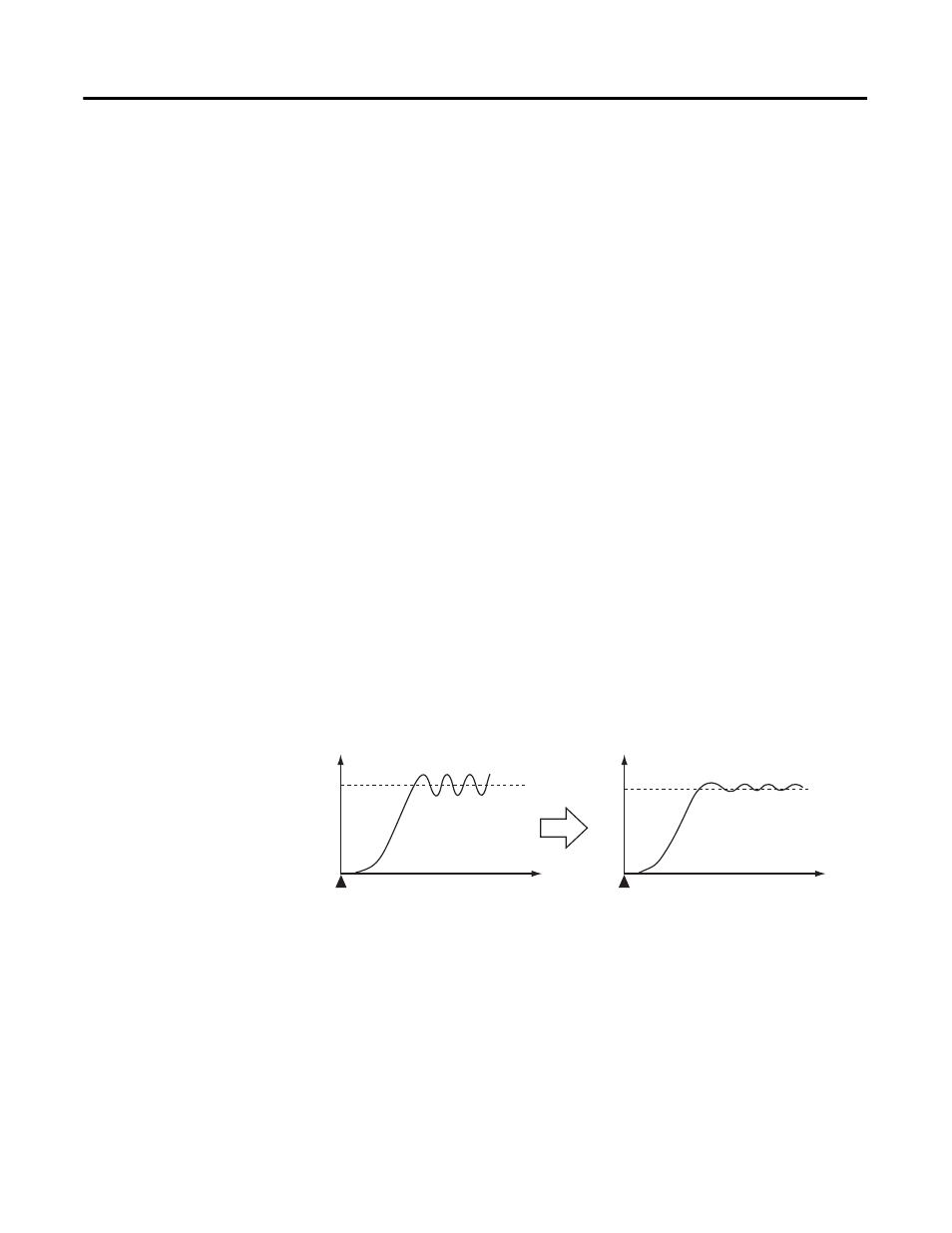
• Even when hunting occurs for PID constants when AT or ST is
executed in normal mode, it is less likely to occur when AT or ST is
executed in RT mode.
Figure 3.71 — Hunting
• When the temperature (PV) falls short of the set point for the PID
constants when using AT or ST in normal mode, executing AT or ST in
RT mode tends to improve performance.
Temperature
Temperature
Hunting occurs
Set point value
Set point value
Start of control
Start of control
Time
Time
Hunting is reduced using RT
