Description – Rainbow Electronics AT89C5132 User Manual
Page 87
87
AT8xC5132
4173A–8051–08/02
Clock Control
The MMC bus clock signal can be used by the host to turn the cards into energy saving
mode or to control the data flow (to avoid under-run or over-run conditions) on the bus.
The host is allowed to lower the clock frequency or shut it down.
There are a few restrictions the host must follow:
•
The bus frequency can be changed at any time (under the restrictions of maximum
data transfer frequency, defined by the cards, and the identification frequency
defined by the specification document).
•
It is an obvious requirement that the clock must be running for the card to output
data or response tokens. After the last MultiMedia Card bus transaction, the host is
required, to provide 8 (eight) clock cycles for the card to complete the operation
before shutting down the clock. Following is a list of the various bus transactions:
•
A command with no response. 8 clocks after the host command End bit.
•
A command with response. 8 clocks after the card command End bit.
•
A read data transaction. 8 clocks after the End bit of the last data block.
•
A write data transaction. 8 clocks after the CRC status token.
•
The host is allowed to shut down the clock of a “busy” card. The card will complete
the programming operation regardless of the host clock. However, the host must
provide a clock edge for the card to turn off its busy signal. Without a clock edge the
card (unless previously disconnected by a deselect command-CMD7) will force the
MDAT line down, forever.
Description
The MMC controller interfaces to the C51 core through the following eight special func-
tion registers:
MMCON0, MMCON1, MMCON2, the three MMC control registers (see Figure 94 to
Figure ); MMSTA, the MMC status register (see Figure 97); MMINT, the MMC interrupt
register (see Figure ); MMMSK, the MMC interrupt mask register (see Figure 99);
MMCMD, the MMC command register (see Figure 100); MMDAT, the MMC data regis-
ter (see Figure ); and MMCLK, the MMC clock register (see Figure 102).
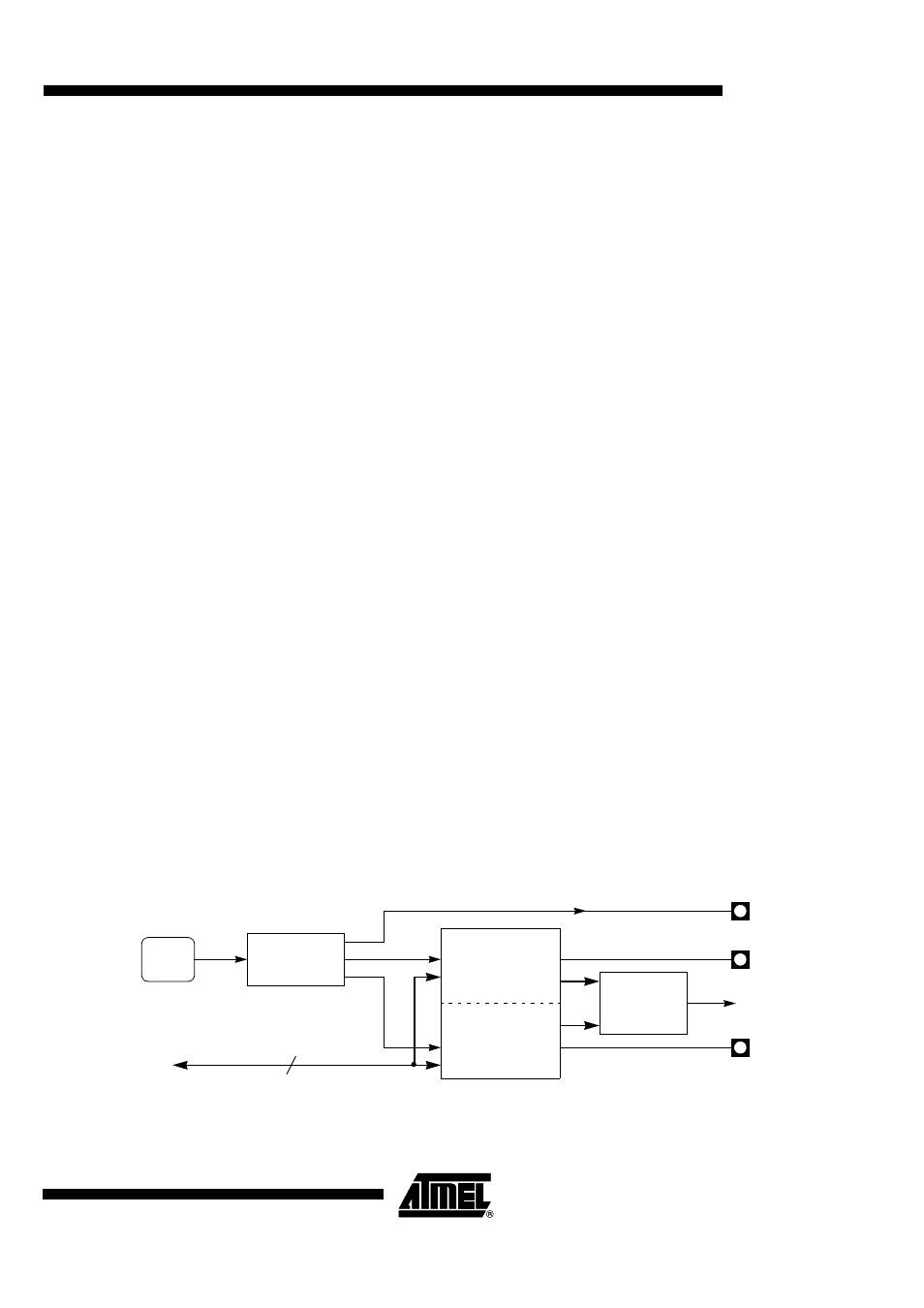
As shown in Figure 60, the MMC controller is divided in four blocks: the clock generator
that handles the MCLK (formally the MMC CLK) output to the card, the command line
controller that handles the MCMD (formally the MMC CMD) line traffic to or from the
card, the data line controller that handles the MDAT (formally the MMC DAT) line traffic
to or from the card, and the interrupt controller that handles the MMC controller interrupt
sources. These blocks are detailed in the following sections.
Figure 60. MMC Controller Block Diagram
OSC
CLOCK
MCMD
MCLK
8
Internal
Bus
MDAT
Command Line
Clock
MMC
Interrupt
Request
Generator
Controller
Data Line
Controller
Interrupt
Controller
