Interrupt, Ee figure 99), Figure 99) – Rainbow Electronics AT89C5132 User Manual
Page 123
123
AT8xC5132
4173A–8051–08/02
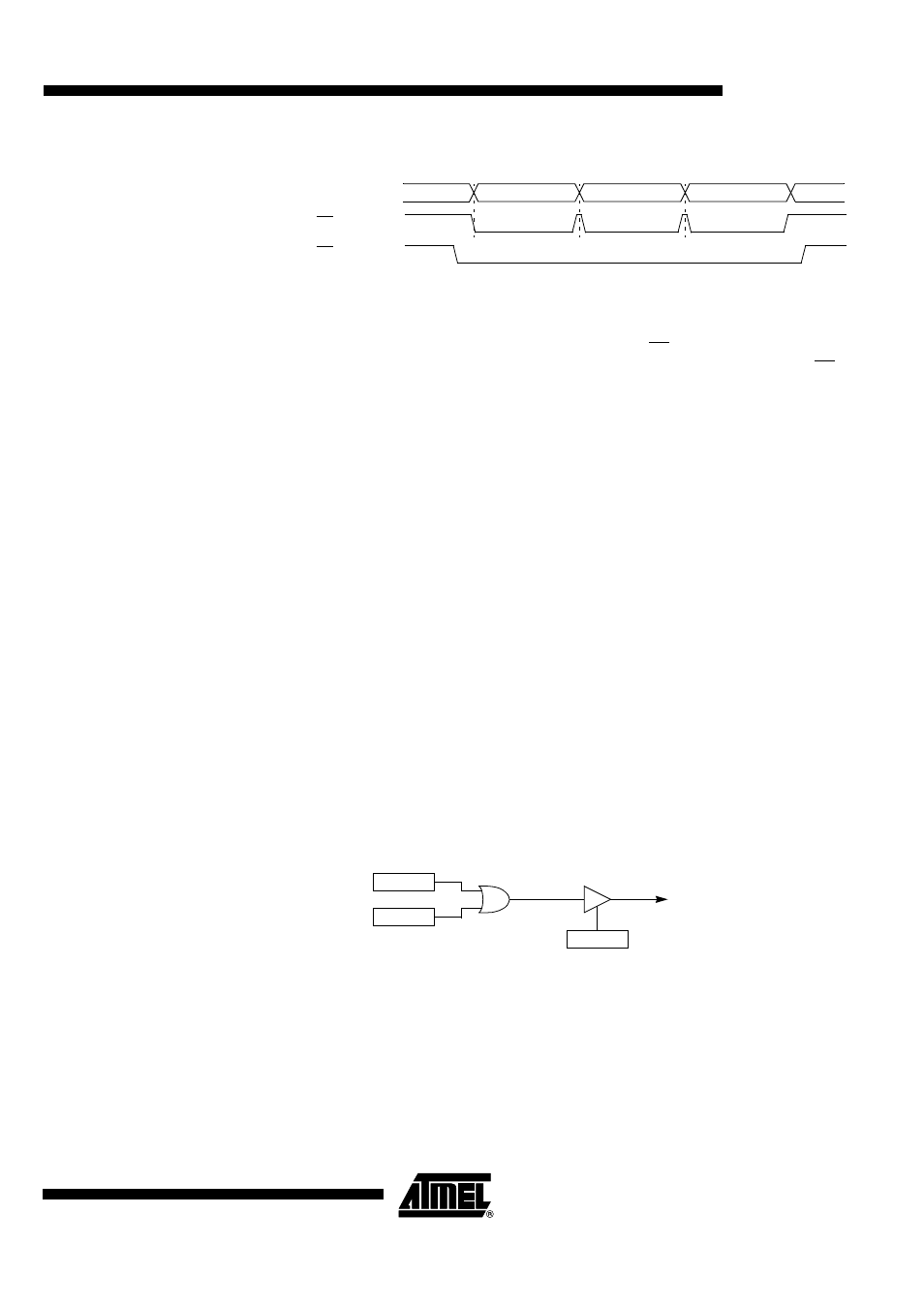
Figure 99. SS# Timing Diagram
Error Conditions
The following flags signal the SPI error conditions:
•
MODF in SPSTA signals a mode fault.
MODF flag is relevant only in master mode when SS usage is enabled (SSDIS bit
cleared). It signals when set that another master on the bus has asserted SS pin
and so, may create a conflict on the bus with two masters sending data at the same
time.
A mode fault automatically disables the SPI (SPEN cleared) and configures the SPI
in slave mode (MSTR cleared).
MODF flag can trigger an interrupt as explained in Section "Interrupt", page 123.
MODF flag is cleared by reading SPSTA and re-configuring SPI by writing to
SPCON.
•
WCOL in SPSTA signals a write collision.
WCOL flag is set when SPDAT is loaded while a transfer is on-going. In this case,
data is not written to SPDAT and transfer continues uninterrupted. WCOL flag does
not trigger any interrupt and is relevant jointly with SPIF flag.
WCOL flag is cleared after reading SPSTA and writing new data to SPDAT while no
transfer is ongoing.
Interrupt
The SPI handles two interrupt sources; the “end of transfer” and the “mode fault” flags.
As shown in Figure 100 these flags are combined together to appear as a single inter-
rupt source for the C51 core. The SPIF flag is set at the end of an 8-bit shift in and out
and is cleared by reading SPSTA and then reading from or writing to SPDAT.
The MODF flag is set in case of mode fault error and is cleared by reading SPSTA and
then writing to SPCON.
The SPI interrupt is enabled by setting ESPI bit in IEN1 register. This assumes inter-
rupts are globally enabled by setting EA bit in IEN0 register.
Figure 100. SPI Interrupt System
SS (CPHA = 1)
SS (CPHA = 0)
SI/SO
Byte 1
Byte 2
Byte 3
ESPI
IEN1.2
SPI Controller
Interrupt Request
SPIF
SPSTA.7
MODF
SPSTA.4
