Description – Rainbow Electronics AT89C5132 User Manual
Page 120
120
AT8xC5132
4173A–8051–08/02
Description
The SPI controller interfaces with the C51 core through three special function registers:
SPCON, the SPI control register (see Table 114); SPSTA, the SPI status register (see
Table 115); and SPDAT, the SPI data register (see Table 116).
Master Mode
The SPI operates in master mode when the MSTR bit in SPCON is set.
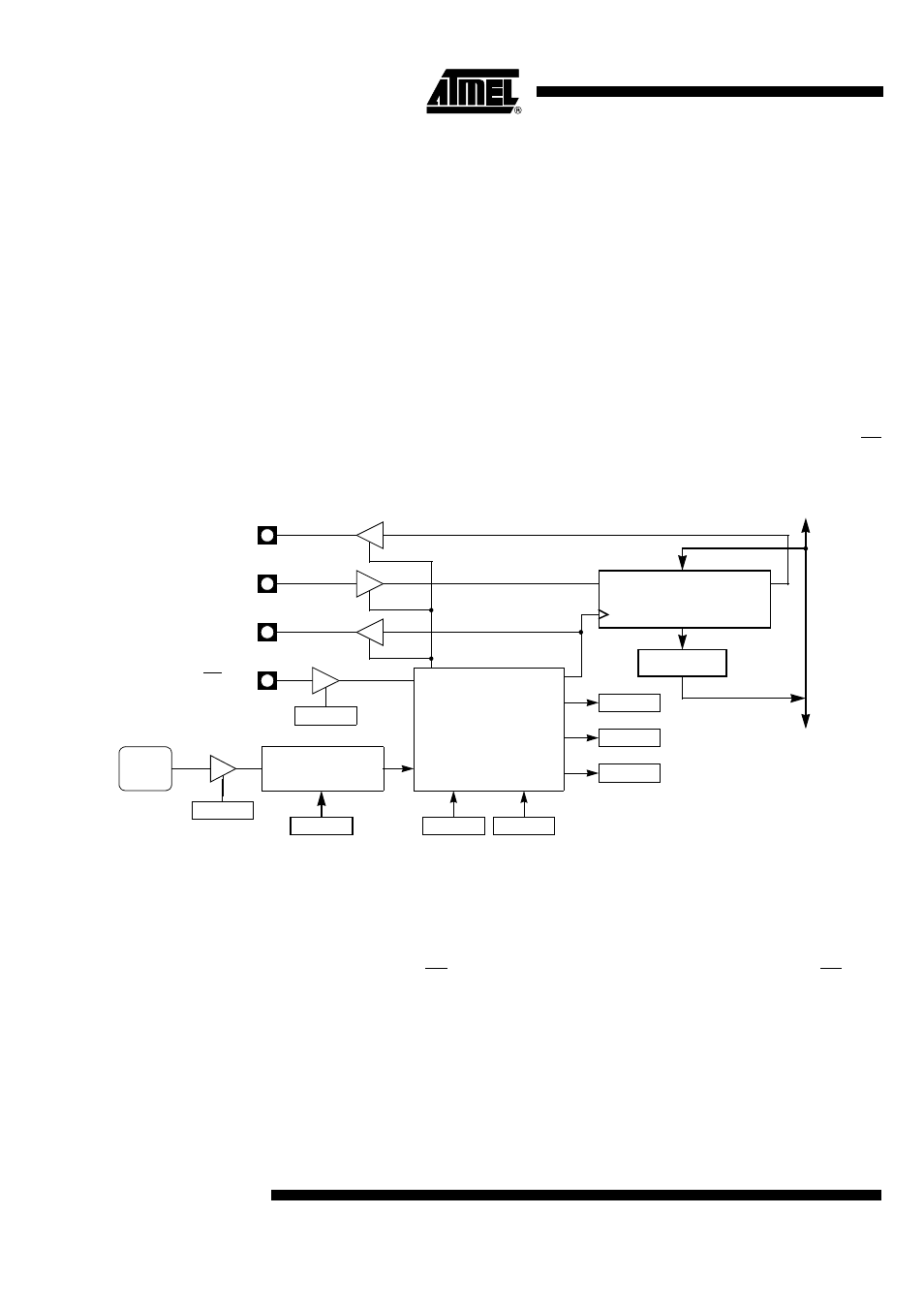
Figure 95 shows the SPI block diagram in master mode. Only a master SPI module can
initiate transmissions. Software begins the transmission by writing to SPDAT. Writing to
SPDAT writes to the shift register while reading SPDAT reads an intermediate register
updated at the end of each transfer.
The byte begins shifting out on the MOSI pin under the control of the bit rate generator.
This generator also controls the shift register of the slave peripheral through the SCK
output pin. As the byte shifts out, another byte shifts in from the slave peripheral on the
MISO pin. The byte is transmitted most significant bit (MSB) first. The end of transfer is
signalled by SPIF being set.
In case of the AT8xC5132 is the only master on the bus, it can be useful not to use SS
pin and get it back to I/O functionality. This is achieved by setting SSDIS bit in SPCON.
Figure 95. SPI Master Mode Block Diagram
Note:
MSTR bit in SPCON is set to select master mode.
Slave Mode
The SPI operates in slave mode when the MSTR bit in SPCON is cleared and data has
been loaded in SPDAT.
Figure 96 shows the SPI block diagram in slave mode. In slave mode, before data trans-
mission occurs, the SS pin of the slave SPI must be asserted to low level. SS must
remain low until the transmission of the byte is complete. In the slave SPI module, data
enters the shift register through the MOSI pin under the control of the serial clock pro-
vided by the master SPI module on the SCK input pin. When the master starts a
transmission, the data in the shift register begins shifting out on the MISO pin. The end
of transfer is signaled by SPIF being set.
In case of the AT8xC5132 is the only slave on the bus, it can be useful not to use SS pin
and get it back to I/O functionality. This is achieved by setting SSDIS bit in SPCON. This
bit has no effect when CPHA is cleared (see Section "SS Management", page 122).
Bit Rate Generator
SPR2:0
SPCON
MOSI/P4.1
MISO/P4.0
SCK/P4.2
CPOL
SPCON.3
SPEN
SPCON.6
CPHA
SPCON.2
PER
CLOCK
8-bit Shift Register
SPDAT WR
I
Q
In
te
rnal
Bus
SPDAT RD
Control and Clock Logic
MODF
SPSTA.4
SS/P4.3
SSDIS
SPCON.5
WCOL
SPSTA.6
SPIF
SPSTA.7
