Table 117) – Rainbow Electronics AT89C5132 User Manual
Page 130
130
AT8xC5132
4173A–8051–08/02
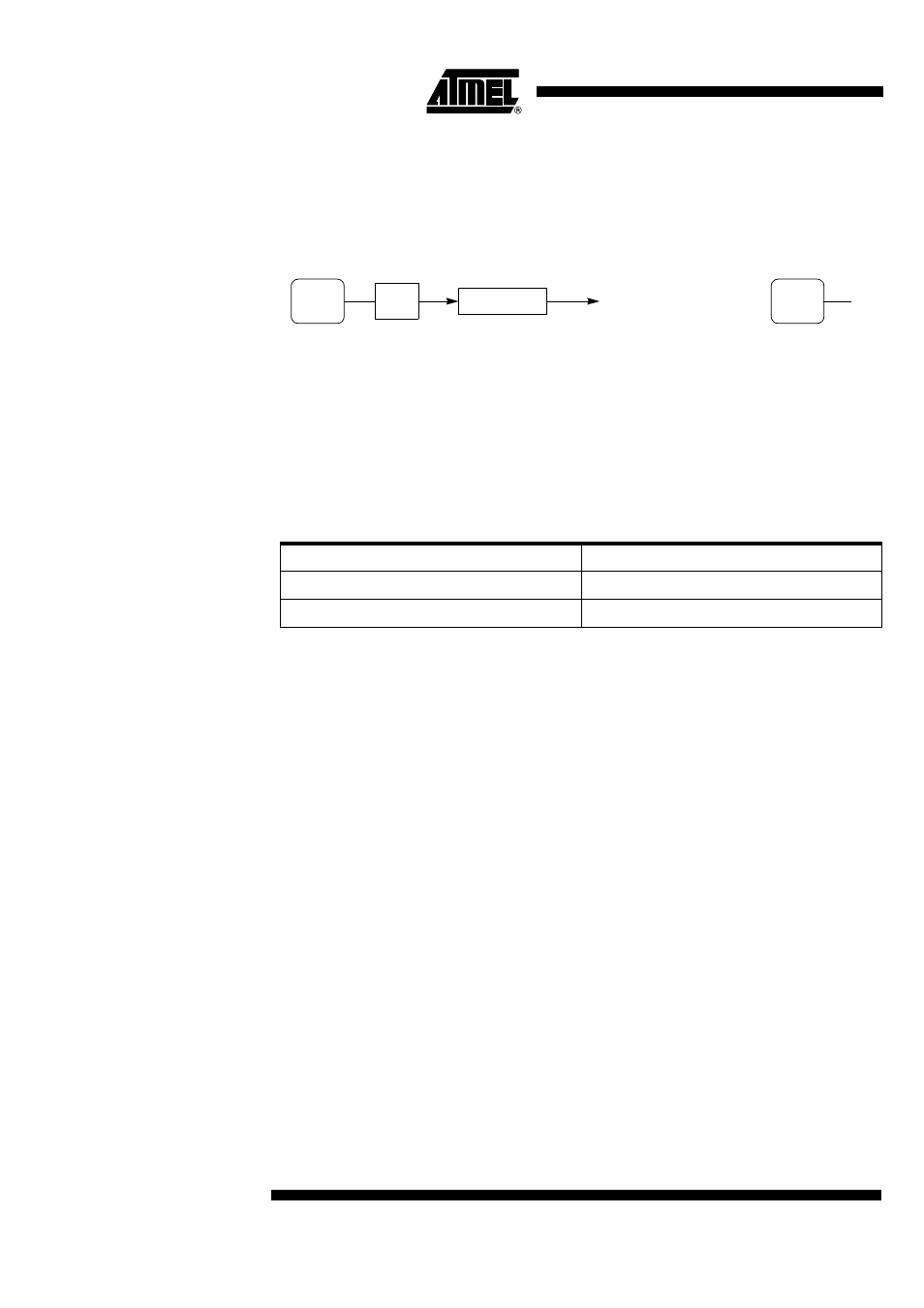
Clock Generation
The ADC clock is generated by division of the peripheral clock (see details in
Section “X2 Feature”, page 12). The division factor is then given by ADCP4:0 Bits in
ADCLK register. Figure 107 shows the ADC clock generator and its calculation
formula
(1)
.
Figure 107. ADC Clock Generator and Symbol Caution:
Note:
In all cases, the ADC clock frequency may be higher than the maximum F
ADCLK
parame-
ter reported in the Section “AC Characteristics”.
Channel Selection
The channel on which conversion is performed is selected by the ADCS bit in ADCON
register according to Table 117.
Table 117. ADC Channel Selection
Conversion Precision
The 10-bit precision conversion is achieved by stopping the CPU core activity during
conversion for limiting the digital noise induced by the core. This mode called the
Pseudo-Idle mode
(1), (2)
is enabled by setting the ADIDL bit in ADCON register. Thus,
when conversion is launched (see Section "Conversion Launching", page 131), the
CPU core is stopped until the end of the conversion (see Section "End of Conversion",
page 131). This bit is cleared by hardware at the end of the conversion.
Notes:
1. Only the CPU activity is frozen, peripherals are not affected by the Pseudo-Idle
mode.
2. If some interrupts occur during the Pseudo-Idle mode, they will be delayed and pro-
cessed according to their priority after the end of the conversion.
Configuration
The ADC configuration consists in programming the ADC clock as detailed in the Sec-
tion "Clock Generation", page 130. The ADC is enabled using the ADEN bit in ADCON
register. As shown in Figure 93, user must wait for the setup time (T
SETUP
) before
launching any conversion.
ADCD4:0
ADCLK
ADC Clock
ADCclk
PERclk
2 ADCD
⋅
-------------------------
=
ADC Clock Symbol
ADC
CLOCK
PER
CLOCK
÷
2
ADCS
Channel
0
AIN1
1
AIN0
