Synchronous peripheral interface – Rainbow Electronics AT89C5132 User Manual
Page 119
119
AT8xC5132
4173A–8051–08/02
Synchronous
Peripheral Interface
The AT8xC5132 implement a Synchronous Peripheral Interface with master and slave
modes capability.
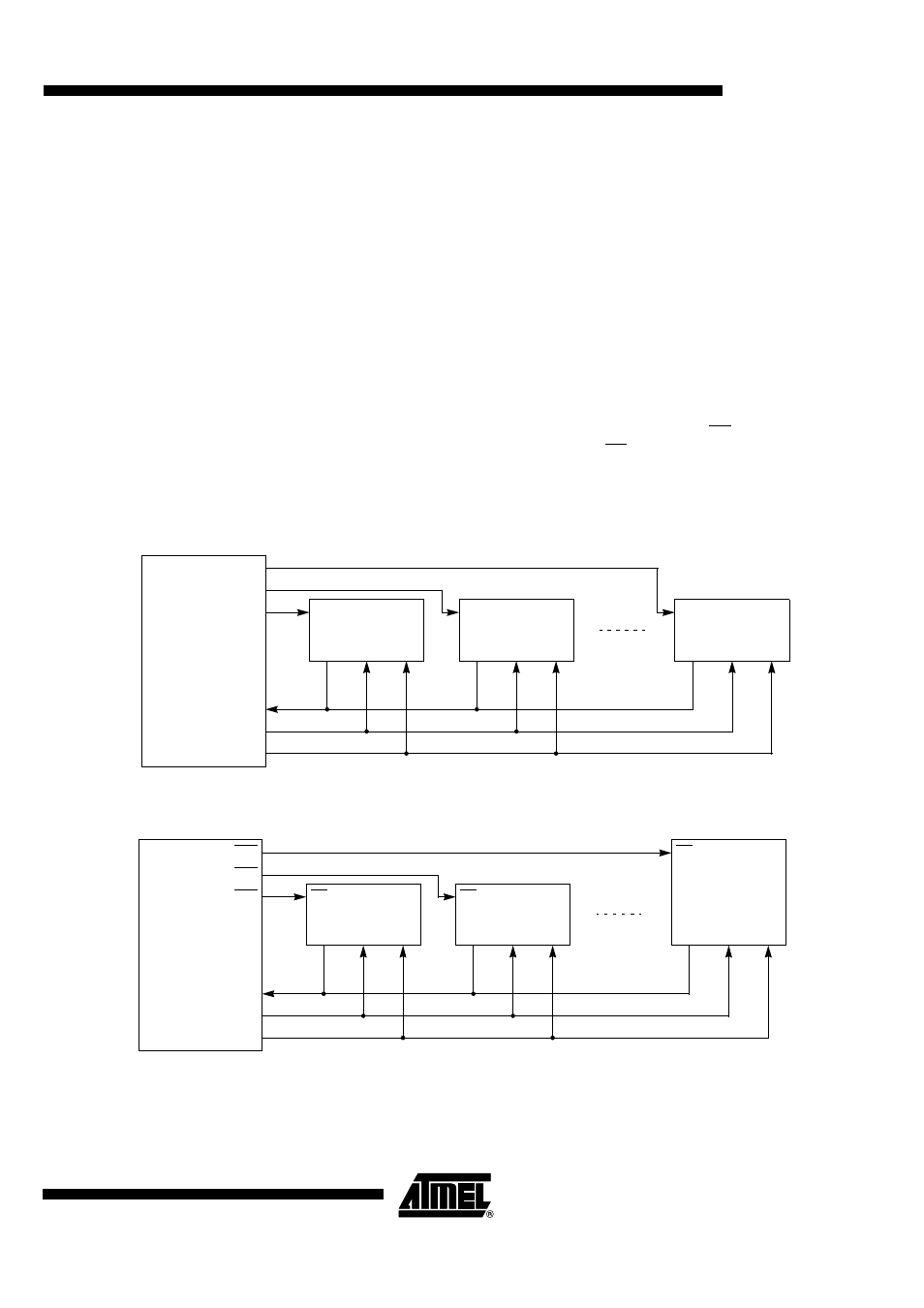
Figure 93 shows an SPI bus configuration using the AT8xC5132 as master connected
to slave peripherals. Figure 94 shows an SPI bus configuration using the AT8xC5132 as
slave of an other master.
The bus is made of three wires connecting all the devices together:
•
Master Output Slave Input (MOSI): it is used to transfer data in series from the
master to a slave. It is driven by the master.
•
Master Input Slave Output (MISO): it is used to transfer data in series from a slave
to the master. It is driven by the selected slave.
•
Serial Clock (SCK): it is used to synchronize the data transmission both in and out
of the devices through their MOSI and MISO lines. It is driven by the master for eight
clock cycles which allows to exchange one byte on the serial lines.
Each slave peripheral is selected by one Slave Select pin (SS). If there is only one
slave, it may be continuously selected with SS tied to a low level. Otherwise, the
AT8xC5132 may select each device by software through port pins (Pn.x). Special care
should be taken not to select two slaves at the same time to avoid bus conflicts.
Figure 93. Typical Master SPI Bus Configuration
Figure 94. Typical Slave SPI Bus Configuration
AT8xC5132
DataFlash 1
SS#
MISO
MOSI
SCK
P4.0
P4.1
P4.2
Pn.z
Pn.y
Pn.x
SO
SI
SCK
DataFlash 2
SS#
SO
SI
SCK
LCD
Controller
SS#
SO
SI
SCK
MASTER
Slave 1
SS
MISO
MOSI
SCK
SSn
SS1
SS0
SO
SI
SCK
Slave 2
SS
SO
SI
SCK
AT8xC5132
Slave n
SS
MISO MOSI SCK
