Program and data addressing modes, Register direct, single register rd, Register direct, two registers rd and rr – Rainbow Electronics ATmega161L User Manual
Page 13: Atmega161(l)
13
ATmega161(L)
1228C–AVR–08/02
The five different Addressing modes for the Data memory cover: Direct, Indirect with
Displacement, Indirect, Indirect with Pre-decrement and Indirect with Post-increment. In
the Register File, registers R26 to R31 feature the indirect Addressing Pointer
Registers.
The direct addressing reaches the entire data space.
The Indirect with Displacement mode features a 63-address locations reach from the
base address given by the Y- or Z-register.
When using Register Indirect Addressing modes with automatic pre-decrement and
post-increment, the address registers X, Y, and Z are decremented and incremented.
The 32 general purpose working registers, 64 I/O Registers and the 1K byte of internal
data SRAM in the ATmega161 are all accessible through all these Addressing modes.
See the next section for a detailed description of the different Addressing modes.
Program and Data
Addressing Modes
The ATmega161 AVR RISC microcontroller supports powerful and efficient Addressing
modes for access to the Program memory (Flash) and Data memory (SRAM, Register
File and I/O memory). This section describes the different Addressing modes supported
by the AVR architecture. In the figures, OP means the operation code part of the instruc-
tion word. To simplify, not all figures show the exact location of the addressing bits.
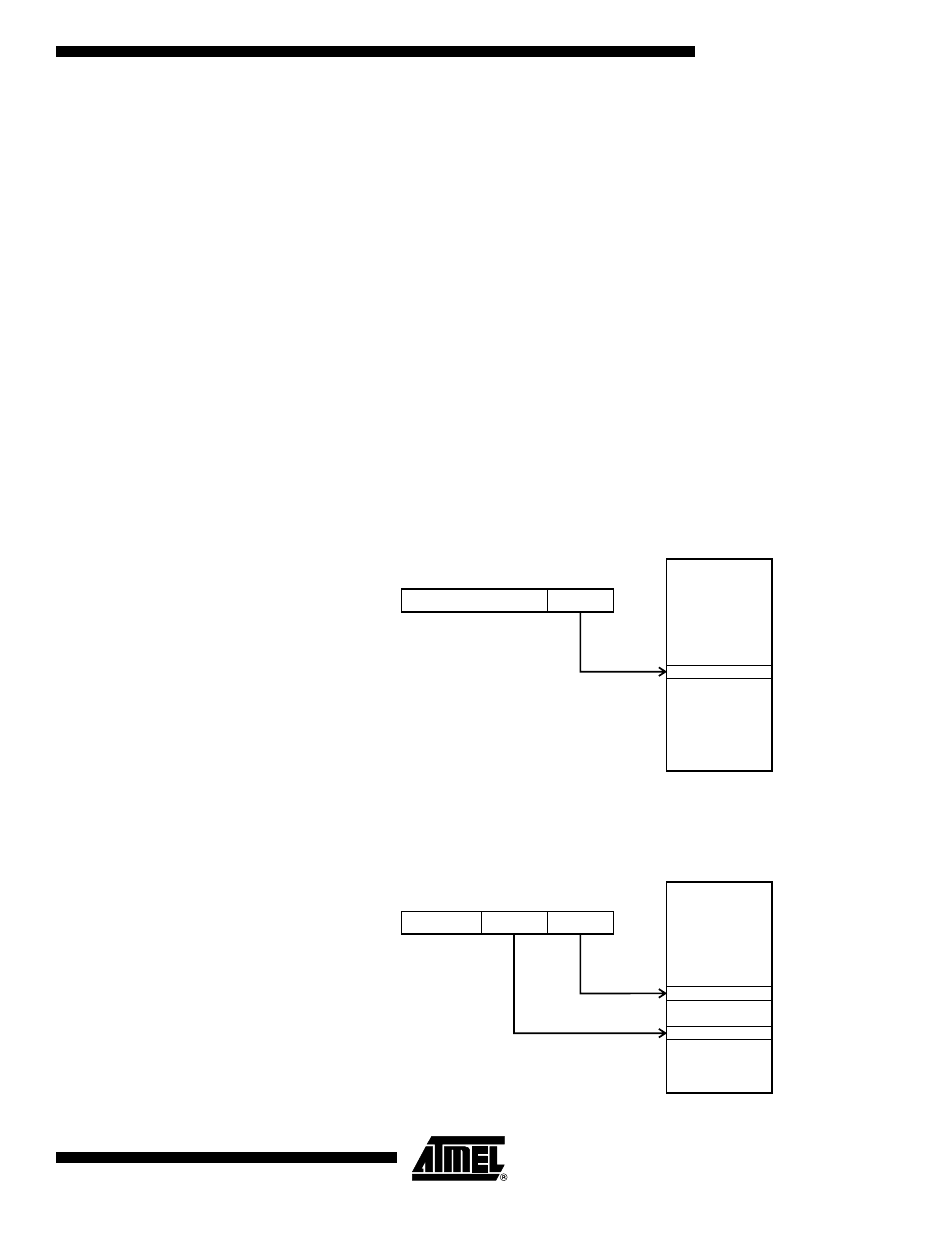
Register Direct, Single
Register Rd
Figure 9. Direct Single Register Addressing
The operand is contained in register d (Rd).
Register Direct, Two Registers
Rd and Rr
Figure 10. Direct Register Addressing, Two Registers
REGISTER FILE
15
OP
d
d
31
0
4
0
0
d
r
31
REGISTER FILE
OP
r
d
15
9
5 4
0
