Offset compensation schemes, Adc accuracy definitions, Atmega128(l) – Rainbow Electronics ATmega128L User Manual
Page 229
229
ATmega128(L)
2467B–09/01
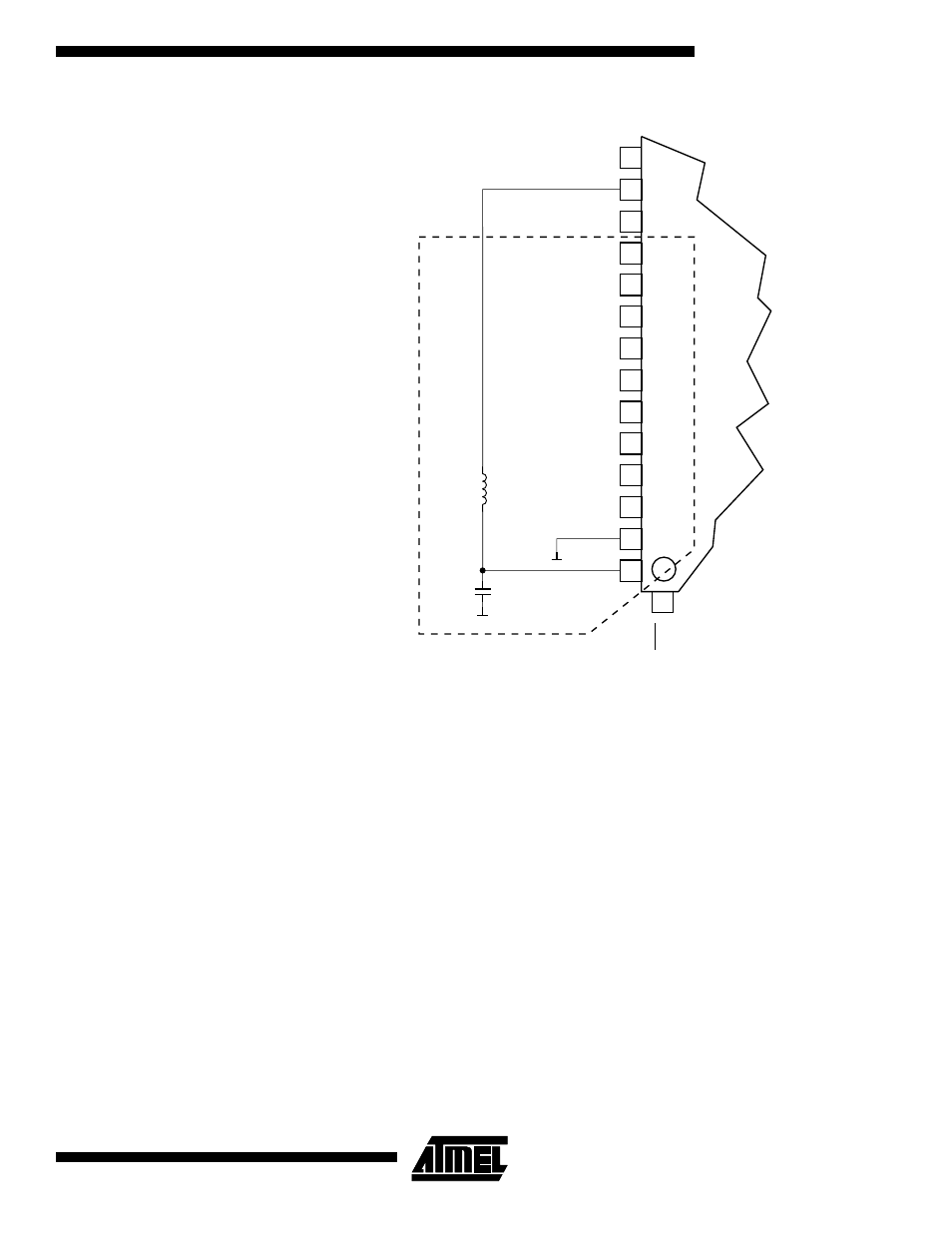
Figure 113. ADC Power Connections
Offset Compensation
Schemes
The gain stage has a built-in offset cancellation circuitry that nulls the offset of differen-
tial measurements as much as possible. The remaining offset in the analog path can be
measured directly by selecting the same channel for both differential inputs. This offset
residue can be then subtracted in software from the measurement results. Using this
kind of software based offset correction, offset on any channel can be reduced below
one LSB.
ADC Accuracy Definitions
An n-bit single-ended ADC converts a voltage linearly between GND and V
REF
in 2
n
steps (LSBs). The lowest code is read as 0, and the highest code is read as 2
n
-1.
Several parameters describe the deviation from the ideal behavior:
•
Offset: The deviation of the first transition (0x000 to 0x001) compared to the ideal
transition (at 0.5 LSB). Ideal value: 0 LSB.
VCC
GND
100nF
Analog Ground Plane
(ADC0) PF0
(ADC7) PF7
(ADC1) PF1
(ADC2) PF2
(ADC3) PF3
(ADC4) PF4
(ADC5) PF5
(ADC6) PF6
AREF
GND
AVCC
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
61
62
62
63
63
64
64
1
51
PEN
(AD0) PA0
10
µΗ
