Data memory access times, Atmega128(l) – Rainbow Electronics ATmega128L User Manual
Page 18
18
ATmega128(L)
2467B–09/01
The five different addressing modes for the data memory cover: Direct, Indirect with Dis-
placement, Indirect, Indirect with Pre-decrement, and Indirect with Post-increment. In
the Register file, registers R26 to R31 feature the indirect addressing pointer registers.
The direct addressing reaches the entire data space.
The Indirect with Displacement mode reaches 63 address locations from the base
address given by the Y- or Z-register.
When using register indirect addressing modes with automatic pre-decrement and post-
increment, the address registers X, Y, and Z are decremented or incremented.
The 32 general purpose working registers, 64 I/O registers, and the 4096 bytes of inter-
nal data SRAM in the ATmega128 are all accessible through all these addressing
modes. The Register file is described in
“General Purpose Register File” on page 10.
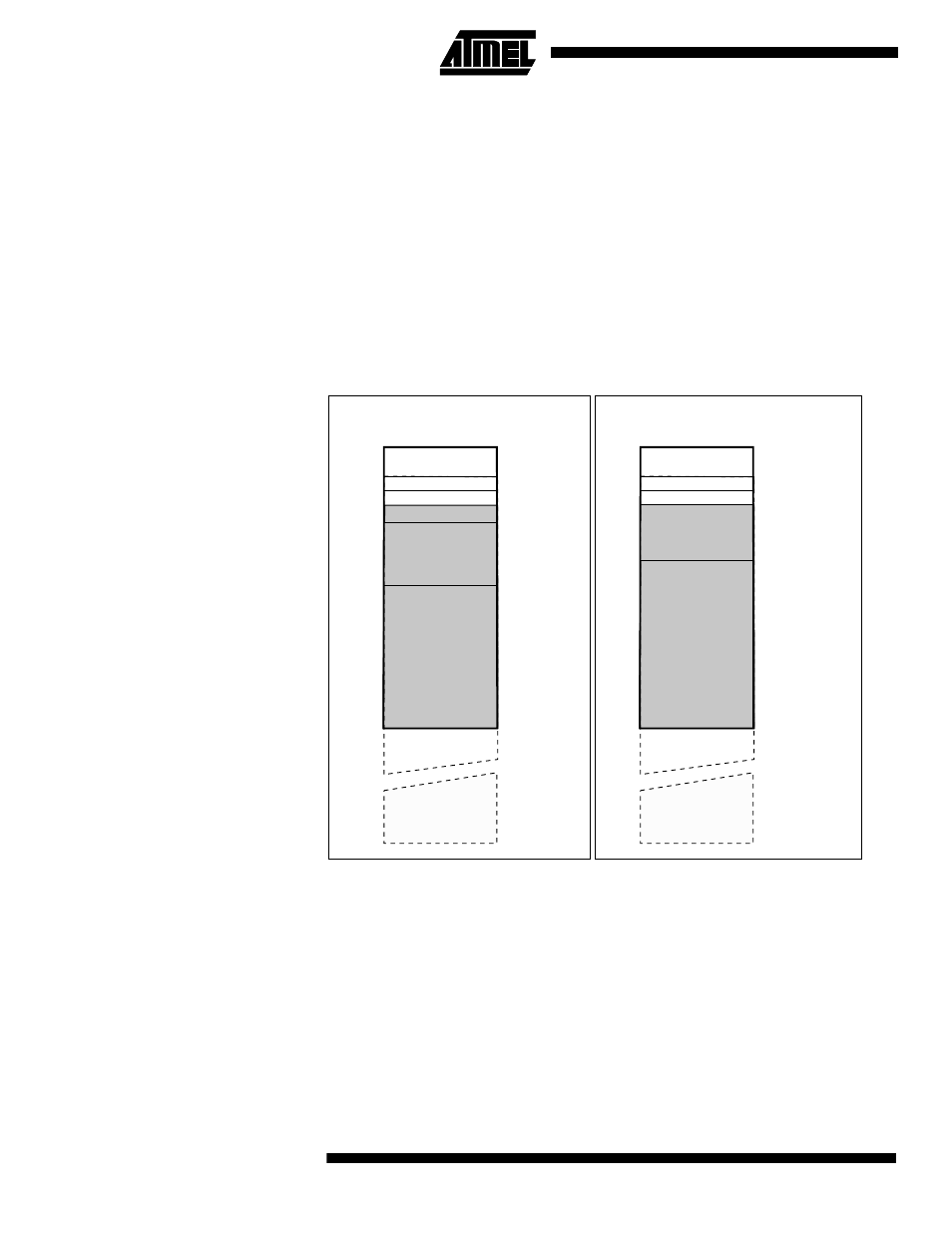
Figure 9. Data Memory Map
Data Memory Access Times
This section describes the general access timing concepts for internal memory access.
The internal data SRAM access is performed in two clk
CPU
cycles as described in
10.
Memory Configuration B
32 Registers
64 I/O Registers
Internal SRAM
(4000 x 8)
$0000 - $001F
$0020 - $005F
$1000
$0FFF
$FFFF
$0060
Data Memory
External SRAM
(0 - 64K x 8)
Memory Configuration A
32 Registers
64 I/O Registers
Internal SRAM
(4096 x 8)
$0000 - $001F
$0020 - $005F
$1100
$10FF
$FFFF
$0060 - $00FF
Data Memory
External SRAM
(0 - 64K x 8)
160 Ext I/O Reg.
$0100
