Serial downloading, Spi serial programming pin mapping, Atmega162/v – Rainbow Electronics ATmega162V User Manual
Page 244
244
ATmega162/V
2513E–AVR–09/03
Notes:
1. t
WLRH
is valid for the Write Flash, Write EEPROM, Write Fuse Bits and Write Lock
Bits commands.
2. t
WLRH_CE
is valid for the Chip Erase command.
Serial Downloading
SPI Serial Programming
Pin Mapping
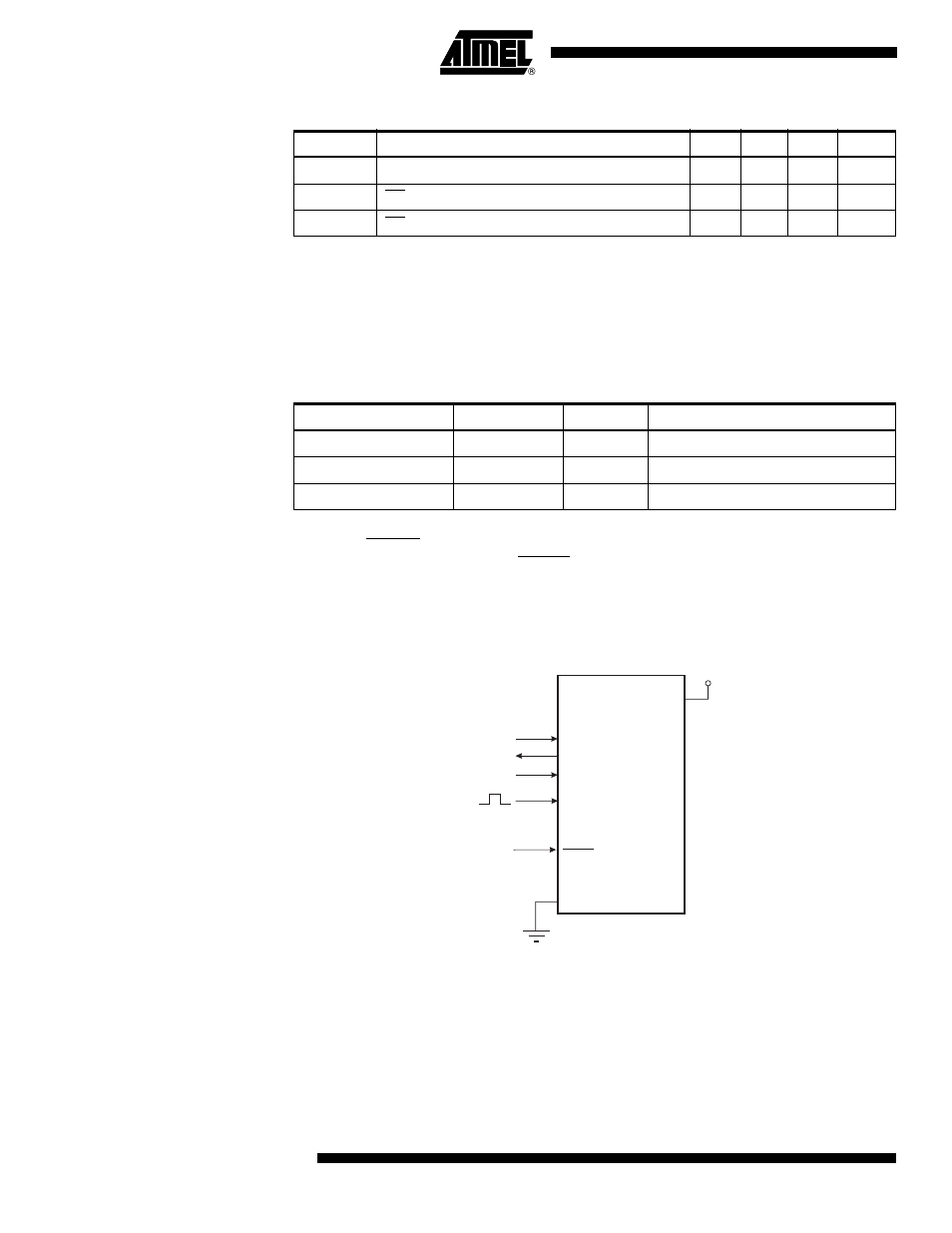
Both the Flash and EEPROM memory arrays can be programmed using the serial SPI
bus while RESET is pulled to GND. The serial interface consists of pins SCK, MOSI
(input) and MISO (output). After RESET is set low, the Programming Enable instruction
needs to be executed first before program/erase operations can be executed. NOTE, in
Table 109 on page 244, the pin mapping for SPI programming is listed. Not all parts use
the SPI pins dedicated for the internal SPI interface.
Figure 105. SPI Serial Programming and Verify
Note:
1. If the device is clocked by the Internal Oscillator, it is no need to connect a clock
source to the XTAL1 pin.
When programming the EEPROM, an auto-erase cycle is built into the self-timed pro-
gramming operation (in the Serial mode ONLY) and there is no need to first execute the
Chip Erase instruction. The Chip Erase operation turns the content of every memory
location in both the Program and EEPROM arrays into 0xFF.
t
BVDV
BS1 Valid to DATA valid
0
250
ns
t
OLDV
OE Low to DATA Valid
250
ns
t
OHDZ
OE High to DATA Tri-stated
250
ns
Table 108. Parallel Programming Characteristics, V
CC
= 5 V ± 10% (Continued)
Symbol
Parameter
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Table 109. Pin Mapping SPI Serial Programming
Symbol
Pins
I/O
Description
MOSI
PB5
I
Serial Data in
MISO
PB6
O
Serial Data out
SCK
PB7
I
Serial Clock
VCC
GND
XTAL1
SCK
MISO
MOSI
RESET
