Atmega162/v, Figure 75. usart block diagram – Rainbow Electronics ATmega162V User Manual
Page 166
166
ATmega162/V
2513E–AVR–09/03
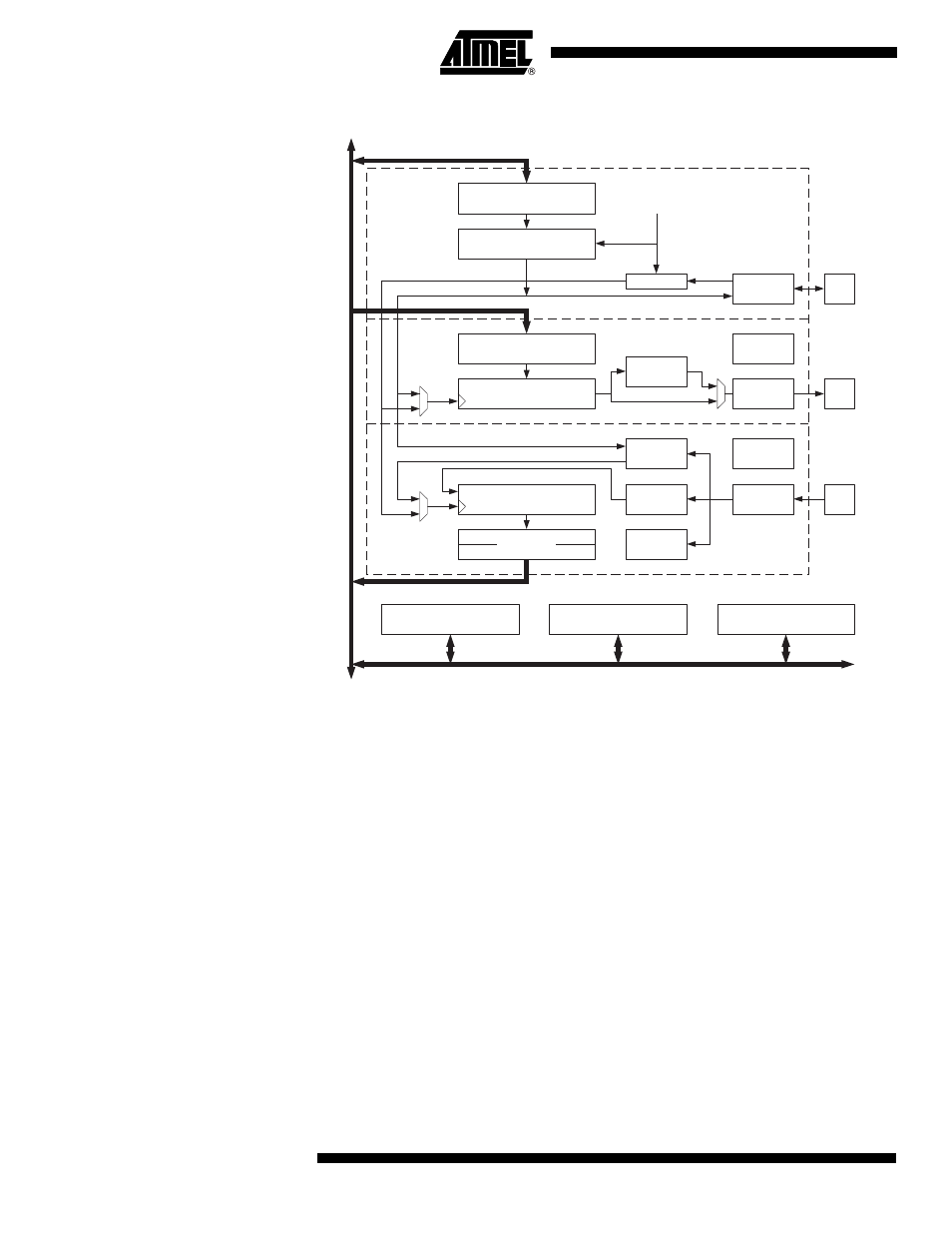
Figure 75. USART Block Diagram
Note:
1. Refer to Figure 1 on page 2, Table 34 on page 73, Table 39 on page 79, and Table
40 on page 79 for USART pin placement.
The dashed boxes in the block diagram separate the three main parts of the USART
(listed from the top): Clock Generator, Transmitter and Receiver. Control registers are
shared by all units. The Clock Generation logic consists of synchronization logic for
external clock input used by synchronous slave operation, and the baud rate generator.
The XCK (Transfer Clock) pin is only used by synchronous transfer mode. The Trans-
mitter consists of a single write buffer, a serial Shift Register, parity generator and
control logic for handling different serial frame formats. The write buffer allows a contin-
uous transfer of data without any delay between frames. The Receiver is the most
complex part of the USART module due to its clock and data recovery units. The recov-
ery units are used for asynchronous data reception. In addition to the recovery units, the
Receiver includes a Parity Checker, Control logic, a Shift Register and a two level
receive buffer (UDR). The receiver supports the same frame formats as the Transmitter,
and can detect Frame Error, Data OverRun and Parity Errors.
PARITY
GENERATOR
UBRR[H:L]
UDR (Transmit)
UCSRA
UCSRB
UCSRC
BAUD RATE GENERATOR
TRANSMIT SHIFT REGISTER
RECEIVE SHIFT REGISTER
RxD
TxD
PIN
CONTROL
UDR (Receive)
PIN
CONTROL
XCK
DATA
RECOVERY
CLOCK
RECOVERY
PIN
CONTROL
TX
CONTROL
RX
CONTROL
PARITY
CHECKER
DATABUS
OSC
SYNC LOGIC
Clock Generator
Transmitter
Receiver
