Alternate functions of port b – Rainbow Electronics ATmega103L User Manual
Page 78
ATmega603/103
78
Note:
n: 7,6...0, pin number
Alternate Functions of Port B
The alternate pin configuration is as follows:
•
OC2/PWM2, Bit 7
OC2/PWM2, Output Compare output for Timer/Counter2 or PWM output when Timer/Counter2 is in PWM Mode. The pin
has to be configured as an output to serve this function.
•
OC1B/PWM1B, Bit 6
OC1B/PWM1B, Output Compare output B for Timer/Counter1 or PWM output B when Timer/Counter1 is in PWM Mode.
The pin has to be configured as an output to serve this function.
•
OC1A/PWM1A, Bit 5
OC1A/PWM1A, Output Compare output A for Timer/Counter1 or PWM output A when Timer/Counter1 is in PWM Mode.
The pin has to be configured as an output to serve this function.
•
OC0/PWM0, Bit 4
OC0/PWM0, Output Compare output for Timer/Counter0 or PWM output when Timer/Counter0 is in PWM Mode. The pin
has to be configured as an output to serve this function.
•
MISO - Port B, Bit 3
MISO: Master data input, slave data output pin for SPI channel. When the SPI is enabled as a master, this pin is configured
as an input regardless of the setting of DDB3. When the SPI is enabled as a slave, the data direction of this pin is controlled
by DDB3. When the pin is forced to be an input, the pull-up can still be controlled by the PORTB3 bit. See the description of
the SPI port for further details.
•
MOSI - Port B, Bit 2
MOSI: SPI Master data output, slave data input for SPI channel. When the SPI is enabled as a slave, this pin is configured
as an input regardless of the setting of DDB2. When the SPI is enabled as a master, the data direction of this pin is con-
trolled by DDB2. When the pin is forced to be an input, the pull-up can still be controlled by the PORTB2 bit. See the
description of the SPI port for further details.
•
SCK - Port B, Bit 1
SCK: Master clock output, slave clock input pin for SPI channel. When the SPI is enabled as a slave, this pin is configured
as an input regardless of the setting of DDB1. When the SPI is enabled as a master, the data direction of this pin is con-
trolled by DDB1. When the pin is forced to be an input, the pull-up can still be controlled by the PORTB1 bit. See the
description of the SPI port for further details.
•
SS - Port B, Bit 0
SS: Slave port select input. When the SPI is enabled as a slave, this pin is configured as an input regardless of the setting
of DDB0. As a slave, the SPI is activated when this pin is driven low. When the SPI is enabled as a master, the data direc-
tion of this pin is controlled by DDB0. When the pin is forced to be an input, the pull-up can still be controlled by the
PORTB0 bit. See the description of the SPI port for further details.
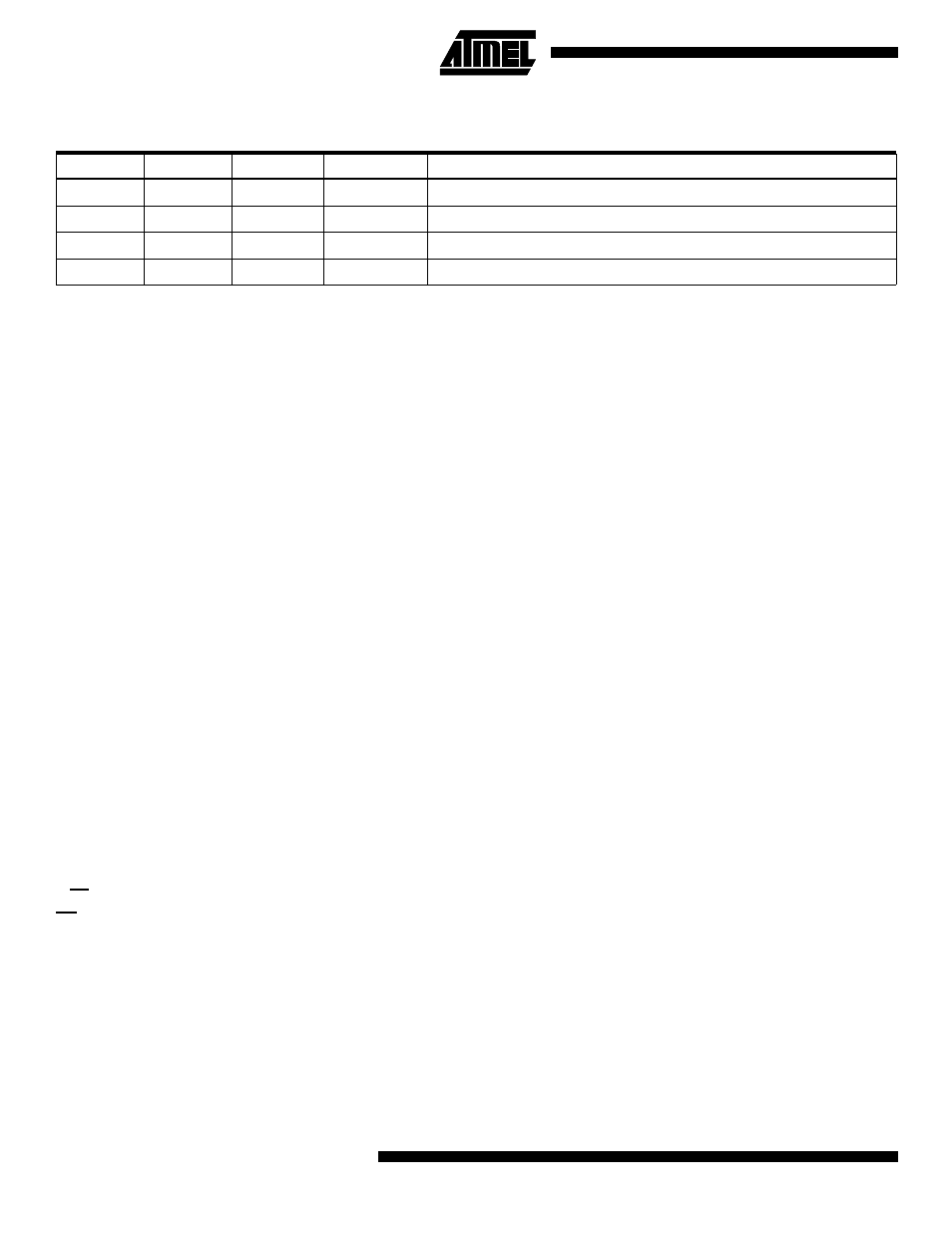
Table 31. DDBn Effects on Port B Pins
DDBn
PORTBn
I/O
Pull up
Comment
0
0
Input
No
Tri-state (Hi-Z)
0
1
Input
Yes
PBn will source current if ext. pulled low
1
0
Output
No
Push-Pull Zero Output
1
1
Output
No
Push-Pull One Output
