Comparison between atmega603 and atmega103, Pin descriptions, Port a (pa7..pa0) – Rainbow Electronics ATmega103L User Manual
Page 4: Port b (pb7..pb0), Port c (pc7..pc0), Port d (pd7..pd0)
ATmega603/103
4
Comparison Between ATmega603 and ATmega103
The ATmega603 has 64K bytes of In-System Programmable Flash, 2K bytes of EEPROM, and 4K bytes of internal SRAM.
The ATmega603 does not have the ELPM instruction.
The ATmega103 has 128K bytes of In-System Programmable Flash, 4K bytes of EEPROM, and 4K bytes of internal
SRAM. The ATmega103 has the ELPM instruction, necessary to reach the upper half of the Flash memory for constant
table lookup.
Table 1 summarizes the different memory sizes for the two devices.
Pin Descriptions
VCC
Supply voltage
GND
Ground
Port A (PA7..PA0)
Port A is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port. Port pins can provide internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The Port A
output buffers can sink 20 mA and can drive LED displays directly. When pins PA0 to PA7 are used as inputs and are
externally pulled low, they will source current if the internal pull-up resistors are activated.
Port A serves as Multiplexed Address/Data bus when using external SRAM.
The port A pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active, even if the clock is not running.
Port B (PB7..PB0)
Port B is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors. The Port B output buffers can sink 20 mA. As inputs,
Port B pins that are externally pulled low, will source current if the pull-up resistors are activated.
Port B also serves the functions of various special features.
The port B pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active, even if the clock is not running.
Port C (PC7..PC0)
Port C is an 8-bit Output port. The Port C output buffers can sink 20 mA.
Port C also serves as Address output when using external SRAM.
Since Port C is an output only port, the port C pins are not tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active.
Port D (PD7..PD0)
Port D is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors. The Port D output buffers can sink 20 mA. As inputs,
Port D pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up resistors are activated.
Port D also serves the functions of various special features.
The port D pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active, even if the clock is not running.
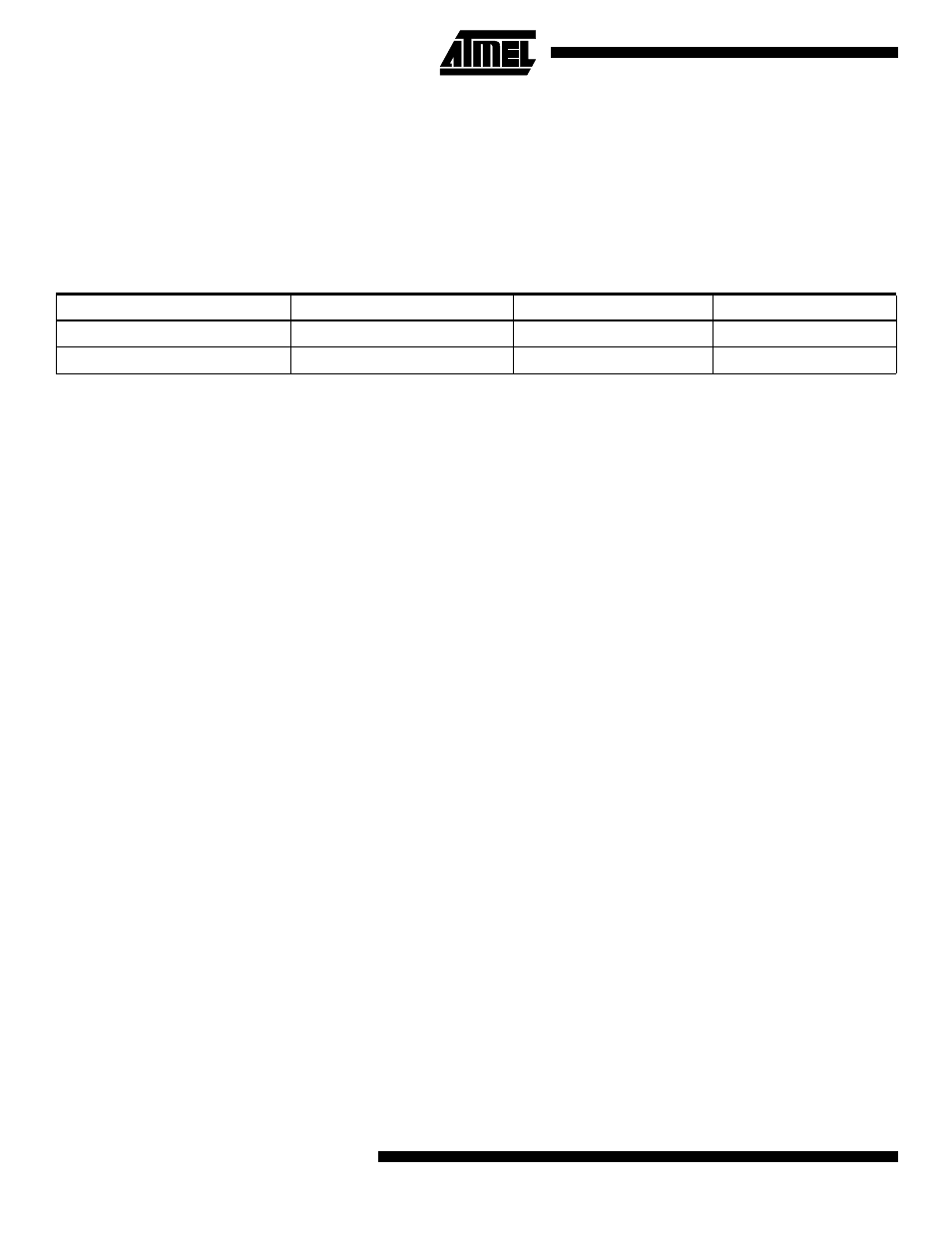
Table 1. Memory Size Summary
Part
Flash
EEPROM
SRAM
ATmega603
64K bytes
2K bytes
4K bytes
ATmega103
128K bytes
4K bytes
4K bytes
