Hazard avoidance, Nexrad l – Garmin G1000 Piper PA-46 Matrix User Manual
Page 320
Garmin G1000 Pilot’s Guide for the Piper PA-46 Mirage/Matrix
190-01108-00 Rev. B
306
HAZARD AVOIDANCE
SY
STEM
O
VER
VIEW
FLIGHT
INSTRUMENTS
EICAS
AUDIO P
ANEL
& CNS
FLIGHT
MANA
GEMENT
HAZARD
AV
OID
ANCE
AFCS
ADDITIONAL FEA
TURES
APPENDICES
INDEX
SY
STEM
O
VER
VIEW
FLIGHT
INSTRUMENTS
EICAS
AUDIO P
ANEL
& CNS
FLIGHT
MANA
GEMENT
HAZARD
AV
OID
ANCE
AFCS
ADDITIONAL FEA
TURES
APPENDICES
INDEX
The different NEXRAD echo intensities are measured in decibels (dB) relative to reflectivity (Z). NEXRAD
measures the radar reflectivity ratio, or the energy reflected back to the radar receiver (designated by the
letter Z). The value of Z increases as the returned signal strength increases.
neXraD l
imitations
NEXRAD radar images may have certain limitations:
• NEXRAD base reflectivity does not provide sufficient information to determine cloud layers or precipitation
characteristics. For example, it is not possible to distinguish between wet snow, wet hail, and rain.
• NEXRAD base reflectivity is sampled at the minimum antenna elevation angle. An individual NEXRAD
site cannot depict high altitude storms at close ranges. It has no information about storms directly over
the site.
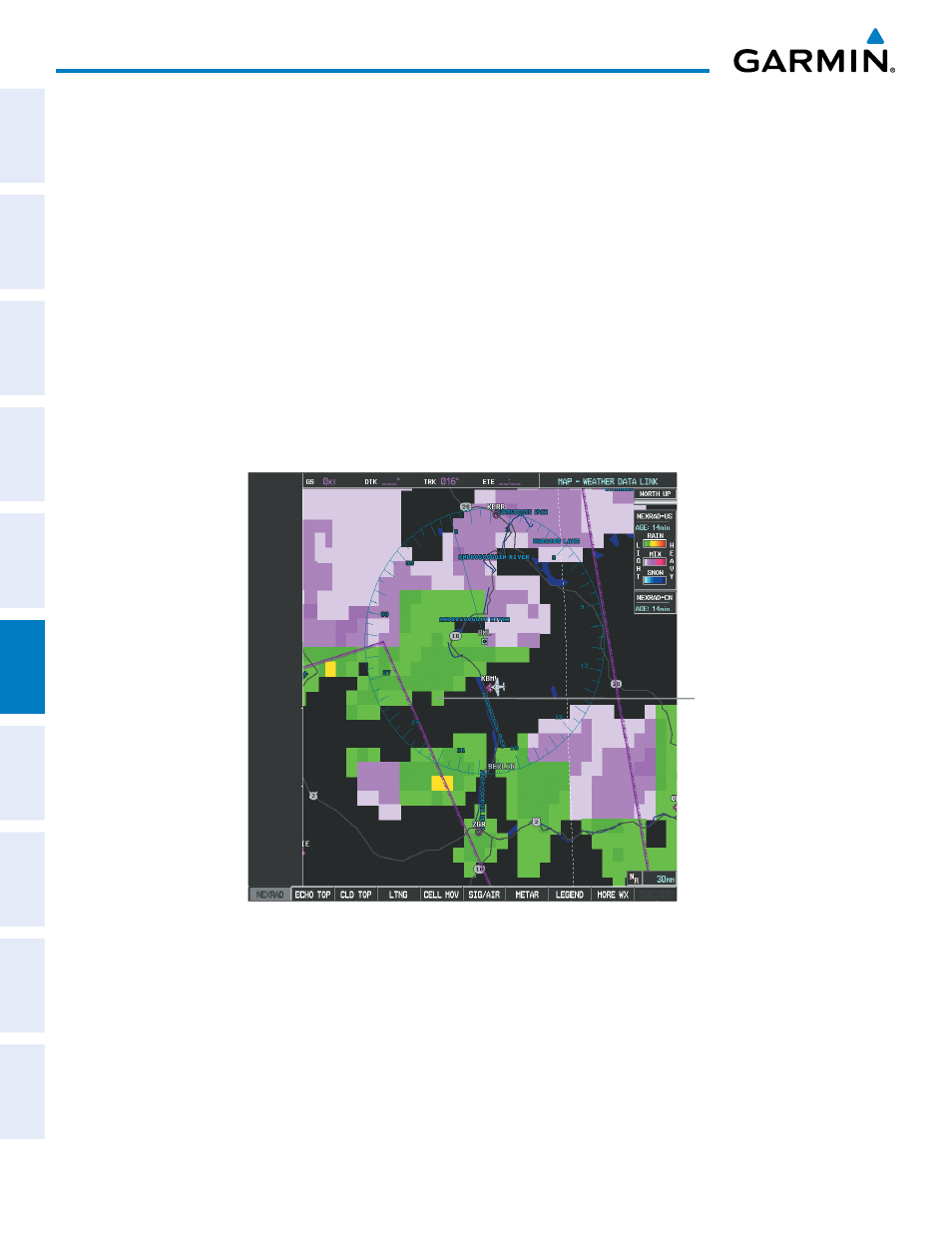
• When zoomed in to a range of 30 nm, each square block on the display represents an area of four square
kilometers. The intensity level reflected by each square represents the highest level of NEXRAD data
sampled within the area.
Figure 6-12 NEXRAD Data - Zoomed
Each block
covers an Area
of 4 sq. km
