Dma register address assignment, Description of dma registers, Table 32: overview of dma registers – Siemens ERTEC200 User Manual
Page 87: Dmac0confreg) channel config (*)
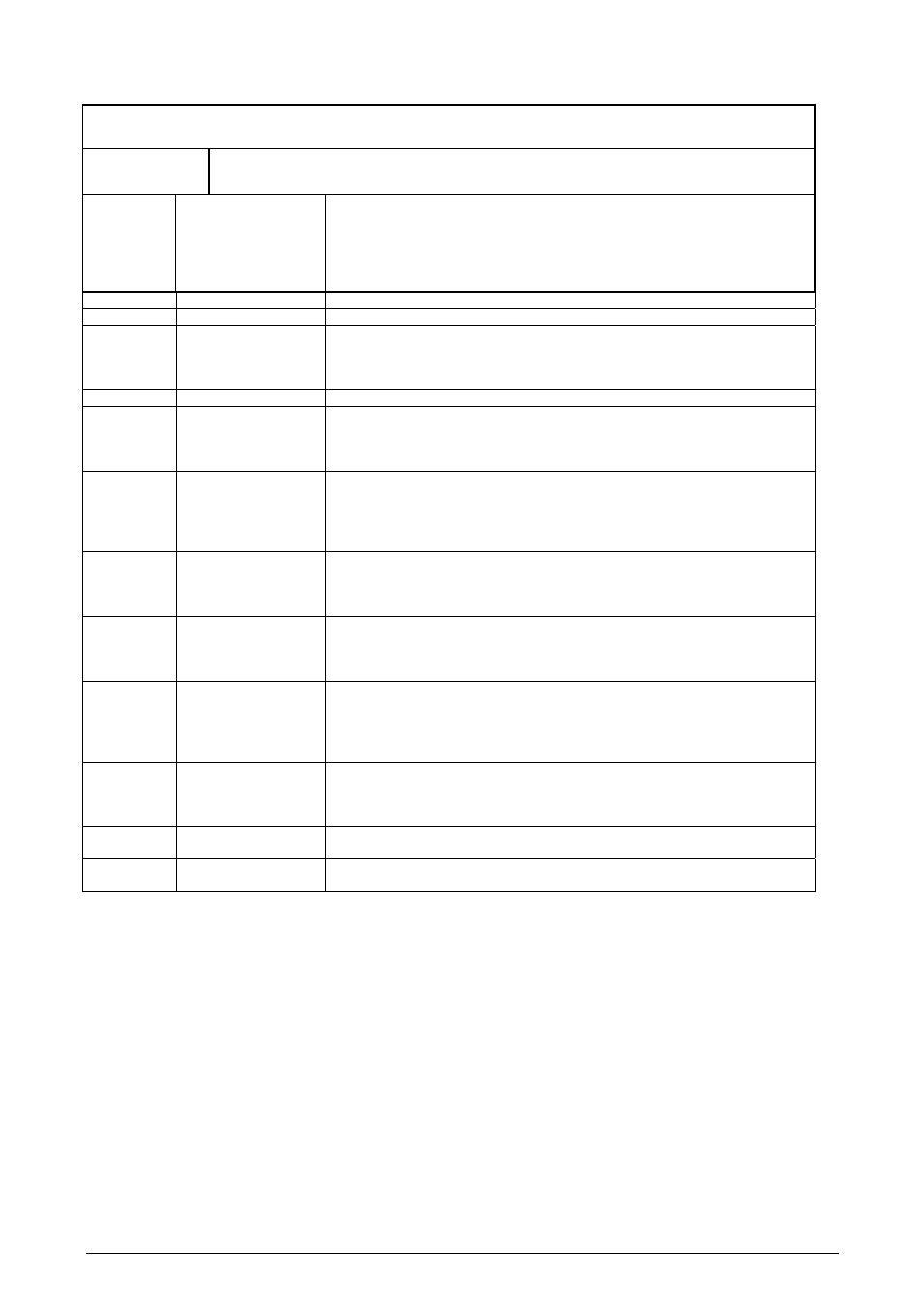
(DMAC0ConfReg)
Channel Config (*)
W/R Addr.: 0x8000_000C Default: 0x0000_0000
Description Control
Bits.
31 START/ABORT
Write:
0: Stop Transfer
1: Start Transfer
Read:
0: Transfer completed or stopped
1: Transfer not yet complete
30 Reserved Reserved
29
INTR_ENABLE (****)
1: Enable interrupt
28..27 SYNCHRONIZATION
00:
None
01: Destination
10: Source
11: Both
26..24
Reserved
23..22
S_ADDR_MODE
00: Increment source address
01: Decrement source address
10: Keep source address
11: Reserved
21..19 S_DMA_REQU 000:
SSP_SSPRXDMA
001: SSP_SSPTXDMA
010: UART_UARTRXINTR
011: UART_UARTTXINTR
Rest: not
used
18..16 S_WIDTH
000:
8
bit
001:
16 bit
010:
32 bit
Rest: not permitted
15..14
D_ADDR_MODE
00: Increment destination address
01: Decrement destination address
10: Keep destination address
11: Reserved (affect destination address incrementation)
13..11 D_DMA_REQU 000:
SSP_SSPRXDMA
001: SSP_SSPTXDMA
010: UART_UARTRXINTR
011: UART_UARTTXINTR
Rest: Not
used
10..8 D_WIDTH
000:
8
bit
001:
16 bit
010:
32 bit
Rest: Not permitted
7..4
D_DELAY(***)
Write inactive delay counter: The DMA controller puts the specified number
of clocks (50 MHz) in between two write access operations.
3..0
S_DELAY(***)
Read inactive delay counter: The DMA controller puts the specified number
of clocks (50 MHz) in between two read access operations.
*: Byte count and destination width (D_Width) must match up. If Halfword is selected in D_Width, then bit 0 is ignored by
byte count (considered to be “0”). If Word is selected in D_Width, then bit 1:0 is ignored by byte count (considered to be
“00”).
**: The DMA is started with 'Start/Abort = 1' and stopped during operation with 'Start/Abort = 0'. The DMA has to be
started by setting bit 31 to ‘1’. The remaining bits are locked while the DMA is in operation. If the DMA has been
stopped, it requires at least 2 clocks (50 MHz) before it can be restarted.
***: With the delay counter, there is a wait time until the next request if the target (UART, SPI 1) is too slow.
With the following settings, the specified delay values must be maintained. Otherwise, the DMA will incorrectly process
the relevant request signal and will access the corresponding I/O module too soon:
- Synchronization = Destination + D_DMA_Requ = SSP_SSPTXDMA:
⇒ D_Delay >= 4
- Synchronization = Destination + D_DMA_Requ = UART_UARTTXINTR:
⇒ D_Delay >= 5
- Synchronization = Source + S_DMA_Requ = SSP_SSPRXDMA:
⇒ S_Delay >= 0
- Synchronization = Source + S_DMA_Requ = UART_UARTRXINTR:
⇒ S_Delay >= 0
****: When synchronization is used, the interrupt takes place only after the target request has been activated again.
When D_Delay is used, the interrupt takes place only after the delay of the last write access.
Copyright © Siemens AG 2007. All rights reserved.
87
ERTEC 200 Manual
Technical data subject to change Version 1.1.0
