Irq interrupt sources, Fiq interrupt sources, Prioritization of interrupts – Siemens ERTEC200 User Manual
Page 25: Trigger modes, Masking the interrupt inputs, Software interrupts for irq, Nested interrupt structure, Eoi end-of-interrupt, Not used pins (16 pins), Not used pins
The CPU accepts an IRQ-/FIQ request by reading the IRVEC/FIVEQ register. This register contains the binary-coded
vector number of the highest priority interrupt request at the moment. Each of the two interrupt vector registers can be
referenced using two different addresses. The interrupt controller interprets the reading of the vector register with the first
address as an “interrupt acknowledge”. This causes the sequences for this interrupt to be implemented in the ICU logic.
Reading of the vector register with the second address is not linked to the “acknowledge function”. This is primarily useful
for the debugging functions in order to read out the content of the interrupt vector register without starting the
acknowledge function of the interrupt controller.
2.9.7
IRQ Interrupt Sources
Interrupts from the following function groups of the ERTEC 200 are available to the IRQ interrupt controller:
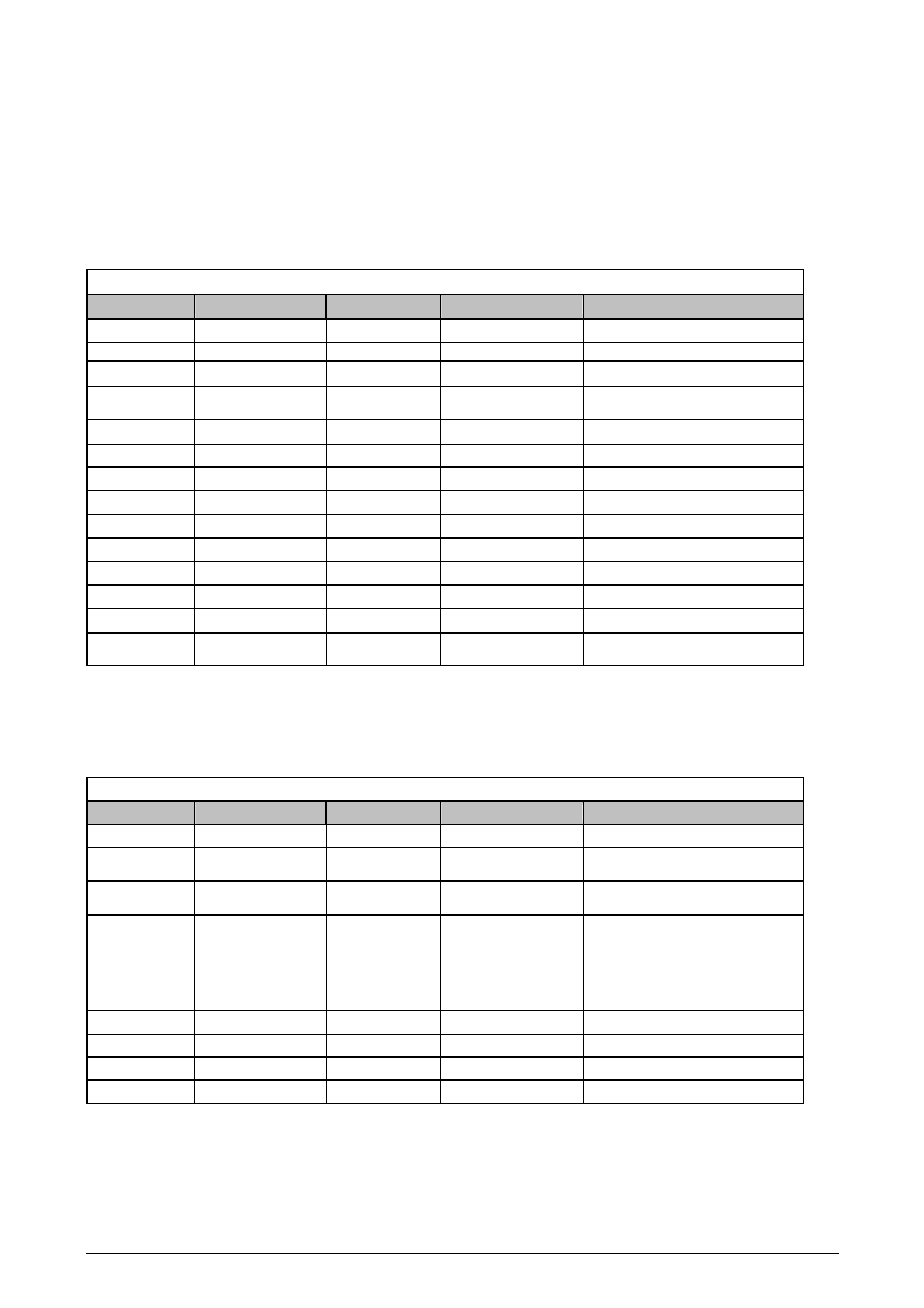
IRQ Interrupts
Interrupt-Nr. Function Block
Signal Name
Default Setting
Comment
0 Timer
TIM_INT0
Rising edge
Timer 0
1 Timer
TIM_INT1
Rising edge
Timer 1
3:2 GPIO
GPIO (1:0)
Assignable
External input ERTEC 200 GPIO[1:0]
5:4 GPIO
GPIO (31:30)
Assignable
External input ERTEC 200
GPIO[31:30]
6 Timer
TIM_INT2
Rising edge
Timer 2
7 ----- ------ -----
Reserved
8 UART
UART_INTR High
level
Group interrupt UART
9 PHY0/1
P0/1_INTERP Rising
edge
Interrupt von PHY 0/1
10 SPI
SSP_INTR Rising
edge
Group interrupt SPI
11 SPI
SSP_ROR_INTR Rising
edge
Receive overrun interrupt SPI
12 IRT
switch
IRQ0_SP
Rising edge
High-priority IRT interrupt
13 IRT
switch
IRQ1_SP
Rising edge
Low-priority IRT interrupt
14 ----- ----- -----
Reserved
15 DMA
DMA_INT Rising
edge
DMA controller, DMA transfer
complete
Table 2: Overview of IRQ Interrupts
2.9.8
FIQ Interrupt Sources
Interrupts from the following function groups of the ERTEC 200 are available to the FIQ interrupt controller:
FIQ Interrupts
Interrupt-Nr. Function Block
Signal Name
Default Setting
Comment
0 Watchdog
Rising edge
1 APB
bus
Rising edge
Access to non-existing address at
the APB (1)
2 Multilayer
AHB
Rising edge
Access to non-existing address at
the AHB (1)
3 PLL-Status-Register
Rising edge
Group interrupt of:
EMIF: I/O time-out
PLL: Loss state
PLL: Lock State
see system control register
"PLL_STAT_REG"
4 ARM-CPU
COMM_Rx
Rising
edge
Receive comm channel interrupt
5 ARM-CPU
COMM_Tx
Rising
edge
Transmit comm channel interrupt
6 Optional
Optional from IRQ
Rising edge
User-programmable IRQ source
7 Optional
Optional from IRQ
Rising edge
User-programmable IRQ source
Table 3: Overview of FIQ Interrupts
(1) Access to non-existing addresses is detected by the individual function groups of the ERTEC 200 and triggers a
pulse with duration Tp = 2/50 MHz. For evaluation of this interrupt, the connected FIQ input must be specified as an
edge-triggered input.
Copyright © Siemens AG 2007. All rights reserved.
25
ERTEC 200 Manual
Technical data subject to change Version 1.1.0
