Bus system of the ertec 200, Multilayer ahb” communication bus, Ahb arbiter – Siemens ERTEC200 User Manual
Page 32: Ahb master-slave coupling, Apb i/o bus, Arm946e-s register, Table 5: cp15 registers - overview, 3bus system of the ertec 200
3
Bus System of the ERTEC 200
Internally, the ERTEC 200 has two buses.
High-performance communication bus (multilayer AHB bus)
I/O bus (APB bus)
The following function blocks are connected directly to the multilayer AHB bus:
ARM946E-S
(Master)
IRT switch
(Master/Slave)
LBU
(Master)
Interrupt
controller
(Slave)
EMIF
interface
(Slave)
DMA-Controller
(Master/Slave)
The master can access the remaining I/O connected to the low-performance APB bus via an AHB/APB bridge.
3.1 “Multilayer AHB” Communication Bus
The multilayer AHB bus is characterized by a high bus availability and data transmission. It is a 32-bit wide bus with
multimaster capability. It operates at a frequency of 50 MHz and has the functionality of the ARM-AHB bus (see
Document /4/ Section 3). Connecting of several AHB segments in the multi-layer AHB bus enables 4 masters to access
different slaves simultaneously.
3.1.1 AHB
Arbiter
Arbiters control the access when multiple masters access a slave simultaneously. Each
AHB arbiter uses the same arbitration process. “Round robin” is specified. Alternatively, a fixed priority assignment of the
AHB master can be set by parameter assignment of the ARB_MODE bit in the M_LOCK_CNTL system control register.
Fixed priority assignment should be avoided due to the dynamic sequences on the multilayer AHB bus. The round robin
arbitration procedure prevents mutual blocking of the AHB master over a long period on the multilayer AHB bus.
With fixed priority assignment, the ARM has the highest priority assignment, followed by IRT, DMA, and LBU with the
lowest priority.
3.1.2
AHB Master-Slave Coupling
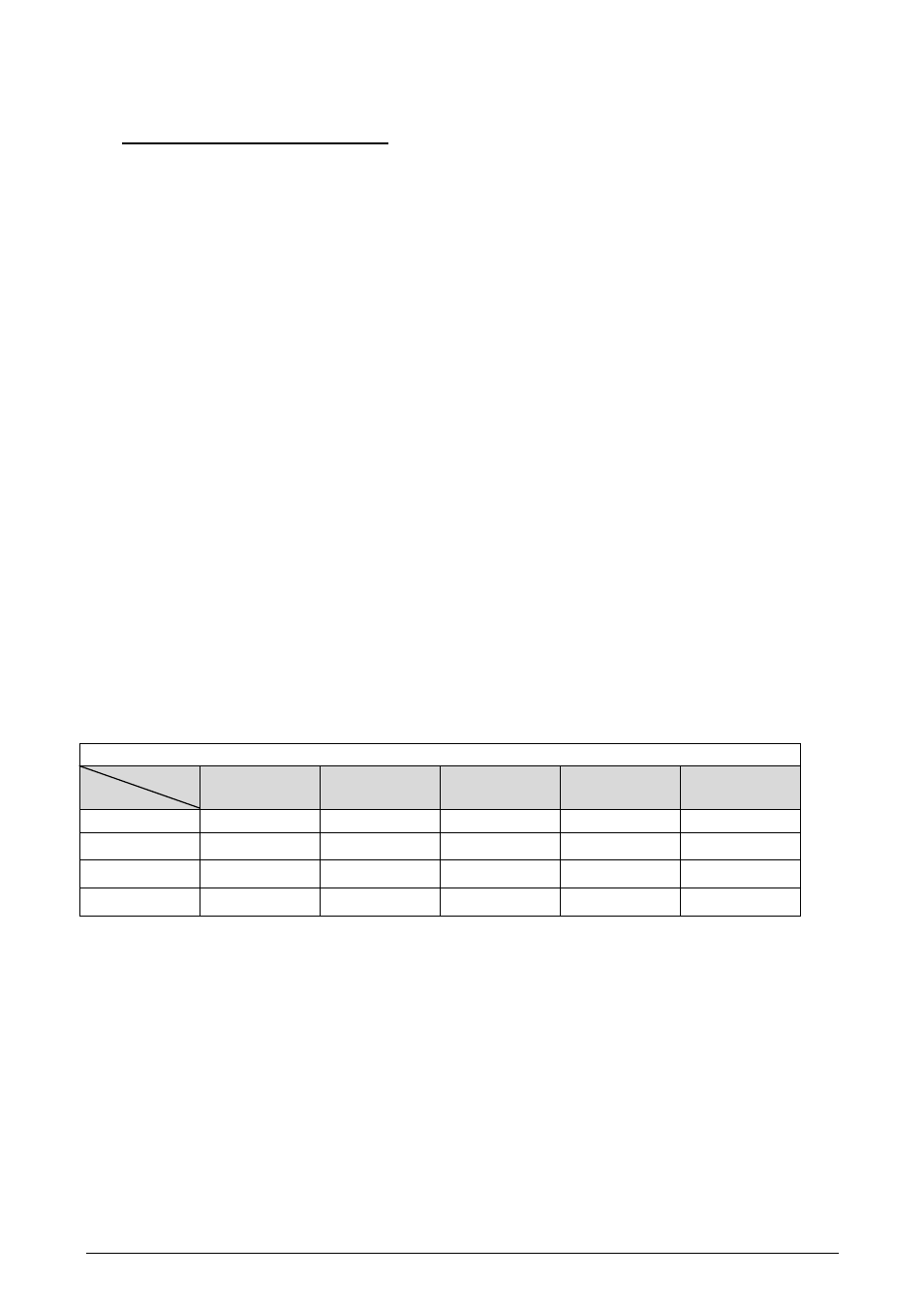
The table below shows which AHB masters can communicate with which AHB slaves.
AHB Master-Slave Coupling
Slave
Master
APB
Slave 1
EMIF
Slave 2
DMA
Slave 3
IRT
Slave 4
INT-Control
Slave 5
ARM
X X
X
X
X
IRT
X
DMA
X
X
LBU
X
X
X
Table 6: Overview of AHB Master-Slave Access
For closed-loop control applications, attention must be paid that AHB masters do not block each other over a long period.
This would be possible if, for example, an IRT master and an ARM master want to access the same EMIF slave with a
time lag. In this case, the ARM master would have to pause in a “Wait” until the IRT master enables the EMIF slave
again. To prevent this situation, monitoring is integrated into the IRT switch, which enables the slave momentarily via an
IDLE state after 8 consecutive data transfers (burst or single access). In this phase, another AHB master can access
this slave.
3.2 APB
I/O
Bus
The APB bus is connected by means of an AHB/APB bridge on the multilayer AHB bus. The APB bus has a width of 32
bits and operates at a frequency of 50 MHz.
Copyright © Siemens AG 2007. All rights reserved.
32
ERTEC 200 Manual
Technical data subject to change Version 1.1.0
