Igmp snooping, Theory – Interlogix GE-DSH-73 Series User Manual User Manual
Page 114
Chapter 5: Web-Based Management
110
GE-DSH-73/DSH-82 and DSH-82-PoE User Manual
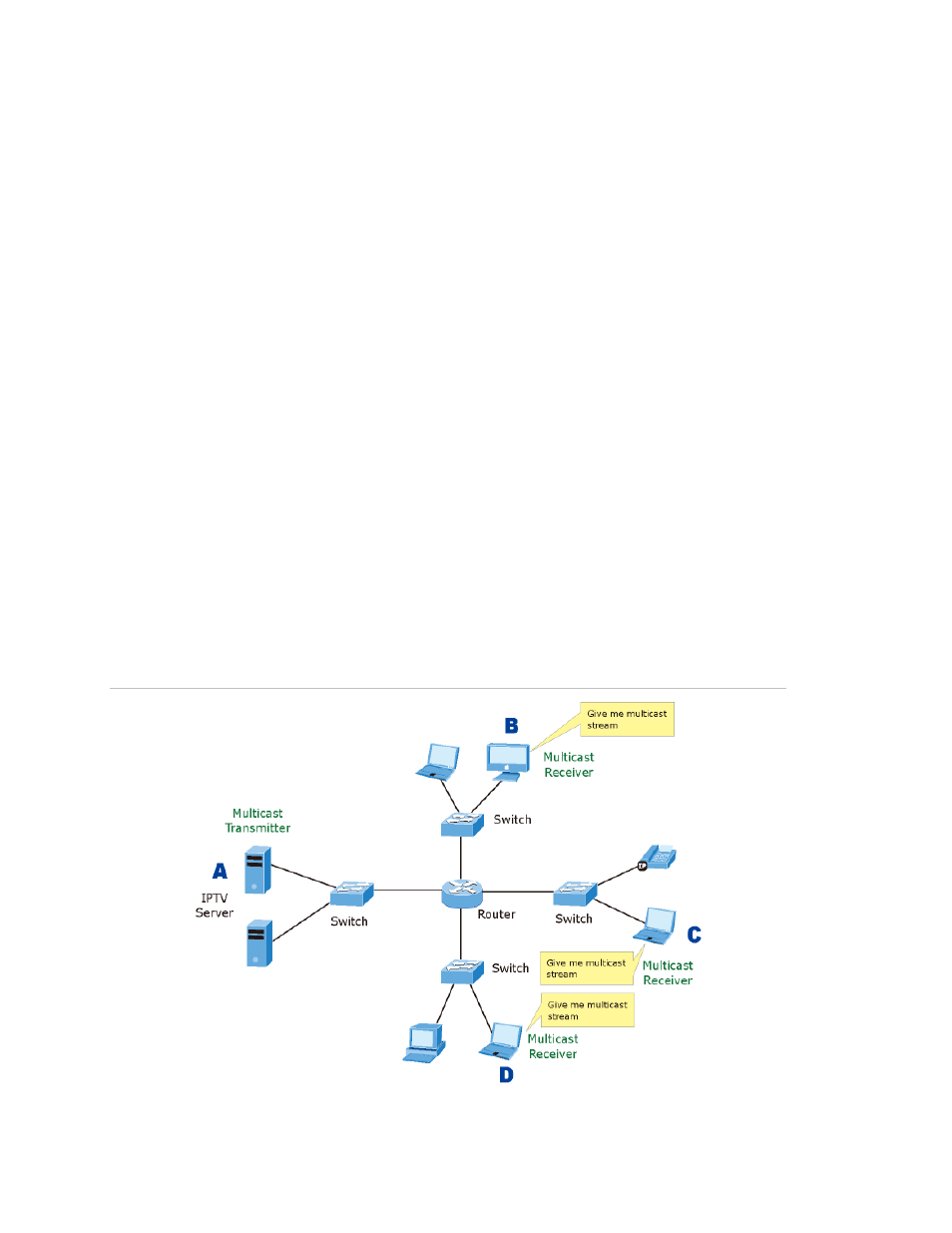
IGMP Snooping
Theory
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) lets host and routers share
information about multicast groups memberships. IGMP snooping is a switch feature
that monitors the exchange of IGMP messages and copies them to the CPU for
feature processing. The overall purpose of IGMP Snooping is to limit the forwarding of
multicast frames to only ports that are a member of the multicast group.
About the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) Snooping
Computers and network devices that want to receive multicast transmissions need to
inform nearby routers that they will become members of a multicast group. The
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is used to communicate this
information. IGMP is also used to periodically check the multicast group for members
that are no longer active. In the case where there is more than one multicast router
on a sub network, one router is elected as the 'queried'. This router then keeps track
of the membership of the multicast groups that have active members. The
information received from IGMP is then used to determine if multicast packets should
be forwarded to a given sub network or not. The router can check, using IGMP, to see
if there is at least one member of a multicast group on a given subnet work. If there
are no members on a sub network, packets will not be forwarded to that sub
network.
Figure 5-54: Multicast Service
