7 filtration, 1 selecting suitable sample types, 2 filtration membrane life – Metrohm 788 IC Filtration Sample Processor User Manual
Page 116
4 Operation
788 IC Filtration Sample Processor
108
4.7 Filtration
4.7.1 Selecting suitable sample types
Due to the small pore size of the filtration membrane, each filtration step
may contribute to possible clogging of the membrane.
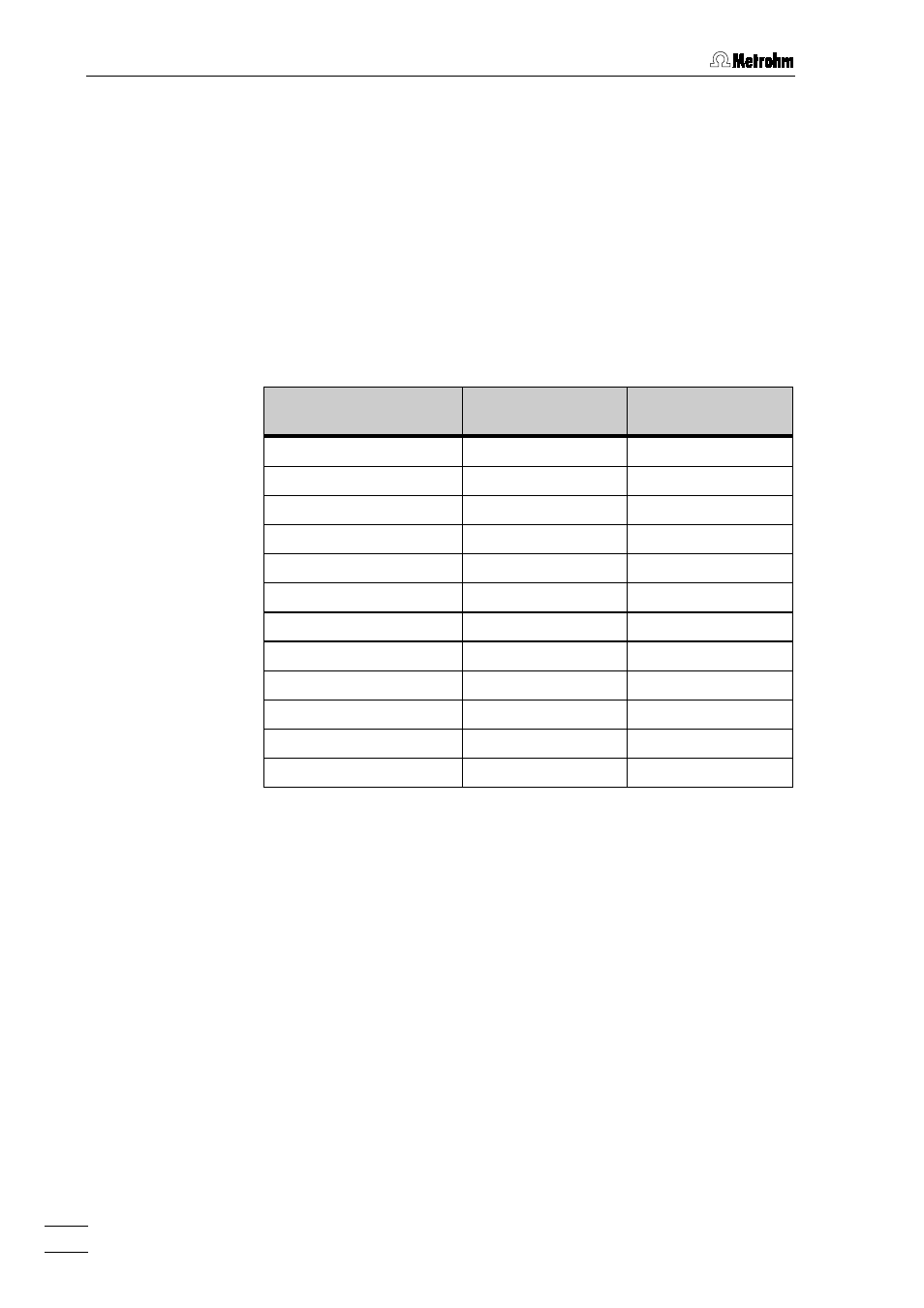
In the following table some sample types are described, which have
been processed by the 788 IC Filtration Sample Processor. Filtration
was performed using the 6.2714.020 filtration membrane (0.15 µm) or a
second filtration membrane (0.2 µm). On a Metrohm IC System 7 stan-
dard anions were analyzed: F
-
, Cl
-
, NO
2
-
, Br
-
, NO
3
-
, HPO
4
2-
, SO
4
2-
.
Sample
Pore size of
filtration membrane
Number of samples
per membrane
orange juice with pulp
0.15
40
surface water
0.15
500
drinking water
0.15
1000
ground water
0.15
500
waste water 1
0.15
1000
waste water 2
0.15
130
waste water 3
0.15
40
waste water 4
0.15
80
NaCl solution (1 %)
0.2
5000
Schöninger decomp. sol.
0.2
100
acid soil extraction
0.2
1000
aqueous soil extraction
0.2
200
The number of samples, which can be filtrated on one membrane with-
out losses of analysis accuracy, is based on experience by Metrohm
and its customers. They are intended for evaluation of employment of
the ultra-filtration cell for automated sample pretreatment. These values
have to be determined for each new application individually.
4.7.2 Filtration membrane life
Analyzing standard solutions, a reducing recovery rate can be taken as
an indicator for possible clogging of the filtration membrane. These
standards are ideally prepared in the corresponding sample matrix.
Therefore, for the analysis of a large number of particle loaded sam-
ples, standard solutions should be included, e.g. after every fifth or
tenth sample.
Nevertheless, a prediction for the number of possible filtration steps on
one membrane cannot be made. Also the development of the recovery
rate may vary. The recovery rate could either be constant for a large
number of samples and drop abruptly or decrease continuously with
another type of sample matrix.
