Pwm frequency – Rockwell Automation 20A PowerFlex 70EC/700VC User Manual
Page 91
PWM Frequency
87
Fault Operation
A fault will occur when the PTC resistance increases above 3230 ohms (5V DC),
and must be cleared (reset) by a fault clear command (see "Faults" on
) after
the resistance has decreased below 3230 ohms (5V DC).
The drive will also fault if the PTC voltage drops below 0.2V DC, indicating a
shorted PTC.
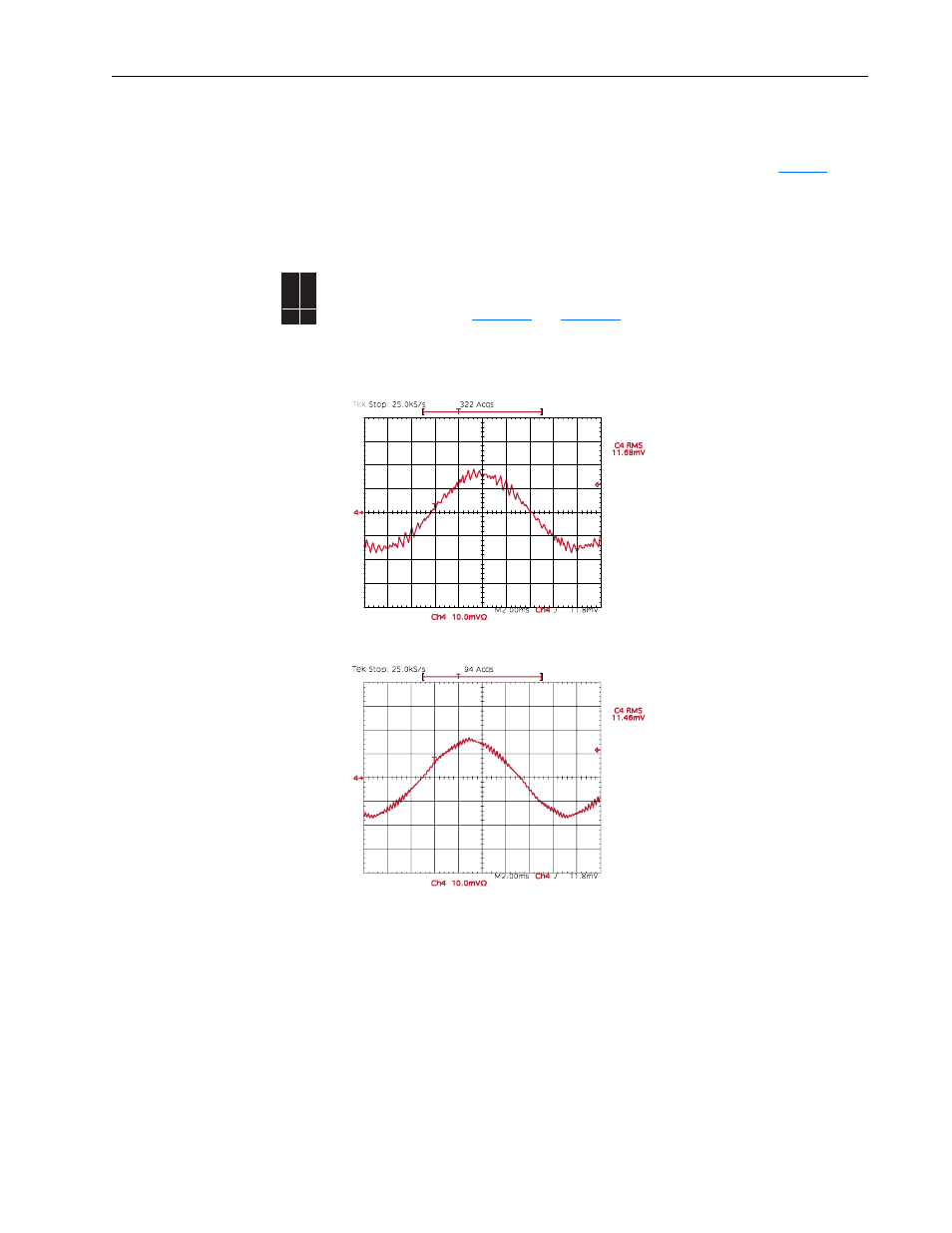
PWM Frequency
In general, it is best to use the lowest possible PWM (switching) frequency that is
acceptable for the application. There are some benefits to increasing the PWM
frequency. Refer to
Figure 13
and
Figure 14
. Note the output current at 2 kHz and 4
kHz. The “smoothing” of the current waveform continues as the PWM frequency is
increased.
Figure 13 Current at 2 kHz PWM Frequency
Figure 14 Current at 4 kHz PWM Frequency
Higher PWM frequencies may result in less motor heating and lower audible noise.
The decrease in motor heating is considered negligible and motor failure at lower
PWM frequencies is very remote. The higher PWM frequency creates less vibration
in the motor windings and laminations thus, lower audible noise. This may be
desirable in some applications.
Some undesirable effects of higher switching frequencies include derating ambient
temperature vs. load characteristics of the drive, higher cable charging currents and
higher potential for common mode noise.
See derating guidelines in the Appendix. Also see the Wiring and Grounding
document for PWM frequency limitations versus motor cable length.
A very large majority of all drive applications will perform adequately at 2-4 kHz.
70EC
700VC
700H
✔ ✔
