Voltage tolerance – Rockwell Automation 20A PowerFlex 70EC/700VC User Manual
Page 120
116
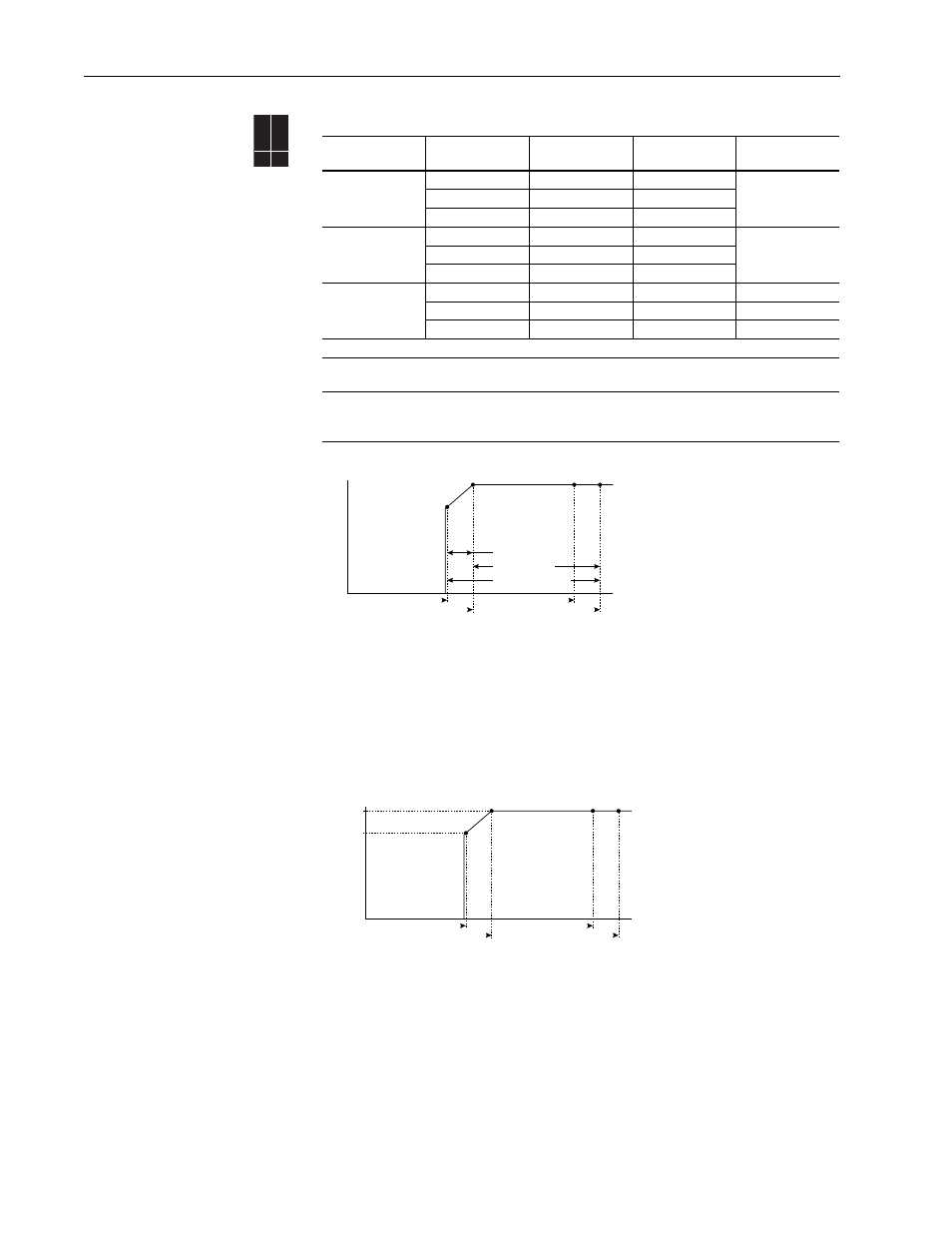
Voltage Tolerance
Voltage Tolerance
Example:
Calculate the maximum power of a 5 HP, 460V motor connected to a 480V rated drive supplied with
342V Actual Line Voltage input.
•
Actual Line Voltage / Nominal Motor Voltage = 74.3%
•
74.3%
× 5 HP = 3.7 HP
•
74.3%
× 60 Hz = 44.6 Hz
At 342V Actual Line Voltage, the maximum power the 5 HP, 460V motor can produce is
3.7 HP at 44.6 Hz.
70EC
700VC
700H
✔ ✔
Drive Rating
Nominal Line
Voltage
Nominal Motor
Voltage
Drive Full Power
Range
Drive Operating
Range
200-240
200
200*
200-264
180-264
208
208
208-264
240
230
230-264
380-480
380
380*
380-528
342-528
400
400
400-528
480
460
460-528
500-600
600
575*
575-660
432-660
600
575*
575-660
475-759
690
690
690-759
475-759
Drive Full Power Range =
Nominal Motor Voltage to Drive Rated Voltage +10%.
Rated power is available across the entire Drive Full Power Range.
Drive Operating Range =
Lowest (*) Nominal Motor Voltage –10% to Drive Rated Voltage +10%.
Drive Output is linearly derated when Actual Line Voltage is less than
the Nominal Motor Voltage.
HP @ Motor (Drive Output)
Actual Line Voltage (Drive Input)
Full Power Range
Drive Operating Range
Nominal Motor Voltage -10%
Nominal Motor Voltage
Derated Power Range
Drive Rated Voltage
Drive Rated Voltage +10%
5 HP
3.7 HP
HP @ Motor (Drive Output)
Actual Line Voltage (Drive Input)
342V
460V
480V
528V
