Campbell Scientific CR9000X Measurement and Control System User Manual
Page 205
Section 6. Data Table Declarations and Output Processing Instructions
LevelCrossing (Source, DataType, DisableVar, NumLevels, 2ndDim,
CrossingArray, 2ndArray, Hysteresis, Option)
Processes data with the Level Crossing counting algorithm.
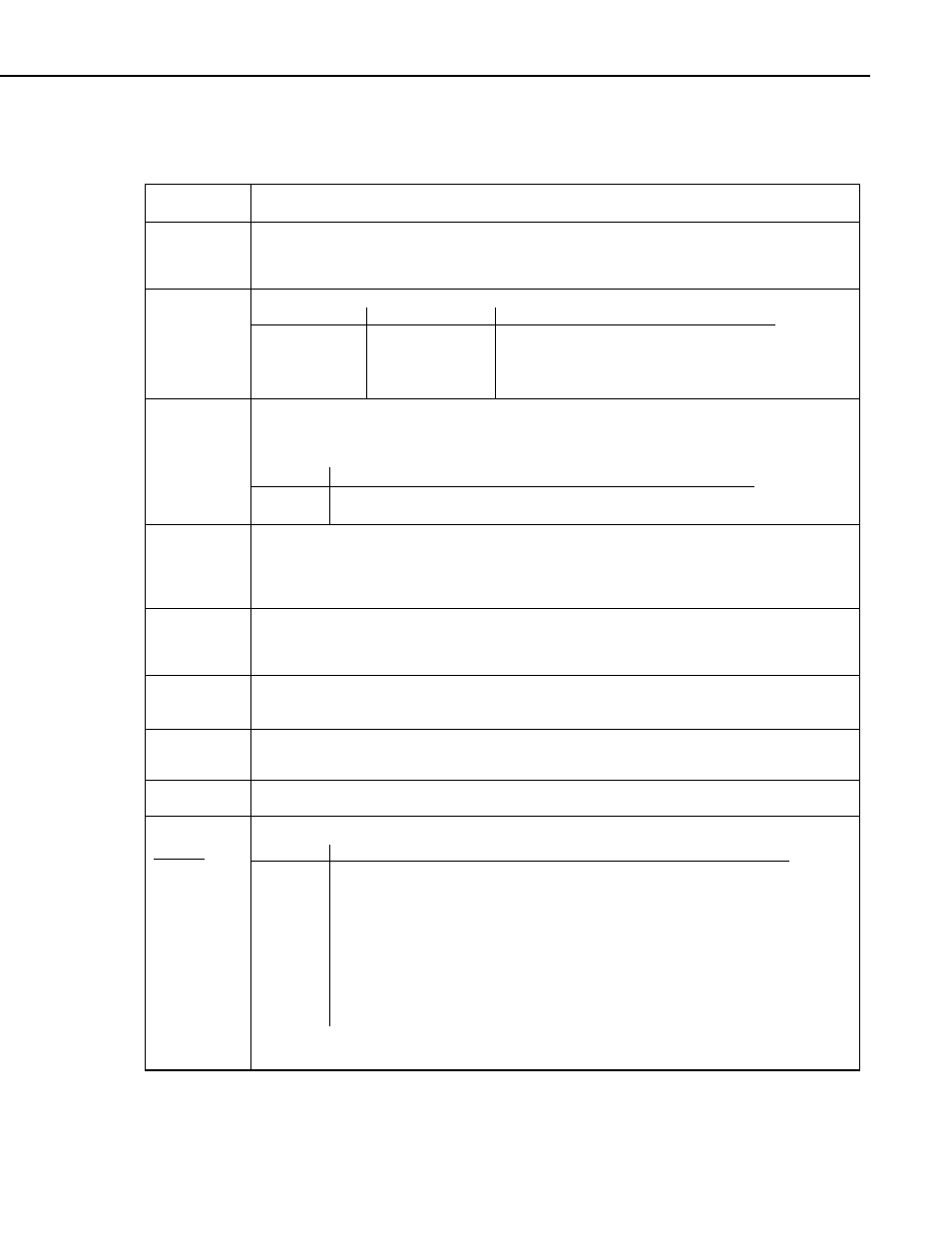
Parameter
& Data Type
Enter
LEVELCROSSING PARAMETERS
Source
Variable or
Array
The variable that is tested to determine if it crosses the specified levels. If a two dimensional level
crossing is selected, the source must be an array. The second element of the array (or the next element
beyond the one specified for the source) is the variable that is tested to determine the second dimension
of the histogram.
DataType
A code to select the data storage format. Read More: See Section 4.2.4.4 Data Types
Constant
Alpha Code
Numeric Code
Data Format
IEEE4
24
IEEE 4 byte floating point
FP2
7
Campbell Scientific 2 byte floating point
UINT2
21
2 Byte unsigned integer
Long
20
4 Byte Integer value
DisableVar
Constant,
Variable, or
Expression
A non-zero value will disable intermediate processing. Normally 0 is entered so all inputs are processed.
For example, when the disable variable is
≠0 the current input is not included in the histogram. The
histogram that is eventually stored includes the inputs that occurred while the disable variable was 0.
Value Result
0
Process current input
≠ 0
Do not process current input
NumLevels
Constant
The number levels on which to count crossings. This is the number of bins in which to store the number
of crossings for the associated level. The actual levels are input in the Crossing Array. A count is added
to a bin when the Source goes from less than the associated level to greater than the associated level
(Rising edge or positive polarity). Or if Falling edge or negative polarity is selected, a count occurs if
the source goes from greater than the level to less than the level.
2ndDim
Constant
The second dimension of the histogram. The total number of bins output = NumLevels*2ndDim. Enter
1 for a one dimensional histogram consisting only of the number of level crossings. If 2ndDim is greater
than 1, the element of the source array following the one tested for level crossing is used to determine
the second dimension.
Crossing
Array
Arrayt
The name of the Array that contains the Crossing levels to check. Because it does not make sense to
change the levels while the program is running, the program should be written to load the values into the
array once before entering the scan.
2ndArray
Array
The name of the Array that contains the levels that determine the second dimension. Because it does not
make sense to change the levels while the program is running, the program should be written to load the
values into the array once before entering the scan.
Hysteresis
Constant
The minimum change in the source that must occur for a crossing to be counted.
Option
t
The Option code is 3 digits - ABC
Constant
Code Form
A = 0
Count on falling edge (source goes form > level to A = 1 Count on rising edge (source goes from < level to >level) A = 2 Standard. Counts when the signal crosses positive and zero crossing B = 0 Reset histogram counts to 0 after each output. B = 1 Do not reset histogram; continue to accumulate counts. C = 0 Divide count in each bin by total number of counts in all bins. C = 1 Output total counts in each bin. 101 means: Count on rising edge, reset count to 0 after each output, output counts. 6-21
levels while rising (positive slope), and when the signal crosses
negative crossing levels while falling (negative slope).
