3 ground potential differences, 1 soil temperature thermocouple, 2 external signal conditioner – Campbell Scientific CR1000 Measurement and Control System User Manual
Page 90
Section 7. Installation
90
grounds (
) and power grounds (G). To take advantage of this design, observe
the following grounding rule:
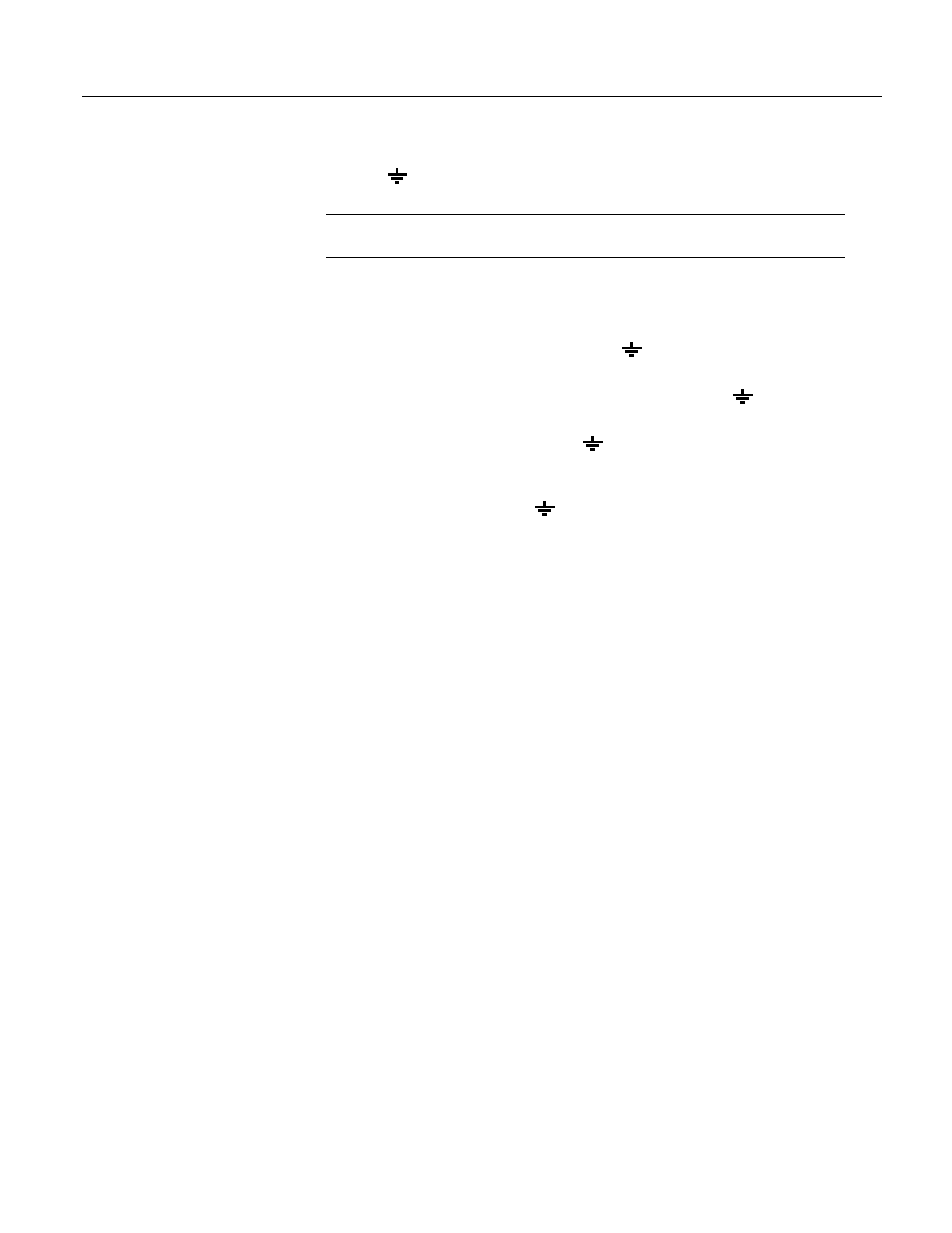
Note Always connect a device ground next to the active terminal associated with
that ground. Several ground wires can be connected to the same ground terminal.
Examples:
• Connect grounds associated with 5V, 12V, and C1 – C8 terminals to G
terminals.
• Connect excitation grounds to the closest ( ) terminal on the excitation
terminal block.
• Connect the low side of single-ended sensors to the nearest ( ) terminal on
the analog input terminal blocks.
• Connect shield wires to the nearest ( ) terminal on the analog input terminal
blocks.
If offset problems occur because of shield or ground leads with large current flow,
tying the problem leads into the (
) terminals next to the excitation and pulse-
counter channels should help. Problem leads can also be tied directly to the
ground lug to minimize induced single-ended offset voltages.
7.5.3 Ground Potential Differences
Because a single-ended measurement is referenced to CR1000 ground, any
difference in ground potential between the sensor and the CR1000 will result in a
measurement error. Differential measurements MUST be used when the input
ground is known to be at a different ground potential from CR1000 ground.
Ground potential differences are a common problem when measuring full-bridge
sensors (strain gages, pressure transducers, etc), and when measuring
thermocouples in soil.
7.5.3.1 Soil Temperature Thermocouple
If the measuring junction of a copper-constantan thermocouple is not insulated
when in soil or water, and the potential of earth ground is, for example, 1 mV
greater at the sensor than at the point where the CR1000 is grounded, the
measured voltage is 1 mV greater than the thermocouple output, which equates to
approximately 25°C higher than actual.
7.5.3.2 External Signal Conditioner
External signal conditioners, an infrared gas analyzer (IRGA) is an example, are
frequently used to make measurements and send analog information to the
CR1000. These instruments are often powered by the same ac line source as the
CR1000. Despite being tied to the same ground, differences in current drain and
lead resistance result in different ground potential at the two instruments. For this
reason, a differential measurement should be made on the analog output from the
external signal conditioner.
