Table 10. data types – Campbell Scientific CR1000 Measurement and Control System User Manual
Page 119
Section 7. Installation
119
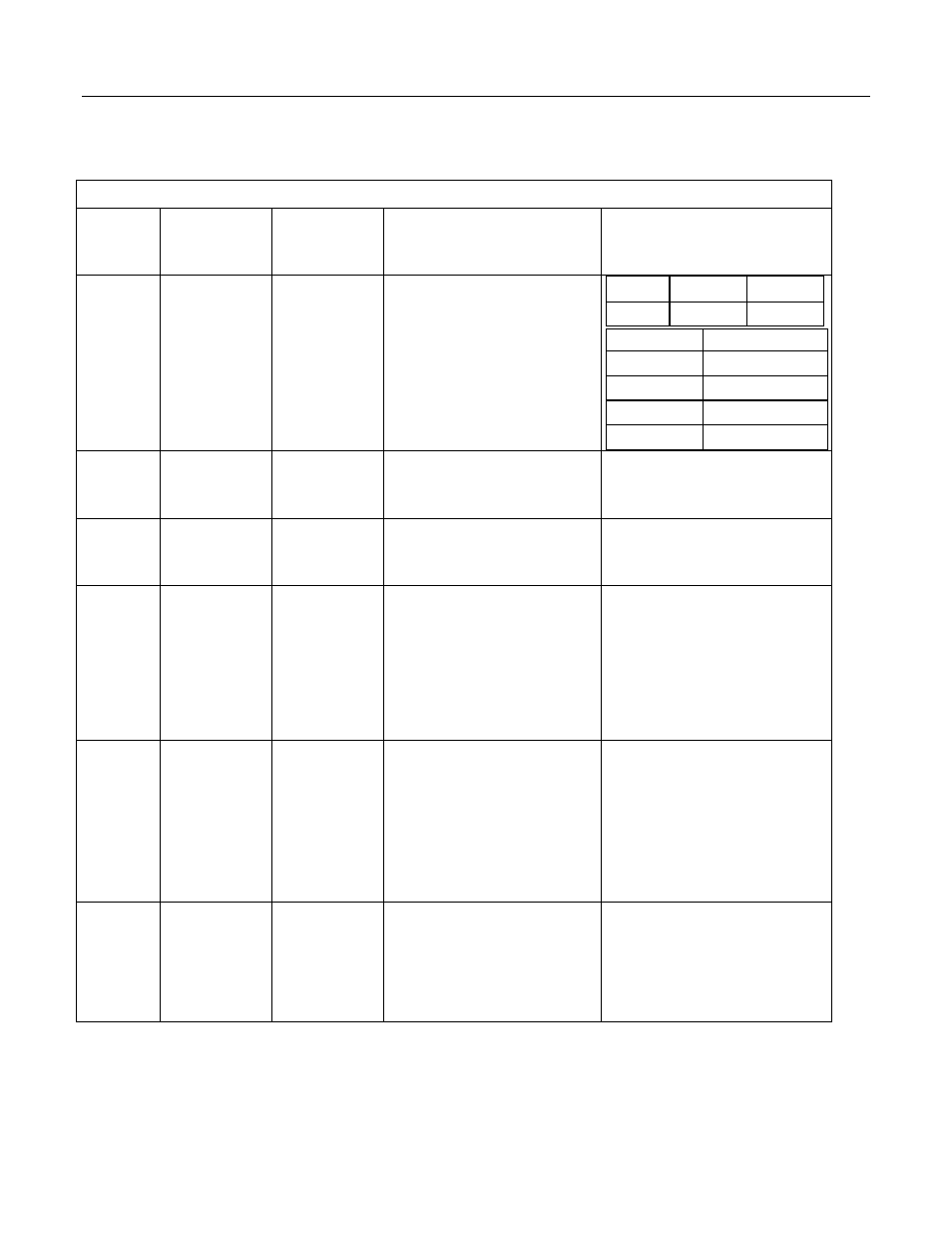
Table 10. Data Types
Name:
Command
or
Argument
Description /
Word Size
Where Used
Notes
Resolution / Range
FP2
Campbell
Scientific floating
point /
2 byte
Final data storage
Default final storage data type. Use
FP2
for stored data requiring 3 or 4
significant digits. If more significant
digits are needed, use
IEEE4
or an offset.
Zero
Minimum
Maximum
0.000
±0.001
±7999.
Absolute Value
Decimal Location
0 -- 7.999
X.XXX
8 -- 79.99
XX.XX
80 - 799.9
XXX.X
800 -- 7999.
XXXX.
As Float
IEEE Floating
Point /
4 byte
Dim & Public
variables
IEEE Standard 754
±1.4 x 10
-45
to
±3.4 x 10
38
IEEE4
IEEE Floating
Point /
4 byte
Final data storage
IEEE Standard 754
±1.4 x 10
-45
to
±3.4 x 10
38
As Long
Signed Integer /
4 byte
Dim & Public
variables
Final data storage
Use to store count data ≤
±2,147,483,648
Speed -- math with integers is faster
than with Floats.
Resolution -- has 32 bits compared to
24-bits in IEEE4.
Usually not suitable for final data
storage (except counts) since fractional
portion of values is lost.
-2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647
UINT2
Unsigned Integer/
2 byte
Final data storage
Use to store positive count data ≤
+65535.
Use to store port or flag status. See
CRBasic example Load binary
information into a variable (p. 112).
When Public FLOATs convert to
UINT2 at final data storage, values
outside the range 0-65535 yield
unusable data. INF converts to 65535.
NAN converts to 0.
0 to 65535
UINT4
Unsigned Integer/
4 byte
Final data storage
Use to store positive count data ≤
2147483647.
Other uses include storage of long ID
numbers (such as are read from a bar
reader), serial numbers, or address.
May also be required for use in some
Modbus devices.
0 to 2147483647
