Appendix c. serial port pinouts, C.1 cs i/o communications port, C.2 rs-232 communications port – Campbell Scientific CR1000 Measurement and Control System User Manual
Page 549: C.2.1 pin-out, Table 123. cs i/o pin description
549
Appendix C. Serial Port Pinouts
C.1 CS I/O Communications Port
Pin configuration for the CR1000 CS I/O port is listed in table CS I/O Pin
Description
(p. 549).
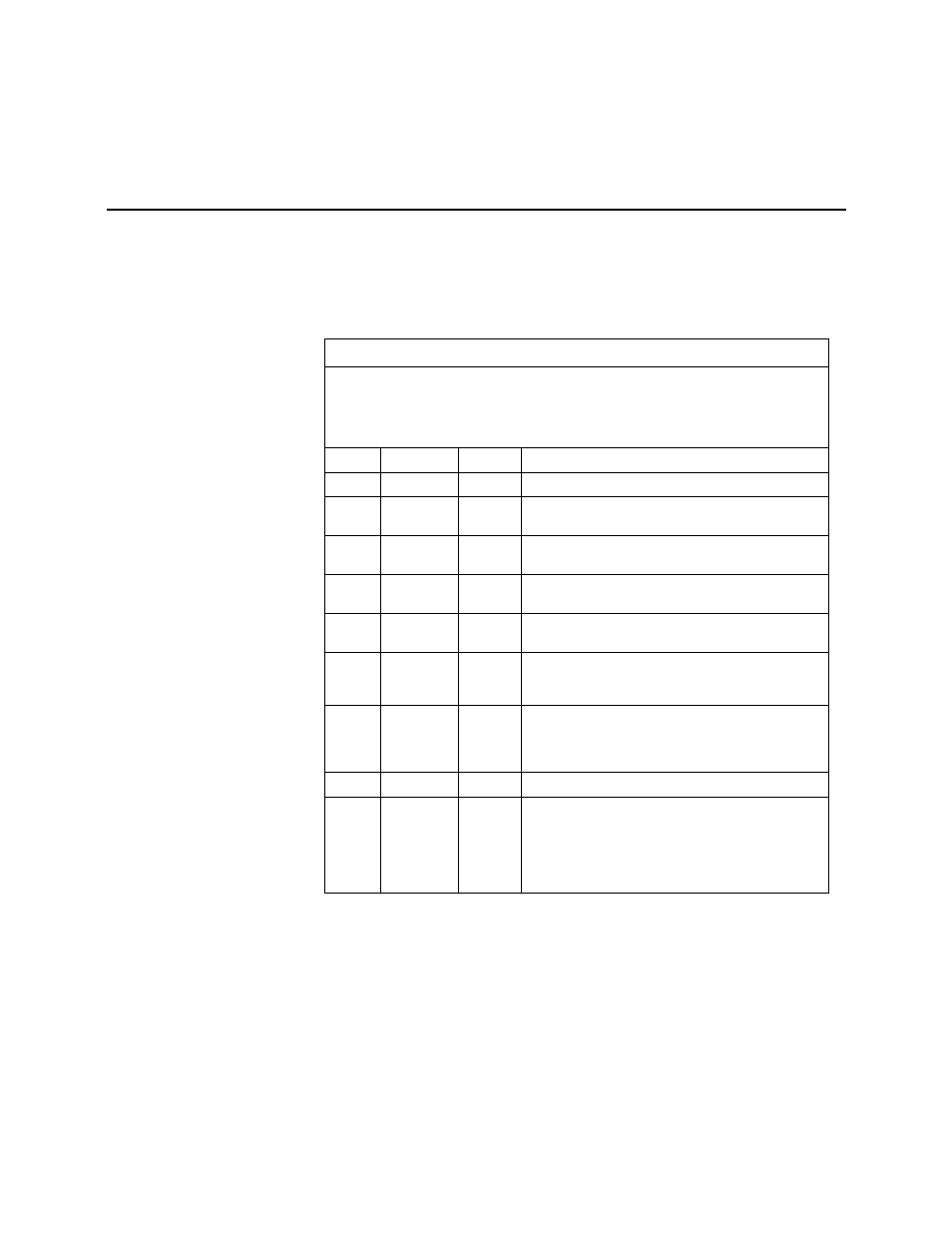
Table 123. CS I/O Pin Description
ABR: Abbreviation for the function name.
PIN: Pin number.
O: Signal Out of the CR1000 to a peripheral.
I: Signal Into the CR1000 from a peripheral.
PIN ABR I/O
Description
1
5 Vdc
O
5V: Sources 5 Vdc, used to power peripherals.
2 SG
Signal Ground: Provides a power return for pin 1 (5V),
and is used as a reference for voltage levels.
3 RING I
Ring: Raised by a peripheral to put the CR1000 in the
telecommunications mode.
4 RXD I
Receive Data: Serial data transmitted by a peripheral are
received on pin 4.
5 ME O
Modem Enable: Raised when the CR1000 determines that
a modem raised the ring line.
6 SDE O
Synchronous Device Enable: Used to address Synchronous
Devices (SDs), and can be used as an enable line for
printers.
7 CLK/HS I/O
Clock/Handshake: Used with the SDE and TXD lines to
address and transfer data to SDs. When not used as a
clock, pin 7 can be used as a handshake line (during
printer output, high enables, low disables).
8 +12
Vdc
9 TXD O
Transmit Data: Serial data are transmitted from the
CR1000 to peripherals on pin 9; logic-low marking (0V),
logic-high spacing (5V), standard-asynchronous ASCII, 8
data bits, no parity, 1 start bit, 1 stop bit, 300, 1200, 2400,
4800, 9600, 19,200, 38,400, 115,200 baud (user
selectable).
C.2 RS-232 Communications Port
C.2.1 Pin-Out
Pin configuration for the CR1000 RS-232 nine-pin port is listed in table CR1000
RS-232 Pin-Out
(p. 550).
Information for using a null modem with RS-232 is given
in table Standard Null-Modem Cable or Adapter-Pin Connections
(p. 551).
The CR1000 RS-232 port functions as either a DCE (data communication
equipment) or DTE (data terminal equipment) device. For RS-232 to function as a
DTE device, a null modem cable is required. The most common use of RS-232 is
