HP XP P9500 Storage User Manual
Page 74
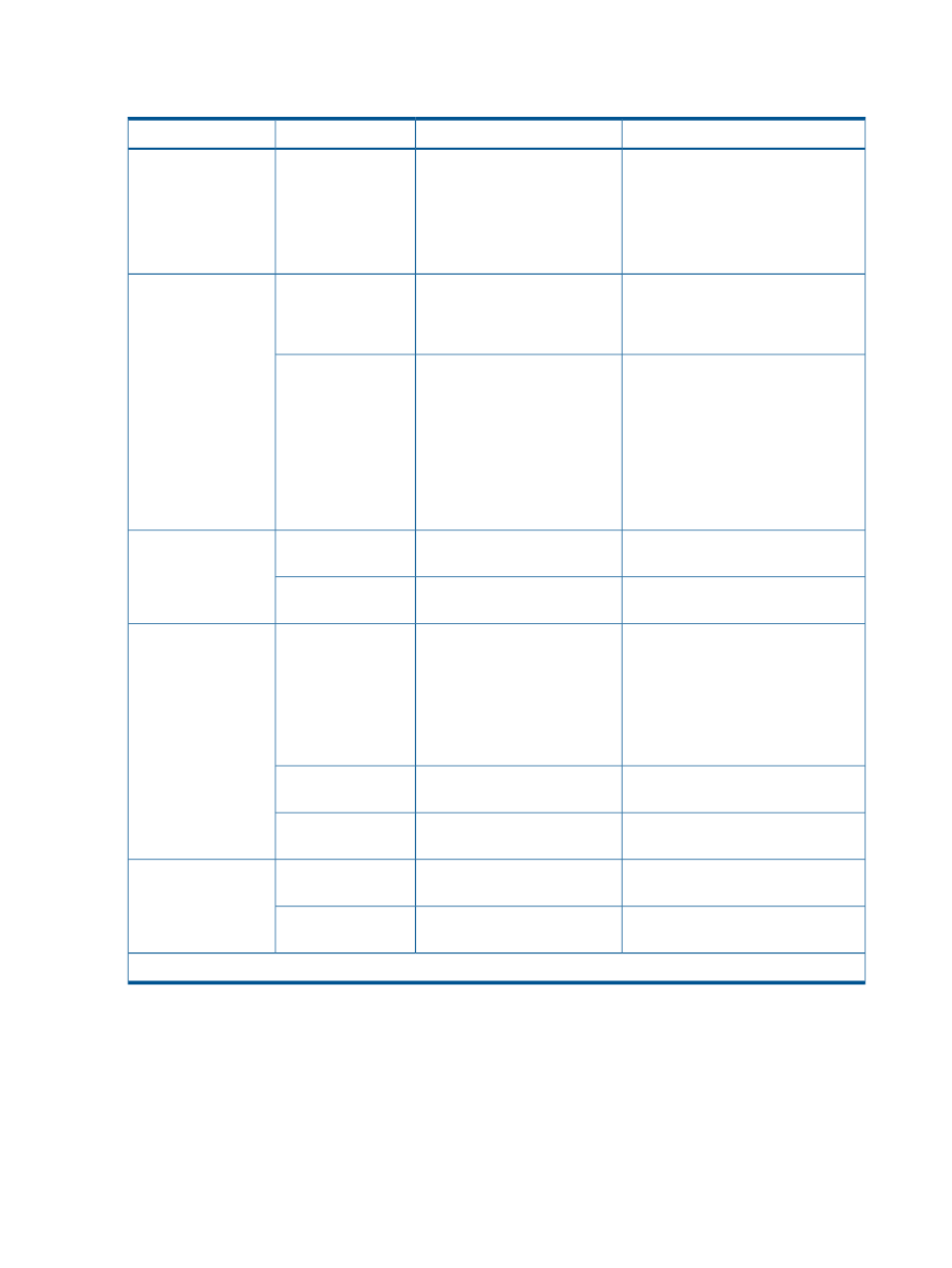
The following table shows the effects of some combinations of operating system and file system
capacity. For more information, contact your HP representative.
Pool Capacity Consumed
Metadata Writing
File System
OS
Small (one page)
Writes metadata to first block.
NTFS
Windows Server
2003 and Windows
Server 2008*
If file update is repeated, allocated
capacity increases when files are
updated (overwritten). Therefore, the
effectiveness of reducing the pool
capacity consumption decreases.
Depends upon allocation group size.
The amount of pool space consumed
Writes metadata in Allocation
Group Size intervals.
XFS
Linux
will be approximately [THP V-VOL
Size]*[42 MB/Allocation Group Size]
About 33% of the size of the THP
V-VOL.
Writes metadata in 128-MB
increments.
Ext2
Ext3
The default block size for these file
systems is 4 KB. This results in 33% of
the THP V-VOL acquiring THP pool
pages. If the file system block size is
changed to 2 KB or less then the THP
V-VOL Page consumption becomes
100%.
Size of THP V-VOL.
Writes metadata in 52-MB
increments.
UFS
Solaris
Small (one page).
Writes metadata to the first
block.
VxFS
Size of THP V-VOL.
Writes metadata in 8-MB
increments.
JFS
AIX
If you change the Allocation Group
Size settings when you create the file
system, the metadata can be written
to a maximum interval of 64 MB.
Approximately 65% of the pool is
used at the higher group size setting.
Small (one page).
Writes metadata to the first
block.
JFS2
Small (one page).
Writes metadata to the first
block.
VxFS
Small (one page).
Writes metadata to the first
block.
JFS (VxFs)
HP-UX
Size of THP V-VOL.
Writes metadata in 10-MB
increments.
HFS
*See
“Formatting LDEVs in a Windows environment” (page 123)
74
Configuring thin provisioning
