Cv capacity by emulation type for open systems, Ssid requirements, Vll size calculations – HP XP P9500 Storage User Manual
Page 42: Ssid requirements vll size calculations
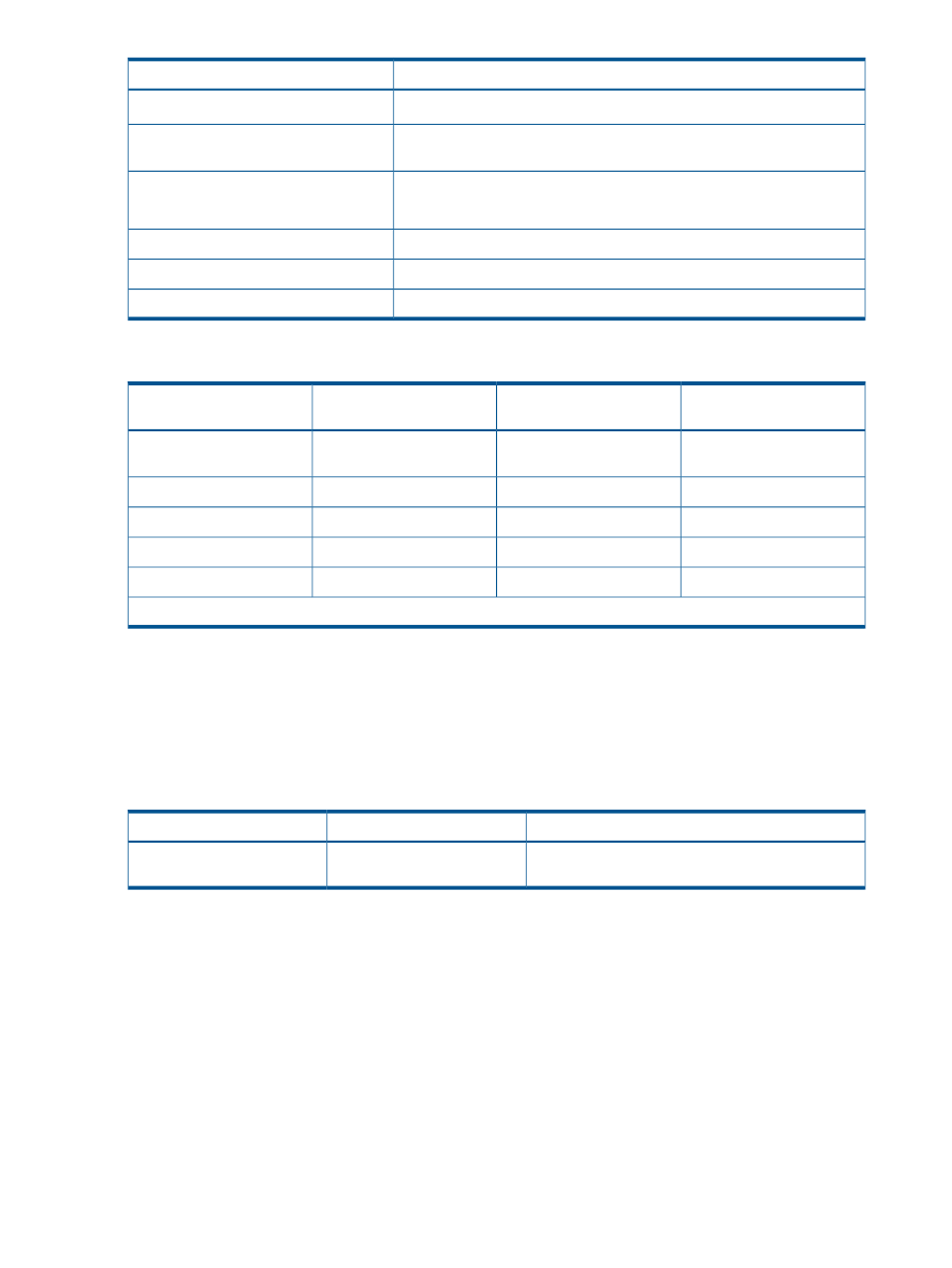
Open system
Parameter
1,024 for other RAID levels
65,280
Maximum number of volumes (normal and
Virtual LUN) per storage system
OPEN-3, OPEN-8, OPEN-9,OPEN-E: 36,000 KB (+ control cylinders)
Minimum size for one Virtual LUN volume
OPEN-V: 48,000 KB (50 cylinders)
See
“CV capacity by emulation type for open systems” (page 42)
Maximum size for one Virtual LUN volume
1 MB
Size increment
Anywhere
Disk location for Virtual LUN volumes
CV capacity by emulation type for open systems
Number of control cylinders
(cyl)
Maximum CV capacity
Minimum CV capacity (CYL)
Emulation type*
None
3,221,159,680 KB (2.99
TB)
48,000 KB
OPEN-V
5,760 KB (8 cyl)
2,403,360 KB
36,000 KB (50 cyl)
OPEN-3
19,440 KB (27 cyl)
7,175,520 KB
36,000 KB (50 cyl)
OPEN-8
19,440 KB (27 cyl)
7,211,520 KB
36,000 KB (50 cyl)
OPEN-9
13,680 KB (19 cyl)
14,226,480 KB
36,000 KB (50 cyl)
OPEN-E
*Virtual LUN operations are not available for OPEN-L volumes.
SSID requirements
The storage system is configured with one SSID (Storage System ID) for each group of 64 or 256
devices, so there are one or four SSIDs per CU image. Each SSID must be unique to each connected
host system. SSIDs are user-specified and are assigned during storage system installation in
hexadecimal format, from 0004 to FEFF.
The following table shows the relationship between controller emulation types and SSIDs.
Virtual LUN support
SSID requirement
Controller emulation type
OPEN-3, OPEN-8, OPEN-9,OPEN-E, and OPEN-V
volumes
0004 to FEFF
2105, 2105-F20 or 2107
VLL size calculations
When creating a CV, you can specify the capacity of each CV. However, rounding will produce
different values for the user-specified CV capacity and the actual entire CV capacity. To estimate
the actual capacity of a CV, use a mathematical formula. The following topics explain how to
calculate the user area capacity and the entire capacity of a CV.
The capacity of a CV or an LDEV consists of two types of capacity. One type is the user area
capacity that stores the user data. The second type is the capacities of all areas that are necessary
for an LDEV implementation including control information. The sum of these two types of capacities
is called the entire capacity.
Implemented LDEVs consume the entire capacity from the parity group capacity. Therefore, even
if the sum of user areas of multiple CVs and the user area of one CV are the same size, the
remaining free space generated when multiple CVs are created may be smaller than the free space
in the parity group when one CV is created.
42
Configuring custom-sized provisioning
