Tiers concept, When to use smart tiers, Data retention strategies – HP XP P9500 Storage User Manual
Page 20: Resource groups strategies, Tiers concept when to use smart tiers
•
Less storage management effort
•
More automation
•
Nondisruptive storage management
•
Reduced costs
•
Improved performance
Tiers concept
When not using Smart Tiers, data is allocated to only one kind of data drive (typically an expensive
high-speed hard disk drive) without regard to the workload to the volumes because the volumes
are configured with only one kind of data drive. When using Smart Tiers, the higher speed data
drive is automatically allocated to the volumes of high workload, and the lower speed drive to the
volumes of low workload. This improves performance and reduces costs.
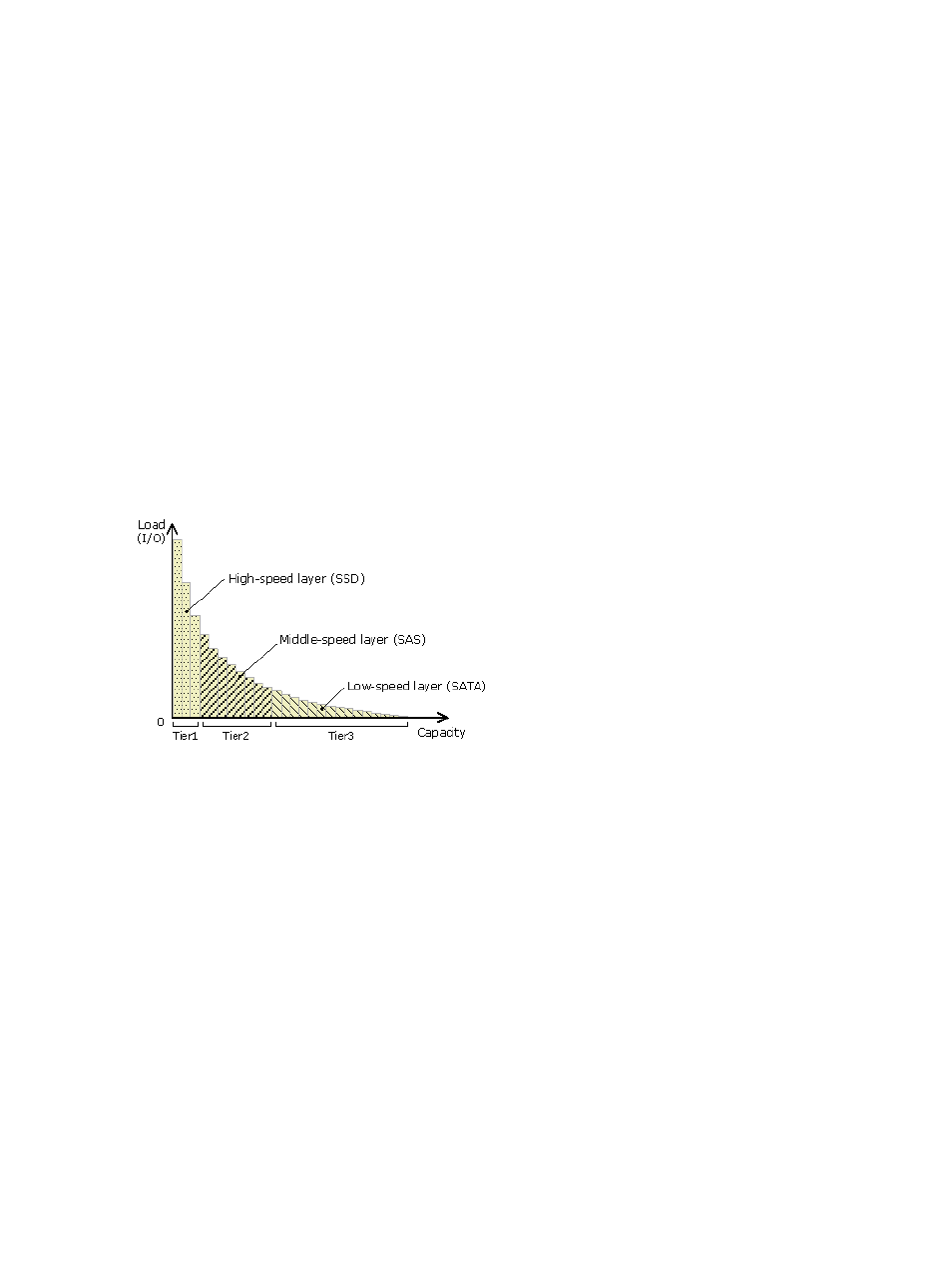
Smart Tiers places the host volume's data across multiple tiers of storage contained in a pool. There
can be up to three tiers (high-, medium-, and low-speed layers) in a pool. Smart Tiers determines
tier usage based on data access levels. It allocates the page with high I/O load to the upper tier,
which contains a higher speed drive, and the page with low I/O load to the lower tier, which
contains a lower speed drive.
The following figure illustrates the basic tier concept.
When to use Smart Tiers
Smart Tiers is a best fit in an open systems environment wherever Thin Provisioning is a good fit.
For detailed information, see
.
Data retention strategies
After provisioning your system, you can assign access attributes to open-system volumes to protect
the volume against read, write, and copy operations and to prevent users from configuring LU
paths and command devices. Use the Data Retention to assign access attributes.
For more information, see
“Configuring access attributes” (page 143)
.
Resource groups strategies
A storage system can connect to multiple hosts and be shared by multiple divisions in a company
or by multiple companies. Many storage administrators from different organizations can access
the storage system. Managing the entire storage system can become complex and difficult. Potential
problems are that private data might be accessed by other users, or a volume in one organization
might be destroyed by mistake by a storage administrator in another organization.
To avoid such problems, use Resource Partition to set up resource groups that allow you to manage
one storage system as multiple virtual private storage systems. The storage administrator in each
20
Introduction to provisioning
