3 configuring raid and managing disks, Configuring and managing raid, Raid levels – HP LeftHand P4000 SAN Solutions User Manual
Page 21: Getting there
3 Configuring RAID and Managing Disks
For each storage system, you can select the RAID configuration and the RAID rebuild options, and
monitor the RAID status. You can also review disk information and, for some models, manage
individual disks.
Getting there
1.
In the navigation window, select a storage system and log in if necessary.
2.
Open the tree under the storage system and select the Storage category.
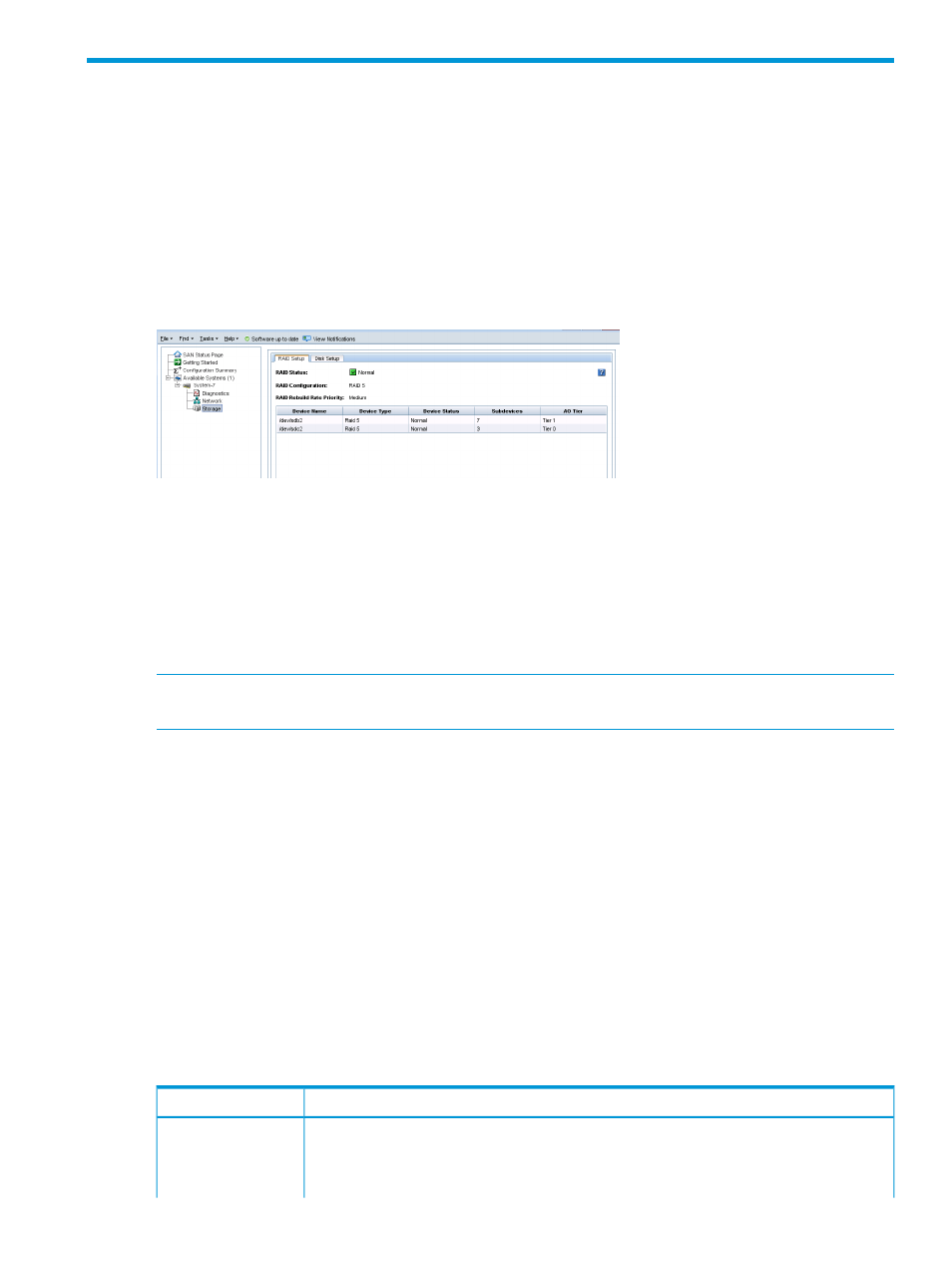
Figure 7 Viewing the storage configuration category for a storage system
Columns in the RAID Setup tab show the following categories:
•
Device Name
•
Device Type or the RAID level
•
Device Status
•
Subdevices
•
AO, if Adaptive Optimization-capable
NOTE:
For hardware-specific LED information for your storage system, see
for document titles and document links.
Configuring and managing RAID
Managing the RAID settings of a storage system includes:
•
Choosing the right RAID configuration for your storage needs
•
Setting or changing the RAID configuration, if necessary
•
Setting the rate for rebuilding RAID
•
Monitoring the RAID status for the storage system
•
Reconfiguring RAID when necessary
•
Reconfiguring tiers for Adaptive Optimization-capable storage systems
RAID Levels
The availability of certain RAID levels is determined by the number of storage system hard drives.
Table 6 Descriptions of RAID levels
Description
RAID level
Offers the best combination of data protection and performance. RAID 1+0 or drive mirroring
creates fault tolerance by storing duplicate sets of data on a minimum of four hard drives.
RAID 10 – Mirroring
and Striping
There must be an even number of drives for RAID 1+0. RAID 1+0 is the most costly fault
tolerance method because it requires 50 percent of the drive capacity to store the redundant
Configuring and managing RAID
21
