Setting up the pc for ip communication with an mlc, Preliminar y – Extron Electronics MLC 226 IP Series Installation User Manual
Page 51
4-7
MLC 226 IP Series • Software-based Confi guration and Control
PRELIMINAR
Y
2.
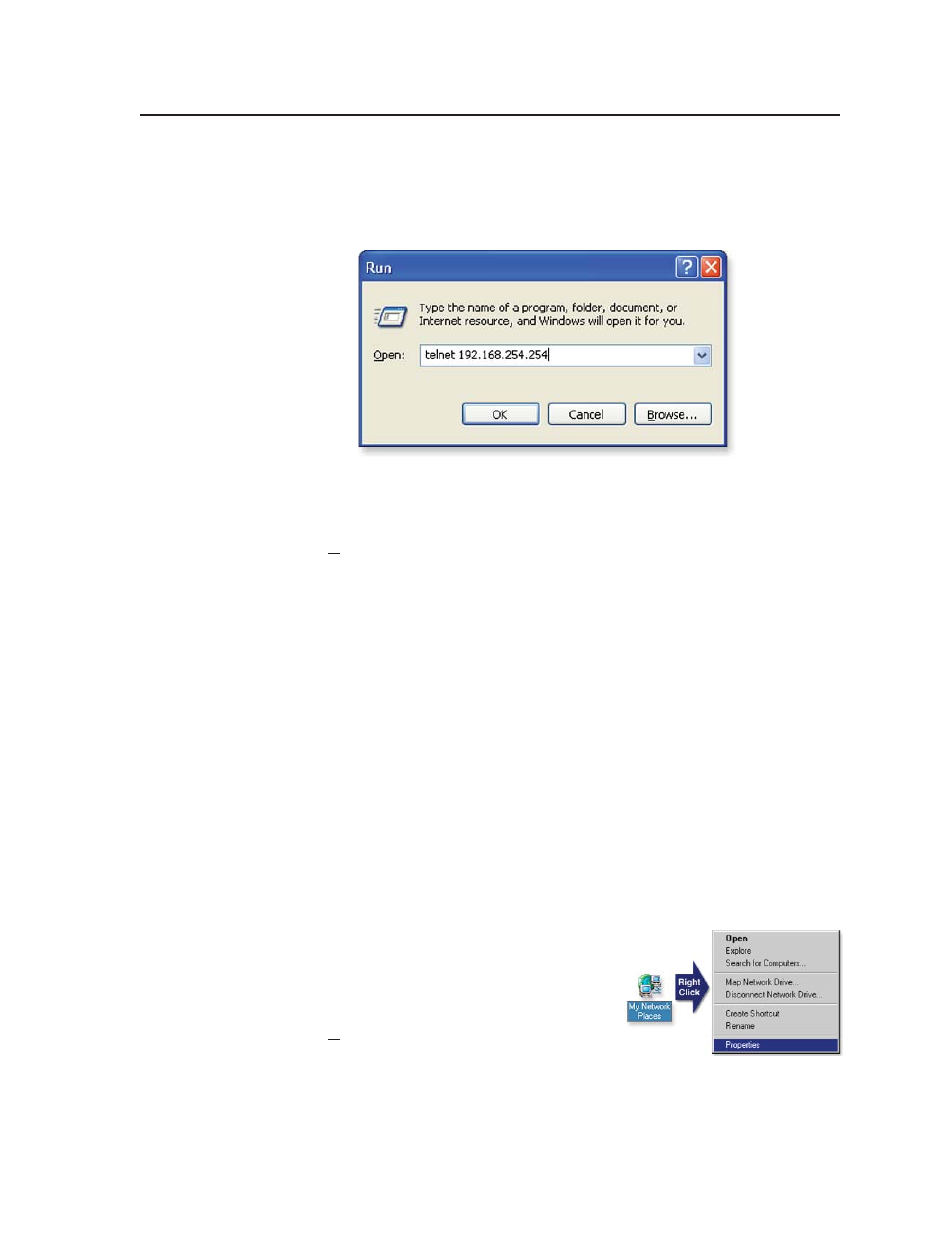
Start Telnet on the PC
a.
Click the Start menu and select Run. The Run dialog box appears.
b.
Type telnet, a space, and the default IP address (192.168.254.254) into the
Open area, and click OK.
3.
Set the MLC for the new IP address by doing one of the following:
•
Enter SIS command
E X1$
CI
}
, where
X1$
is the new IP address (see
chapter 5, “SIS
™
Programming and Control”) to set the IP address.
or
•
Enter SIS command 1DH
}
to enable DHCP.
4.
After changing the controller’s IP address, change your PC’s TCP/IP settings
back to their original confi guration.
Setting up the PC for IP communication with an MLC
You need a Windows-based (Windows 2000, XP, or higher) PC equipped with an
operating network adapter. To allow your PC to work with Extron’s Ethernet-
controlled products, the TCP/IP protocol must be installed and properly
confi gured.
When setting up the MLC for network communication via a Web browser or Telnet
connection, you must change the IP address of the PC to one that is on the same
subnet as the MLC. This is not required if you are setting up the MLC for network
communication via Global Confi gurator, the ARP command, or SIS commands via
an RS-232 connection.
If you use an existing Ethernet LAN intranet, your network administrator can
provide you with a unique IP address for the controller or confi rm whether you
need to set up the MLC 226 IP for DHCP (Dynamic Host Confi guration Protocol) to
have an address assigned automatically when you sign on.
1.
Open the Network Connections page as follows:
•
Locate and right-click on My Network
Places on the Windows (2000, XP,
or higher) desktop, then click on
Properties.
or
•
Click on the Start menu, click on
Settings (if needed), click on Control Panel, then double-click on
Network and Dial-up Connections (Windows 2000) or Network
Connections (Windows XP).
