One wan port) – ZyXEL Communications Centralized Network Management Vantage CNM User Manual
Page 70
Chapter 5 Device Network Settings
Vantage CNM User’s Guide
70
5.3.1.1 Ethernet Encapsulation
The following table describes the labels in the Ethernet encapsulation screen.
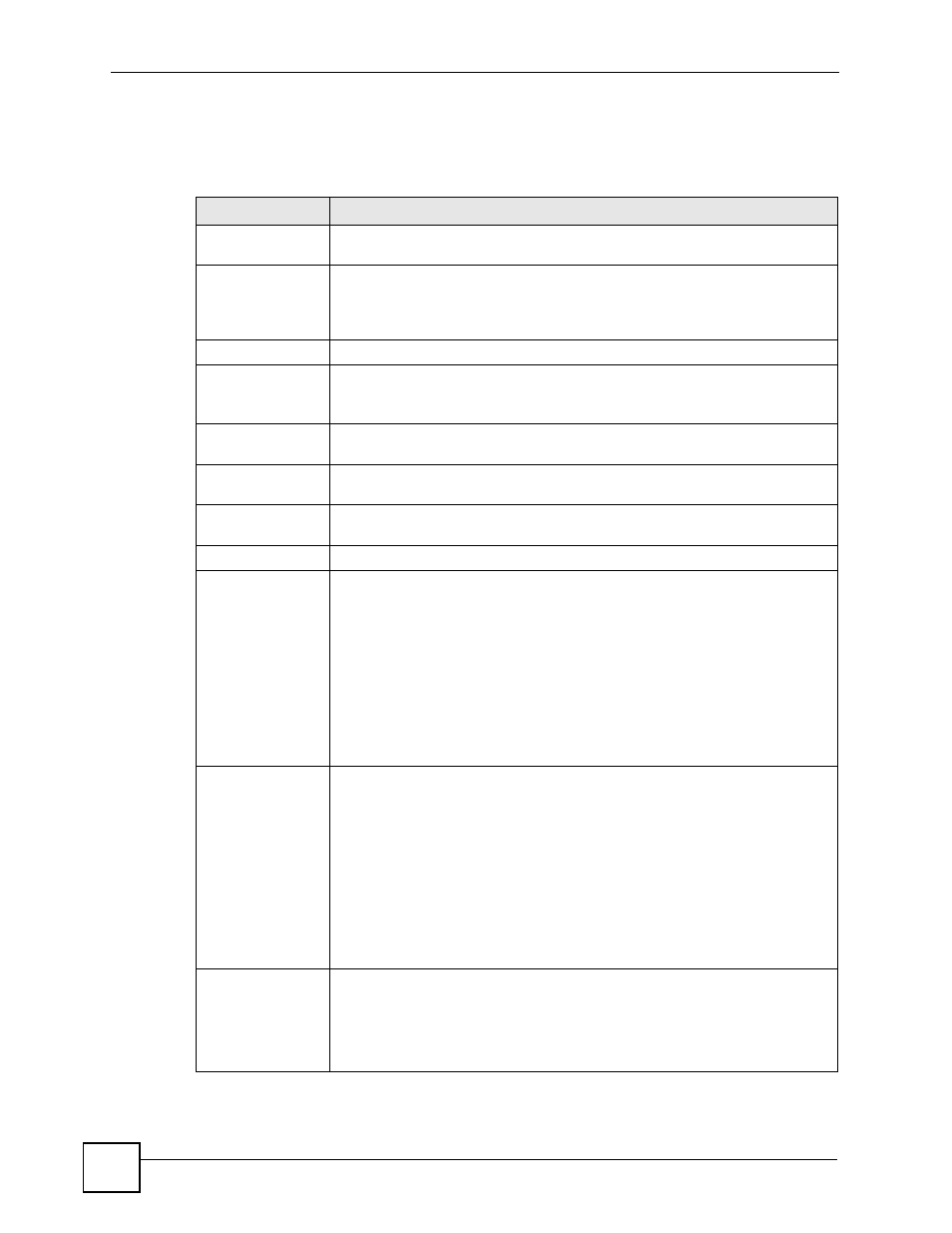
Table 18 Device Operation > Device Configuration > Network > WAN > ISP (Ethernet) –
ZyNOS ZyWALL (one WAN port)
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Encapsulation
You must choose the Ethernet option when the WAN port is used as a regular
Ethernet.
Service Type
Choose from Standard, Telstra (RoadRunner Telstra authentication method),
RR-Manager (Roadrunner Manager authentication method), RR-Toshiba
(Roadrunner Toshiba authentication method) or Telia Login.
The following fields do not appear with the Standard service type.
WAN:IP
WAN IP Address
Assignment
Select Get automatically from ISP If your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP
address. This is the default selection.
Select Use fixed IP address If the ISP assigned a fixed IP address.
My WAN IP
Address
Enter your WAN IP address in this field if you selected Use Fixed IP Address.
My WAN IP Subnet
Mask
Enter the IP subnet mask (if your ISP gave you one) in this field if you selected
Use Fixed IP Address.
Gateway IP
Address
Enter the gateway or remote IP address (if your ISP gave you one) in this field if
you selected Use Fixed IP Address.
Advanced Setup
RIP Direction
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) allows a router to exchange routing
information with other routers. The RIP Direction field controls the sending and
receiving of RIP packets.
Choose Both, None, In Only or Out Only.
When set to Both or Out Only, the device will broadcast its routing table
periodically.
When set to Both or In Only, the device will incorporate RIP information that it
receives.
When set to None, the device will not send any RIP packets and will ignore any
RIP packets received.
By default, RIP Direction is set to Both.
RIP Version
The RIP Version field controls the format and the broadcasting method of the
RIP packets that the device sends (it recognizes both formats when receiving).
Choose RIP-1, RIP-2B or RIP-2M.
RIP-1 is universally supported; but RIP-2 carries more information. RIP-1 is
probably adequate for most networks, unless you have an unusual network
topology. Both RIP-2B and RIP-2M sends the routing data in RIP-2 format; the
difference being that RIP-2B uses subnet broadcasting while RIP-2M uses
multicasting. Multicasting can reduce the load on non-router machines since
they generally do not listen to the RIP multicast address and so will not receive
the RIP packets. However, if one router uses multicasting, then all routers on
your network must use multicasting, also. By default, the RIP Version field is set
to RIP-1.
Multicast
Choose None (default), IGMP-V1 or IGMP-V2. IGMP (Internet Group Multicast
Protocol) is a network-layer protocol used to establish membership in a Multicast
group - it is not used to carry user data. IGMP version 2 (RFC 2236) is an
improvement over version 1 (RFC 1112) but IGMP version 1 is still in wide use. If
you would like to read more detailed information about inter operability between
IGMP version 2 and version 1, please see sections 4 and 5 of RFC 2236.
