Figure 5-5 example of arbitration among nodes – FUJITSU CAN-Motor Board MB91F267N User Manual
Page 89
AN07-00180-3E
- 89 -
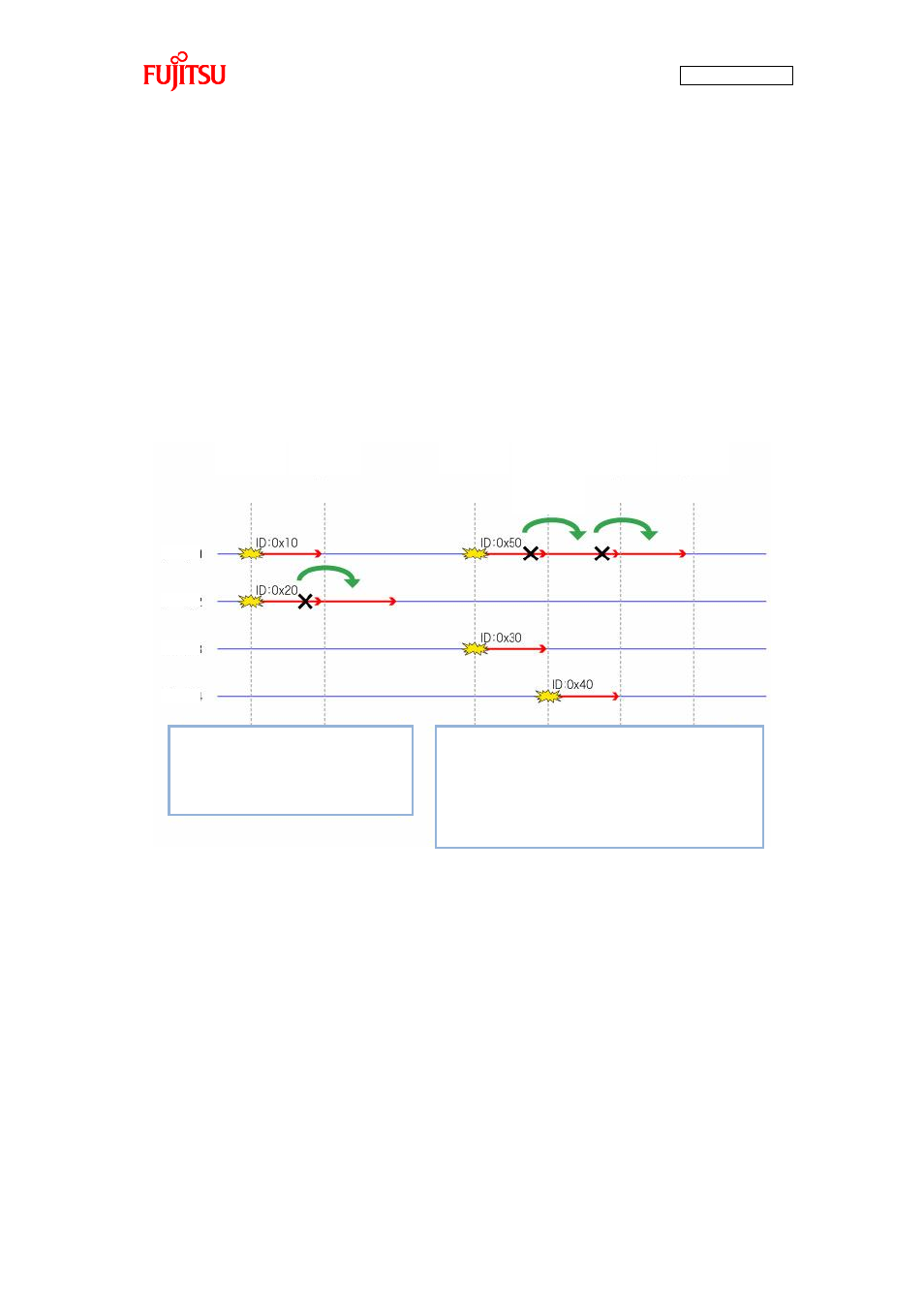
giving priority to the Node 1 transmission with a lower ID. After Node 1 ends its transmission, Node 2
resumes transmission.
After that, Node 1 and Node 3 starts transmission simultaneously. The arbitration is also performed and
results in giving priority to the Node 3 transmission. After that, Node 4 starts transmission as soon as
Node 3 ends its transmission. On this occasion, arbitration between Node 1 retransmission and Node 4
transmission is performed. This results in transmission in order of Node 4 to Node 1. That is, setting a
lower ID to those of preference allows priorities to be settled for communication.
The ID is assigned by the command, information, and type of transmit data. The ID settings can be
configured as desired.
Figure 5-5 Example of arbitration among nodes
Node 1
Node 2
Node 3
Node 4
Start of
transmission
Completion of
Node 1
transmission
Start of
transmission
Completion of
Node 3
transmission
+
Start of
transmission
Completion of
Node 4
transmission
Completion of
Node 1
transmission
Node 1 and Node 2 starts transmission
simultaneously. The arbitration results in
giving priority to the Node 1 transmission.
Node 1 ends its transmission, Node 2
resumes transmission.
Node 1 and Node 3 starts transmission simultaneously.
The arbitration results in giving priority to the Node 3
transmission. Node 4 starts transmission as soon as
Node 3 ends its transmission. On this occasion,
arbitration between Node 1 retransmission and Node 4
transmission is performed and it results in giving priority to
the Node 4 transmission. Node 1 is allowed to start
transmission last.
