Measurement Computing eZ-PostView rev.2.0 User Manual
Page 87
eZ-Analyst
969795
Edit Menu 4-9
Edit Menu > Configuration >
Analyzer Tab:
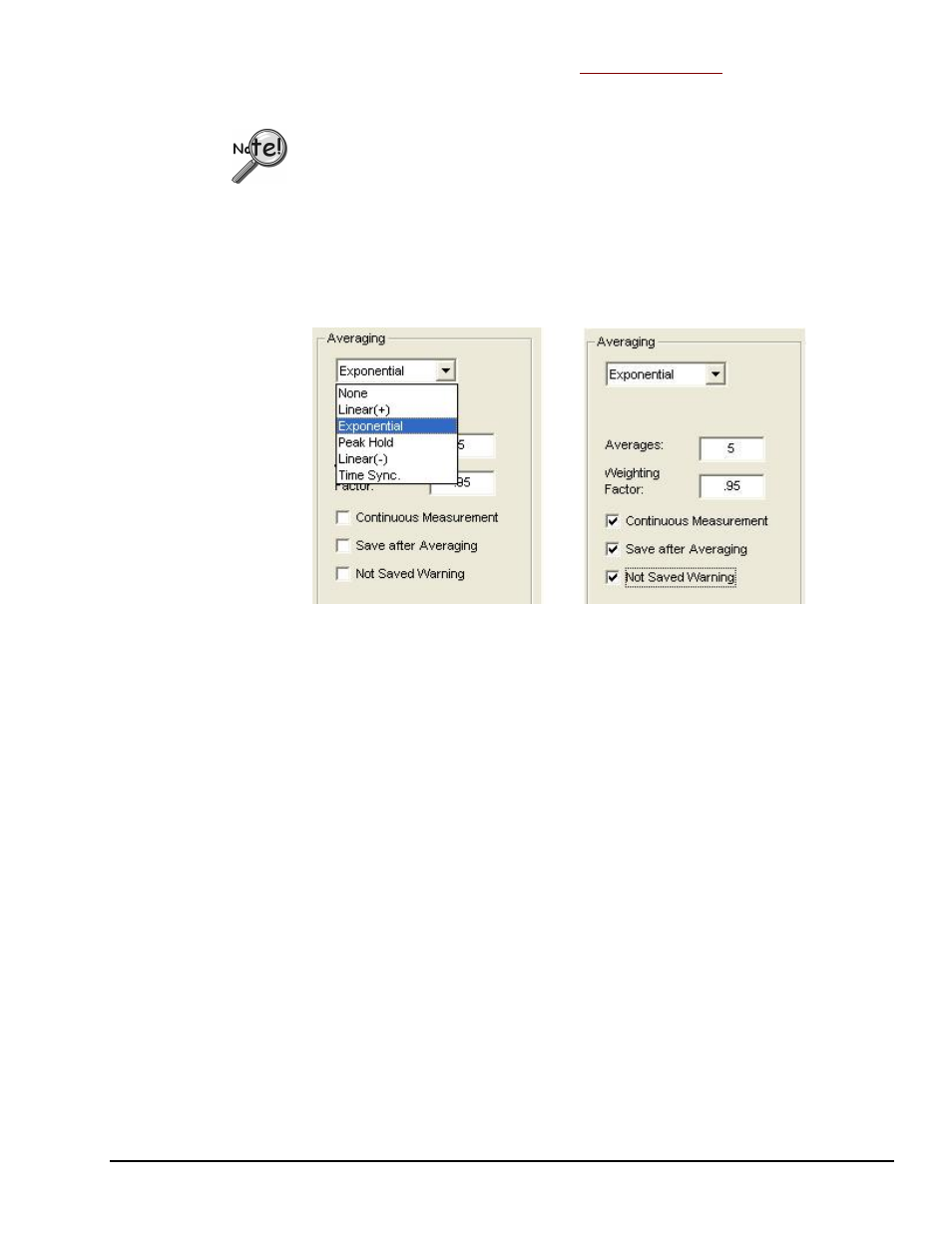
Averaging Panel
The Averaging Panel is used to select the type of averaging that will be calculated during data
acquisition.
¾ To apply averaging to time-demand data, the Function View Window
must be changed to a Windowed “Time Function,” otherwise all
averaging will be applied to a spectral date.
¾ Averaging can be used to decrease the noise in a measurement.
In the figure below, the first scenario shows the pull-down menu expanded, revealing the
types of averaging that can be selected. The second scenario shows that “Exponential” has
been selected. Exponential makes use of a Weighting Factor, which is not used by the other
averaging types.
Averaging Panel of Analyzer Tab (2 Views)
A brief description of averaging types and other panel terms now follows.
Linear (+): All blocks of data are treated equally in terms of their effect on the averaged
result.
Exponential: Similar to linear averaging, Exponential requires a weighting factor that either
increases or decreases the effect of each new data block on the resultant average.
Weighting Factor: The Weighting Factor either increases or decreases the effect of each
new data block on the resultant average when Exponential Averaging is used.
New Average = ((New Data) * A.W.F.) + (Old Average * (1-A.W.F))
Peak Hold: The resultant block of data is a collection of points that represent the peak
amplitude for each point in the block. With each new block of data, the current data is
compared with the new data on a point by point basis. The highest amplitude for each point
in the block is retained.
Linear (-): Also known as Negative Averaging; Linear (-) Averaging is a technique used to
identify the natural frequencies of in-service machines that cannot be shut down for analysis.
Linear (-) Averaging is a two step process. First, a reference average is acquired. Second, a
normal linear average is acquired for each frame. The running average is subtracted from the
reference average and the result is displayed. The first time you attempt to start data
acquisition after you select Linear (-) averaging, the Negative Averaging Setup/ Measurement
window opens. An example of
how to perform negative averaging
follows these definitions.
