Measurement Computing eZ-PostView rev.2.0 User Manual
Page 128
5-10 Interactive Plot Display
969895
eZ-Analyst
Function
Description / Comments
28
Differential
Differential (also referred to as Differentiation) is for display purpose only
and does not modify the data. Differentiation is only active when frequency
domain data is displayed. Select single or double differentiation or none by
continuous clicks of the button (#28). In the plot display’s “Y-Axis” label, a
“&” indicates single differentiation, “&&” indicates double differentiation, and
no ampersand indicates no differentiation. Note that both Differentiation
and Integration are calculated by dividing each element of the function by
(jw)^n, where j is the square root of -1; w is the product of 2 pi times the
frequency of the block element; and n is an integer from +2 to -2.
If the signal is displacement, then single differentiation (&) results in
velocity, and double differentiation (&&) results in acceleration.
29
Integral
Integral (also referred to as Integration) is for display purpose only and
does not modify the data. Integration is only active when frequency domain
data is displayed. Select single or double integration or none by continuous
clicks of the button (#29). In the plot display’s “Y-Axis” label, a “~”
indicates single integration, “~~” indicates double integration, and no
ampersand indicates no integration. Note that both Differentiation and
Integration are calculated by dividing each element of the function by
(jw)^n, where j is the square root of -1; w is the product of 2 pi times the
frequency of the block element; and n is an integer from +2 to -2. If the
signal is acceleration, then single integration (~) results in velocity, and
double integration (~~) results in displacement.
Note: Engineering Units change when the instrument type is Acceleration
and integration is implemented.
30
Scale - RMS, Pk,
Pk-Pk
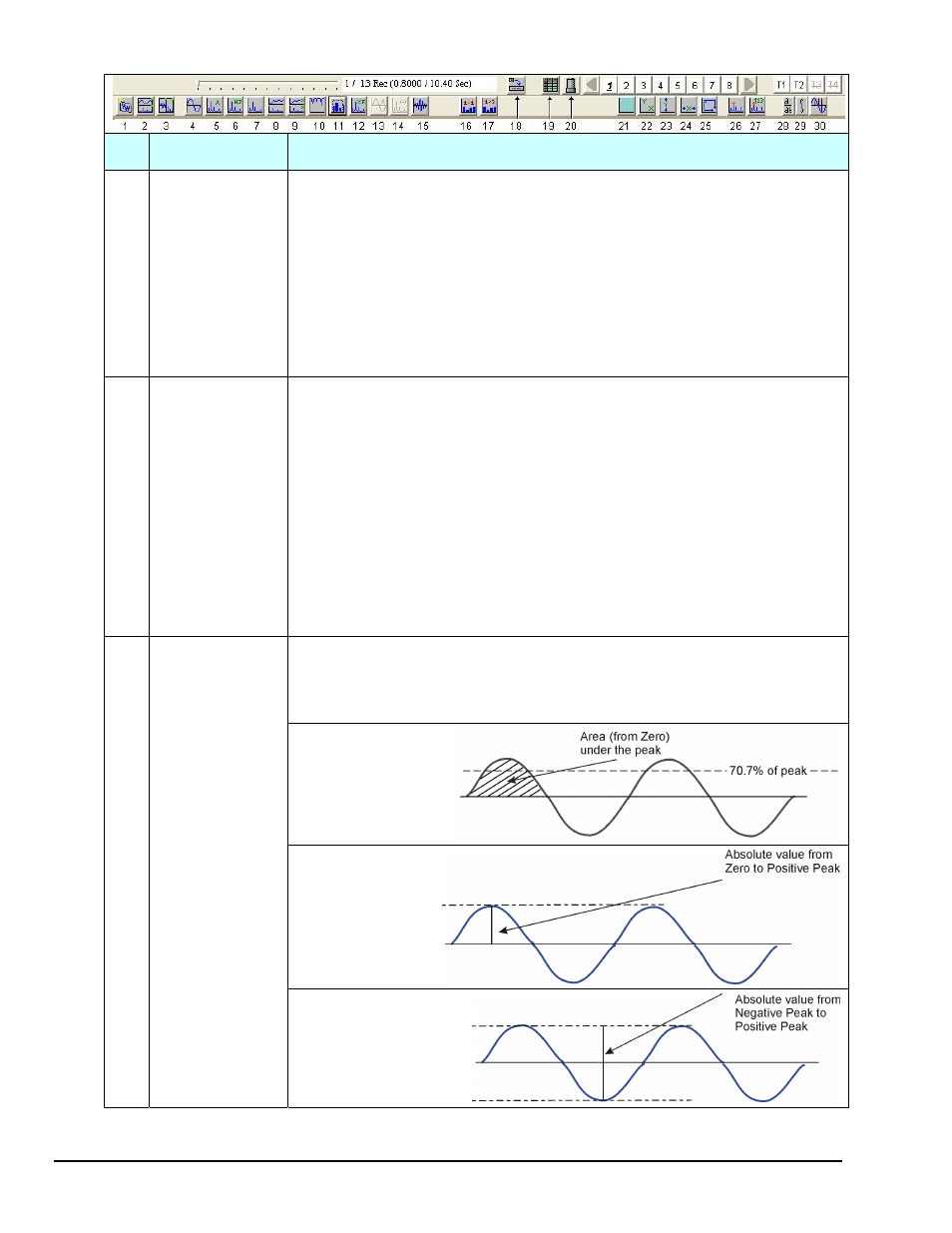
The Scale button allows the user to cycle through the following scales:
RMS: (Root Mean Square): The square root of the average of the square of
the value of the function taken throughout one period. Peak: Zero to
Peak. Pk-Pk: Peak to Peak. Refer to the following illustrations.
RMS
Peak
Peak-to-Peak
RMS Level
