Calibration, Calibration……… -6, Task menu > calibration – Measurement Computing eZ-PostView rev.2.0 User Manual
Page 64
3-6 Menus
979595
eZ-Analyst
Task Menu >
Calibration
When calibration is performed, a signal of known Peak level [or RMS value] is supplied to a
transducer that is connected to an active input channel. An accelerometer calibrator or piston
phone is typically used to generate the calibration signal for vibration sensors and microphones,
respectively.
Examples:
Accelerometer calibrators typically make use of linear engineering
units and, as their name implies, are used for calibrating
accelerometers.
Piston phones are most often used for calibrating microphones. Piston
phones typically make use of decibel (dB) engineering units.
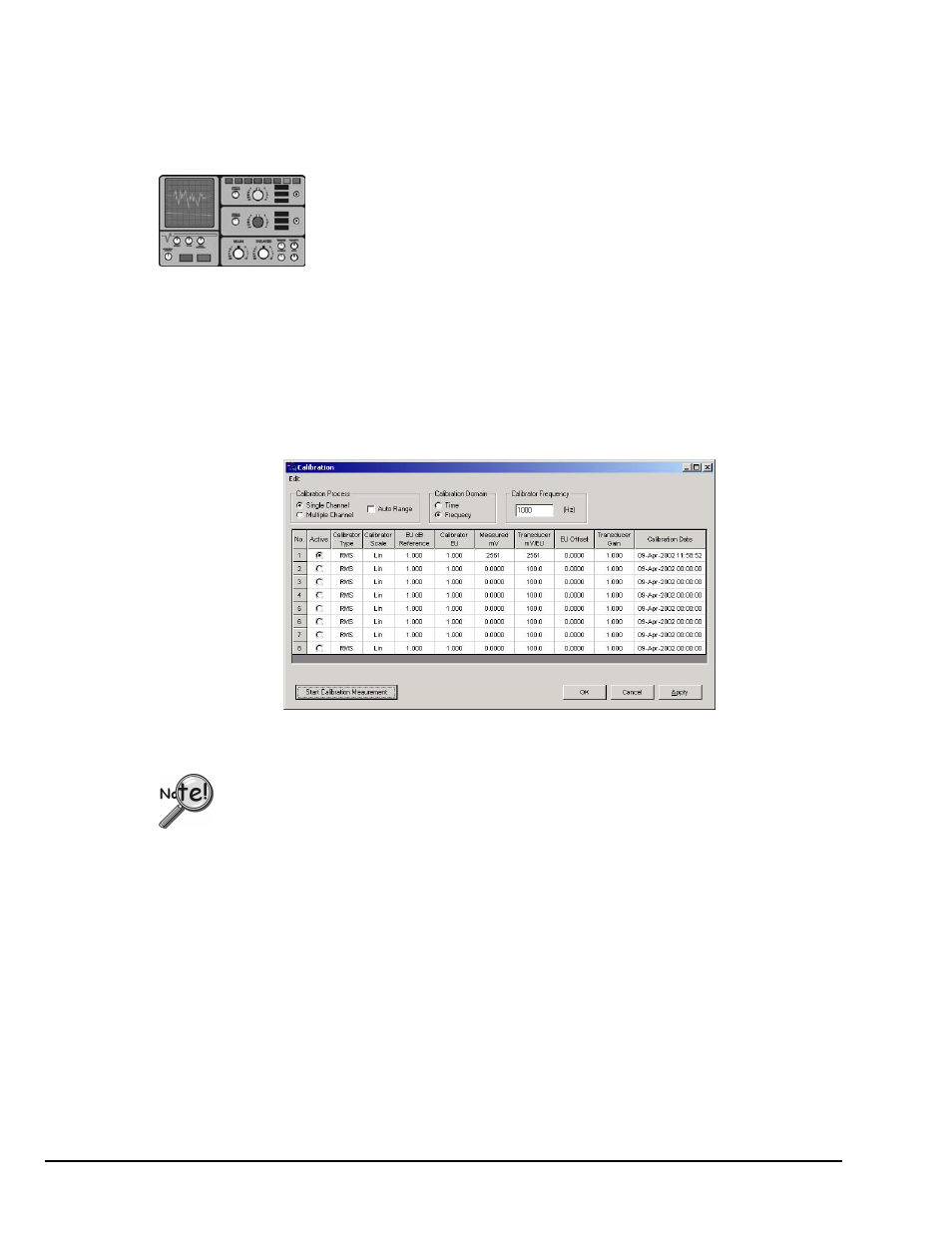
eZ-Analyst includes a Calibration window for selecting the channels to be calibrated and for
entering several signal-related parameters. In addition, the calibration is actually started from
the window.
When you are in “Measurement Mode” you can access the Calibration window from the Task
Menu or from the Input/Output Channels tab.
Calibration Display Screen
¾ When a channel is calibrated, the number of averages used will be 5, or
the number that is designated in the “No. of Averages” field (located on
the Analyzer Tab). The greater of the two values will be used,
automatically.
¾ When a channel is calibrated, the blocksize of the acquisition will
automatically be 4096, or the blocksize value that is stated on the
Analyzer Tab, providing it is 4096
or higher.
A discussion of the various regions of the Calibration window now follows.
The section concludes with an example.
